Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eept - Cervical Region
Uploaded by
Lovely GopezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eept - Cervical Region
Uploaded by
Lovely GopezCopyright:
Available Formats
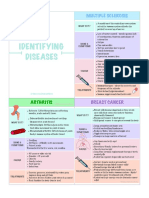
EEPT: CERVICAL REGION
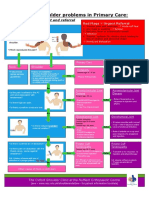
Red Flags
Red Flags Cervical Neoplastic Upper Vertebral Inflammatory Cervical
Myelopathy Conditions Cervical Artery or Systemic Fracture
Ligamentous Insufficiency Disease
Instability
Signs & • Sensory • Age >50 years. • Occipital • Drop attacks. • Temperature • Trauma
Symptoms disturbances of • Previous headache and • Dizziness >100 Degrees F
the hands. history of numbness. • Dysphasia • BP >160/95
• Hand intrinsic cancer. • Severe • Dysarthria mmHg
muscle testing. • Unexplained limitation • Diplopia • Resting Pulse
• Unsteady gait. weight loss. during neck • (+) Cranial >100 bpm
• Hoffman’s • Constant pain, active range of nerve signs. • Resting
reflex. not relieved motion • Ataxia respiration >25
• Babinski with bed rest. (AROM) in all • Nausea bpm
• Clonus • Night pain. directions. • Fatigue
• Inverted • Signs of
supinator sign cervical
• Hyperreflexia myopathy.
• Bowel and • Post trauma.
bladder • Rheumatoid
disturbances. Arthritis
• Multisegmental • Down
weakness. syndrome
• Multisegmental
sensory
changes.
Yellow Flags
• Pain is harmful or disabling
• Pain must be eliminated before returning to activity
• Passive attitudes towards therapy
• Patient utilization of extended rest, reduced activity level and withdrawal from daily
activities
• Patient reports of extreme pain intensity
• High intake of alcohol or other substances
Palpation
Supine
• Palpate bilateral sternoclavicular joints for mobility assessment or tenderness.
• Palpate acromioclavicular joint for mobility assessment or tenderness.
• Palpate sub-occipital muscles, upper trapezius, levator scapula, and pectoralis minor to
assess shortness or tenderness.
Prone
• Central and peripheral Cervical and Thoracic Spine.
• Palpate ribs 1 - 7 of the upper and mid thoracic region.
• Ribs 1 - 7 posterior to anterior accessory motion.
Seated
• Palpate for tissue texture changes down medial groove of cervical and thoracic spine.
• Palpate for tissue texture changes on either side of the spinous processes of the cervical
and thoracic spine.
• Palpate for any scoliotic deviations.
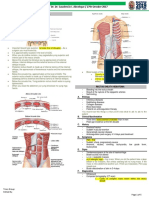
EEPT: CERVICAL REGION
Reflexes
• C5 - C6 – biceps
• C5 – C6 – brachioradialis
• C7 – triceps
Manual Muscle Testing
• Elbow
◦ Flexion (C5,C6)
◦ Extension (C7)
• Shoulder
◦ Flexion (C5)
◦ Extension (C6, C7, C8)
◦ Abduction (C5)
• Wrist
◦ Flexion (C6 – 7)
◦ Extension (C6 – 7)
• Finger
◦ Flexion (C7 – C8)
◦ Extension (C7 – C8
◦ Abduction (T1)
Sensory Examination
• C3 – Occiput
• C4 – Supraclavicular space
• C5 – Anterior shoulder
• C6 – Lateral shoulder
• C7 – Posterior arm
• C8 – Phalanxes 4 – 5
• T1 – Medial arm and axilla
Special Tests
• Cranial Cervical Flexion Test
• Neck Flexor Muscle Endurance Test
• Upper Limb Tension Test (ULTT)
• Spurling’s Test
• Distraction Test
• Valsalva Test
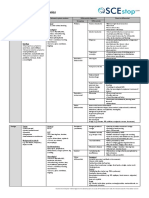
EEPT: CERVICAL REGION
Differential Diagnosis
1. Are the patient’s symptoms reflective of a visceral disorder or a serious or potentially life-
threatening illness? This may indicate non-mechanical conditions such as:
◦ Cervical Myelopathy
◦ Cervical Instability
◦ Fracture
◦ Neoplastic Conditions
◦ Vascular Compromise
◦ Systemic / Visceral Disease
