0% found this document useful (0 votes)
205 views4 pagesCommon Math Formulas for Class 7
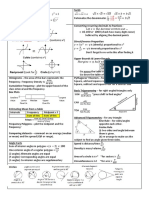
This document contains formulas for calculating area, surface area, perimeter, volume, distance, slope, and other geometric shapes and equations. It includes the formulas for finding the area of squares, rectangles, parallelograms, triangles, circles, and trapezoids. Surface area formulas are provided for cubes, cylinders, and spheres. Perimeter formulas are given for squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles. Volume formulas include those for cubes, rectangular containers, square pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres.
Uploaded by
Zulekha MohammedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
205 views4 pagesCommon Math Formulas for Class 7
This document contains formulas for calculating area, surface area, perimeter, volume, distance, slope, and other geometric shapes and equations. It includes the formulas for finding the area of squares, rectangles, parallelograms, triangles, circles, and trapezoids. Surface area formulas are provided for cubes, cylinders, and spheres. Perimeter formulas are given for squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles. Volume formulas include those for cubes, rectangular containers, square pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres.
Uploaded by
Zulekha MohammedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd