Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab #18 - P&D. Relationship Between Drop Height and Rebound Height of A Ball
Uploaded by
Faith DormarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab #18 - P&D. Relationship Between Drop Height and Rebound Height of A Ball
Uploaded by
Faith DormarCopyright:
Available Formats
Planning and Designing lab
Date: January 12, 2022
Title: Investigating the relationship between drop height and rebound height of a
ball
Problem Statement:
A student suggests that there is a proportional relationship between the height from
which a ball is dropped and its rebound height. Design an experiment to determine
if this suggestion is true or not.
Hypothesis: If I release a ball from a greater height then the rebound distance
will be greater.
Aim: To determine how the height of the ball’s release affects its rebound
height.
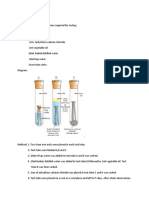
Apparatus: Tape measure and a ball.
Diagram of apparatus
Variables: Manipulated: The height at which the ball bounces.
Responding: Hardness of the bounce surface.
Control: The ball used, the height the ball is dropped from, the tape
measure.
Method:
1). Obtain a handball
2). Place the tape measure vertically on the floor with 0cm pointing down
4). Hold the ball at a height of 1cm and carefully drop the ball then observe
the bounce height.
3). Record the height
Expected Results: It is expected that the ball will have a greater rebound
distance if it is released at a greater height.
Table Showing: The starting height of the ball vs the rebound height.
Starting height (cm) Rebound height (cm)
Interpretation of results: A typical ball bounces at 60% of its original height
because it stores and returns 60% of the energy it had before. As the drop
height increases, the kinetic energy of the ball before it hits the ground is
larger as velocity has increased. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the
rebound height therefore increases.
Precautions/possible sources of errors/assumptions:
Possible sources of errors are; ball height not recorded on time, incorrect
apparatus used.
You might also like
- Jamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideFrom EverandJamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideNo ratings yet
- Project 3 - Bouncing Energy - Lab ReportDocument5 pagesProject 3 - Bouncing Energy - Lab ReportKOBE2401No ratings yet
- LAB Physics P and DDocument3 pagesLAB Physics P and DAldayne ParkesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Personal Power Lab - AtharvaDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - Personal Power Lab - AtharvaAtharva Satpute50% (4)
- SBA 2 ModifiedDocument3 pagesSBA 2 Modifiedannmarie100% (1)
- Projectile Motion TrajectoryDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Trajectoryvictoria kairoo100% (1)
- Physics SBA 4Document3 pagesPhysics SBA 4annmarieNo ratings yet
- Math SbaDocument9 pagesMath SbaNevishae RichardsNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws in ActionDocument48 pagesNewton's Laws in ActionMarissa FreemanNo ratings yet
- Csec Math January 2020 Paper 2Document34 pagesCsec Math January 2020 Paper 2Simion MillwoodNo ratings yet
- 1A Student Investigates The Relationship Between The Volume and Temperature of A Fixed Mass of GasDocument2 pages1A Student Investigates The Relationship Between The Volume and Temperature of A Fixed Mass of GasA.BensonNo ratings yet
- Additional Maths SbaDocument1 pageAdditional Maths Sbawaseem555100% (6)
- Lab 6Document6 pagesLab 6Brandon SookdeoNo ratings yet
- Csec Physics Implementation LabDocument6 pagesCsec Physics Implementation LabJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report #15 D, DCP & CE Verifying Snell's Law Ngan DinDocument8 pagesLab Report #15 D, DCP & CE Verifying Snell's Law Ngan DinImran Ariffin75% (8)
- CSEC Mathematics June 2002 P2Document13 pagesCSEC Mathematics June 2002 P2zarzsultan12100% (1)
- English SbaDocument13 pagesEnglish SbaKelsey Wilson0% (1)
- CSEC Physics - The AtomDocument5 pagesCSEC Physics - The AtomCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Maths CoverSheetForESBA Fillable Feb2020Document2 pagesCSEC Maths CoverSheetForESBA Fillable Feb2020Daniel Dowding100% (2)
- Circuits Physic LabDocument5 pagesCircuits Physic LabAaliyah SeniorNo ratings yet
- Csec Physics Lab ListDocument5 pagesCsec Physics Lab ListJC0% (1)
- Untitled DocumentDocument6 pagesUntitled DocumentDandre Williams100% (1)
- Physics Lab 7Document4 pagesPhysics Lab 7omario norman100% (1)
- Kimberly Lee Phyz Ed SbaDocument17 pagesKimberly Lee Phyz Ed SbaNicholas Porter0% (3)
