Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neo Clasical
Uploaded by
kaveesha sathsarani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe neoclassical school of thought was founded by Alfred Marshall in his 1890 book "Principles of Economics", defining economics as the science of material welfare. It focuses on demand and supply as driving market forces and efficient allocation of limited resources. Some key assumptions of neoclassical theory include rational consumer behavior, the profit motive for companies, and market equilibrium influenced by utility. However, it has also received criticism for making unrealistic assumptions and being overly dependent on mathematical models.
Original Description:
Original Title
neo clasical
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe neoclassical school of thought was founded by Alfred Marshall in his 1890 book "Principles of Economics", defining economics as the science of material welfare. It focuses on demand and supply as driving market forces and efficient allocation of limited resources. Some key assumptions of neoclassical theory include rational consumer behavior, the profit motive for companies, and market equilibrium influenced by utility. However, it has also received criticism for making unrealistic assumptions and being overly dependent on mathematical models.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageNeo Clasical
Uploaded by
kaveesha sathsaraniThe neoclassical school of thought was founded by Alfred Marshall in his 1890 book "Principles of Economics", defining economics as the science of material welfare. It focuses on demand and supply as driving market forces and efficient allocation of limited resources. Some key assumptions of neoclassical theory include rational consumer behavior, the profit motive for companies, and market equilibrium influenced by utility. However, it has also received criticism for making unrealistic assumptions and being overly dependent on mathematical models.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
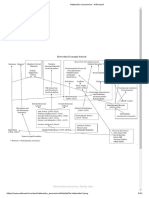
Neo classical school of thought has foundered by prof. Dr.
Alfred Marshall and who described
that “economics” as a science of material welfare in his book “principles of economics” in 1890.
So that not only was founded on neo classical thought about Alfred Marshall that other
scientists are presented by definition and ideas about this theory. Who are w. Stanley
Jevons(English) that his idea of theory of political economy 1871, carl menger(Australian)
Grundsatze der volkswirthschaftslehre 1871, Leon warlras(French) elements of economic
politique pure 1874, and John bates Clark (American) the philosophy of wealth Alfred Marshall
1885.
Mostly this thought focuses on demand and supply as the driving forces under the following
characteristics. There are production, pricing, income distribution and goods and services
consumption.
This theory divided by three types and there are classic block, temple and palladian.
Neo classical thought mostly used that efficiently allocated of limited productive resources and
also considered the growth of the resources long term.
This thought has four basic assumptions that there are consumers are very rationality, the
importance of the profit motive for companies, government need to advocate that market
equilibrium and influence of the utility on prices.
Neo classical school of thought that example for that we want to buy designer apparel because
of the attached brand label.
This theory has different definitions that it’s focus on the allocation of resources for that c
certain point in time, utilitarianism, general equilibrium and methodological individualism etc.
This theory has some criticism that there are used that unrealistic assumption, overdependence
on that mathematical approaches and it’s complex, unrealistic on that mathematical models.
The neo classical theory rejected that cost theory and utility theory value and classical
malthusian law.
This theory was introduced by marginal theory of production and distribution accept theory of
compare to the advantages.
This theory we can see in micro and neoclassical economics.
You might also like
- Neoclassical Economics: Economic Science, To DistinguishDocument35 pagesNeoclassical Economics: Economic Science, To DistinguishWan Sek ChoonNo ratings yet
- BBA Introduction To Business Economics and Fundamental ConceptsDocument30 pagesBBA Introduction To Business Economics and Fundamental ConceptsLeamae Lacsina Garcia100% (1)
- Module 1 MicroEconomicsDocument29 pagesModule 1 MicroEconomicsjustin vasquezNo ratings yet
- Business EmailsDocument25 pagesBusiness Emailskaveesha sathsarani100% (1)
- Economics and EconomistsDocument94 pagesEconomics and EconomistsbrokenwingsfairyNo ratings yet
- Marxian Critique of Classical EconomicsDocument11 pagesMarxian Critique of Classical EconomicsPravin Dhas100% (1)
- HET Chapter OneDocument22 pagesHET Chapter OneSoul AbNo ratings yet
- Neoclassical EconomicsDocument8 pagesNeoclassical EconomicsYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Normative Ethics Is Interested in Determining The Content of Our Moral BehaviorDocument6 pagesNormative Ethics Is Interested in Determining The Content of Our Moral BehaviorEllieNo ratings yet
- Neo ClassicalDocument24 pagesNeo ClassicalNics b0rjaNo ratings yet
- The Binding Force of Economics, Harris, Myers, Briol, and CarlenDocument45 pagesThe Binding Force of Economics, Harris, Myers, Briol, and CarlenIoproprioioNo ratings yet
- Heterodox Economics - WikipediaDocument45 pagesHeterodox Economics - Wikipediaime858218No ratings yet
- Neo Classical EconomicsDocument5 pagesNeo Classical EconomicsLadiaBagrasNo ratings yet
- Normative and Positive Economics: e-Publications@MarquetteDocument5 pagesNormative and Positive Economics: e-Publications@Marquettesadiq farhanNo ratings yet
- Politics Philosophy Economics 2004 Mueller 59 76Document19 pagesPolitics Philosophy Economics 2004 Mueller 59 76D. Silva EscobarNo ratings yet
- ECN 315 Update PDFDocument132 pagesECN 315 Update PDFadekoya eniolaNo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Economic TheoryDocument6 pages11 Types of Economic Theorydinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three HET II General Equilibrium and Welfare EconomicsDocument13 pagesChapter Three HET II General Equilibrium and Welfare Economicsgetacher kassaNo ratings yet
- Eigna QueenDocument12 pagesEigna QueenAngie May Castroverde CañoneroNo ratings yet
- Abm 503MEDocument31 pagesAbm 503MEbhbinduNo ratings yet
- Block 4Document41 pagesBlock 4Binita SherpaNo ratings yet
- Economic TheoryDocument9 pagesEconomic TheoryAlano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Alfred Marshall: Founding Neoclassical Thought & Behavioral ScienceDocument15 pagesAlfred Marshall: Founding Neoclassical Thought & Behavioral ScienceChhavi ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of The Classical Theory Under Modern ConditionsDocument10 pagesThe Relevance of The Classical Theory Under Modern ConditionsPawa12No ratings yet
- Deco101 Micro Economics EnglishDocument240 pagesDeco101 Micro Economics EnglishSushma SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1othmane.hamidiNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Neoclassical Economic Thought and Its CriticsDocument35 pagesPart 3 Neoclassical Economic Thought and Its CriticsFe MagbooNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Study Material First SemesterDocument122 pagesManagerial Economics: Study Material First SemesterSharanReddyNo ratings yet
- Arne Heise - Whither Economic Complexity - A New Heterodox Economic Paradigm or Just Another Variation Within The MainstreamDocument15 pagesArne Heise - Whither Economic Complexity - A New Heterodox Economic Paradigm or Just Another Variation Within The MainstreamRobertoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document46 pagesLesson 1Maurice ZorillaNo ratings yet
- On The Relationship Between Ethics and Economics: Cuadernos de Economía June 2006Document27 pagesOn The Relationship Between Ethics and Economics: Cuadernos de Economía June 2006Malik AliNo ratings yet
- History of Consumer Demand TheoryDocument41 pagesHistory of Consumer Demand TheoryAhmed Hashaam HadiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer BehaviourDocument81 pagesTheory of Consumer Behavioursupriya dasNo ratings yet
- ME Unit 1&2Document51 pagesME Unit 1&2YoNo ratings yet
- The Bubble EffectDocument5 pagesThe Bubble EffectLavanya YadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Managerial EconomicsmussaiyibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Economi Theories of EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesLesson 3 Economi Theories of EntrepreneurshipAlexaLJaralbaNo ratings yet