- How Much Money Do Students Spend On A Daily Basis?: Tables of ContactsDocument16 pagesHow Much Money Do Students Spend On A Daily Basis?: Tables of ContactsEnrique HawthorneNo ratings yet
- CXC CSEC Additional Mathematics Formulas SheetDocument1 pageCXC CSEC Additional Mathematics Formulas SheetDanielle Cunningham100% (1)
- Biology CXC 2022 ReviewDocument46 pagesBiology CXC 2022 ReviewLatoya Scottland100% (2)
- Add Maths Sba 1Document13 pagesAdd Maths Sba 1Ruchi Marajh100% (1)
- Csec Math SbaDocument8 pagesCsec Math SbaNeyshia AndersonNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab 3Document5 pagesPhysics Lab 3Brandon Sookdeo100% (7)
- CSEC English A January 2011 P2Document6 pagesCSEC English A January 2011 P2Jhanett RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Physical Education SBADocument8 pagesPhysical Education SBAShafan Leslie100% (1)
- Relationship Between Paperclip Length and PeriodDocument4 pagesRelationship Between Paperclip Length and PeriodJadie BabyyyNo ratings yet
- Observe Osmosis Potato StripsDocument2 pagesObserve Osmosis Potato StripsCrystal Newton50% (2)
- CSEC Physics - Wave Motion - SPQDocument9 pagesCSEC Physics - Wave Motion - SPQA.BensonNo ratings yet
- CXC Physics LabDocument42 pagesCXC Physics Labteam TSOTARE67% (3)
- Loki Maths SbaDocument11 pagesLoki Maths SbaUnruly BossNo ratings yet
- Refractive Index Physics LabDocument6 pagesRefractive Index Physics LabAaliyah SeniorNo ratings yet
- Physics Implementation LabDocument9 pagesPhysics Implementation LabTriston McDermott100% (1)
- Typing v. Handwriting InvestigationDocument5 pagesTyping v. Handwriting InvestigationPaul Hamilton11nNo ratings yet
- 2017 A Level 9758 H2 Math Paper 1 Solution and Paper 2 Likely QuestionsDocument20 pages2017 A Level 9758 H2 Math Paper 1 Solution and Paper 2 Likely QuestionsKeiran Tan100% (1)
- Viscosity Lab CoefficientDocument4 pagesViscosity Lab CoefficientDaniel KellyNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION - Effect of Exercise On Breathing RateDocument1 pageRESPIRATION - Effect of Exercise On Breathing RateJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: School Based Assessment (SBA)Document10 pagesMathematics: School Based Assessment (SBA)Mujah ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Science Conclusion - States of MatterDocument2 pagesScience Conclusion - States of Matterapi-287882693No ratings yet
- Rusting Lab ORRDocument2 pagesRusting Lab ORRShailis SeonarineNo ratings yet
- Hookes LawDocument9 pagesHookes LawBrandon Sookdeo100% (1)
- Agricultre Science Sba (Animal Science)Document12 pagesAgricultre Science Sba (Animal Science)LenizaJones50% (6)
- Physics PD LabDocument6 pagesPhysics PD Labforevapure_bar88162No ratings yet
- How Much Do High School Students Spend DailyDocument11 pagesHow Much Do High School Students Spend DailyRS sheedNo ratings yet
- Cape Unit 1 Phys Ia #1 Sept 2019Document6 pagesCape Unit 1 Phys Ia #1 Sept 2019Ariel BroderickNo ratings yet
- Lab # P/D: Topic - Waves Plan and Design An Experiment To Investigate The Speed of Sound in AirDocument6 pagesLab # P/D: Topic - Waves Plan and Design An Experiment To Investigate The Speed of Sound in AirTyrese SmithNo ratings yet
- 2023 SBA - Pure Math Guidelines - R. Berment PDFDocument41 pages2023 SBA - Pure Math Guidelines - R. Berment PDFmark woo lingNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneDocument20 pagesCSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneBill BobNo ratings yet
- Grenada Boys' Football Coach SBADocument10 pagesGrenada Boys' Football Coach SBARondell James100% (1)
- My Chemistry SbaDocument9 pagesMy Chemistry SbaCamaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- English Sba 2Document25 pagesEnglish Sba 2Rebecca Junor0% (1)
- CSEC Mathematics OutlineDocument2 pagesCSEC Mathematics OutlineKeri-ann Millar67% (3)
- Bouncing Balls Gcse CourseworkDocument5 pagesBouncing Balls Gcse Courseworkrhpvslnfg100% (2)
- Projectile MotionDocument2 pagesProjectile Motionanniemarieevans100% (1)
- Caribbean Examination Council Ahhhhh WordDocument7 pagesCaribbean Examination Council Ahhhhh WordFaith DormarNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Examination CouncilDocument8 pagesCaribbean Examination CouncilFaith DormarNo ratings yet
- Faith Dormar - PLANNING AN DESIGNING LABDocument4 pagesFaith Dormar - PLANNING AN DESIGNING LABFaith DormarNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Examination Council - Docx SOCIAL STUDIESDocument11 pagesCaribbean Examination Council - Docx SOCIAL STUDIESFaith DormarNo ratings yet