- The Central Focus of Modern Economic ThoughtDocument5 pagesThe Central Focus of Modern Economic ThoughtМ-ва ДжейранNo ratings yet
- The Theory of ImplementationDocument41 pagesThe Theory of ImplementationHakunaNo ratings yet
- LiteratureDocument34 pagesLiteratureCharlz JennynNo ratings yet
- IB Foundation of Economics MR - WillDocument84 pagesIB Foundation of Economics MR - Willwillwei01No ratings yet
- HeterodoxDocument4 pagesHeterodoxFebbyNo ratings yet
- Is Marketing A Science-FDocument8 pagesIs Marketing A Science-FBen KiturNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: University of CalicutDocument73 pagesManagerial Economics: University of CalicutaaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Unit1and 2Document28 pagesManagerial Economics Unit1and 2jatinNo ratings yet
- History: DiscoveringDocument20 pagesHistory: DiscoveringDaniel Gabriel PunoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Criticism of The Neo-Classical Theory of The Firm The Marginalist ControversyDocument74 pagesUnit 1 Criticism of The Neo-Classical Theory of The Firm The Marginalist ControversySaim IjazNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Its TheoriesDocument20 pagesEntrepreneurship and Its TheoriesKarthik DNo ratings yet
- Humphrey (1999) Mercantilists and Classicals - Insights From Doctrinal HistoryDocument28 pagesHumphrey (1999) Mercantilists and Classicals - Insights From Doctrinal HistorySaúl Lucio FloresNo ratings yet
- Hunt and Morgan 1995, Comparative Advantage Theory of CompetitionDocument16 pagesHunt and Morgan 1995, Comparative Advantage Theory of CompetitionNiklas Laage-PetersenNo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Economic Theories Aspiring Economists Should KnowDocument4 pages11 Types of Economic Theories Aspiring Economists Should Knowkiere VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Costing 1Document15 pagesCosting 1pepepepe86No ratings yet
- Concept of MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesConcept of MicroeconomicsBalNo ratings yet
- History of Economic ThoughtDocument29 pagesHistory of Economic ThoughtMasud SanvirNo ratings yet
- Understanding Economics and The Overwiew of The EconomyDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Economics and The Overwiew of The EconomyKathkath PlacenteNo ratings yet
- 1-The Nature and Scope of EconomicsDocument28 pages1-The Nature and Scope of EconomicsHassan AliNo ratings yet
- The Classical Theory of Supply and DemandDocument32 pagesThe Classical Theory of Supply and Demandubik59No ratings yet
- Consumer'S Behaviour - An Approach From The Perspective of Behavioural EconomicsDocument11 pagesConsumer'S Behaviour - An Approach From The Perspective of Behavioural EconomicsLucia DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- Heterodox Economics - WikiwandDocument11 pagesHeterodox Economics - WikiwandDaniel Victoriano BremontNo ratings yet
- PDF - Tute 06 - Reported Speech - ImperativesDocument7 pagesPDF - Tute 06 - Reported Speech - Imperativeskaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Infer Implied MeaningDocument25 pagesInfer Implied Meaningkaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Padlet - Business Email WritingDocument40 pagesPadlet - Business Email Writingkaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Listening Year I Semester II - 2020 - PaperDocument3 pagesListening Year I Semester II - 2020 - Paperkaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Listening Year I Semester II - 2020 - Examiners ScriptDocument5 pagesListening Year I Semester II - 2020 - Examiners Scriptkaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- 2016-2017 - Listening Paper 1260 TranscriptDocument3 pages2016-2017 - Listening Paper 1260 Transcriptkaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- 2021MM326Document2 pages2021MM326kaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- 2016-2017 - Listening Paper 1260Document4 pages2016-2017 - Listening Paper 1260kaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Business Emails - PhrasesDocument3 pagesBusiness Emails - Phraseskaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- 2021MM326Document2 pages2021MM326kaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument57 pagesDifferentiationkaveesha sathsaraniNo ratings yet