EEPT: CERVICAL REGION
OTHER SPECIAL TESTS:
You might also like
- Generic Name: Brand Names:: VincristineDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Names:: VincristineMaria Eliza AgustinoNo ratings yet
- Revision 21.7.23-Y3Document7 pagesRevision 21.7.23-Y3leexinyiNo ratings yet
- Diseases 2Document11 pagesDiseases 2Kristy CostelloNo ratings yet
- History Taking in HematologyDocument1 pageHistory Taking in HematologyNarmin Abubaker AliNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ExaminationDocument61 pagesNervous System ExaminationJaaydevNo ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument3 pagesMultiple SclerosisBryan Lloyd RayatNo ratings yet
- Neurology Final 05.06.2023Document10 pagesNeurology Final 05.06.2023Ahmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Head and NeckDocument5 pagesTumors of The Head and NeckMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Neuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisDocument4 pagesNeuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisShakina FareedNo ratings yet
- Cerebral HistoriesDocument2 pagesCerebral HistoriesgibreilNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis-1Document20 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis-1Peterson Wachira HscNo ratings yet
- Pre Gabal in Drug StudyDocument1 pagePre Gabal in Drug StudyHailMarieSBarcenasNo ratings yet
- 6 NEUROPATHIC PAIN For FKWKDocument52 pages6 NEUROPATHIC PAIN For FKWKPrinces Mentari Dwi NurainiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Exam: FACEM Part II Notes Eunicia TanDocument28 pagesCardiovascular Exam: FACEM Part II Notes Eunicia TanGolam SarwarNo ratings yet
- Cervical PathologiesDocument27 pagesCervical PathologiesCrystal Lynn Keener SciariniNo ratings yet
- Bubble He Assessment: Vital SignsDocument11 pagesBubble He Assessment: Vital SignsFregen Mae ApoyaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Abdominal WallDocument5 pagesAnterior Abdominal WallAnonymous 2TzM1ZNo ratings yet
- Small BowelDocument4 pagesSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- HSF Stroke Assessment Pocket Guide PDFDocument24 pagesHSF Stroke Assessment Pocket Guide PDFPeter FritzNo ratings yet
- Integumentry Dermatitis Bacterial Impetigo Cellulitis Abscess DefDocument17 pagesIntegumentry Dermatitis Bacterial Impetigo Cellulitis Abscess DefMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Integumentry PDFDocument17 pagesIntegumentry PDFMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument7 pagesDrugsAbdul-Hakeem AL-GhammariNo ratings yet
- Signs Symptoms Children TeensDocument1 pageSigns Symptoms Children TeensPatsy YazdiNo ratings yet
- BreathlessnessDocument3 pagesBreathlessnessHengkai NeoNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument3 pagesPhysical AssessmentahrhicxNo ratings yet
- Emergenze Addome RXDocument9 pagesEmergenze Addome RXBrovazzo PieroNo ratings yet
- Examination: Short History Positioning of The PatientDocument1 pageExamination: Short History Positioning of The PatientAshan BopitiyaNo ratings yet
- Category 3 Week 8Document1 pageCategory 3 Week 8api-468093714No ratings yet
- Nausea and VomitingDocument16 pagesNausea and VomitingJosiah Noella BrizNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Neuropathy Clinical ApproachDocument19 pagesPeripheral Neuropathy Clinical ApproachNur Nadzifah Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- NHS UK Diagnosis of Shoulder ProblemsDocument1 pageNHS UK Diagnosis of Shoulder ProblemsmertNo ratings yet
- 111 Peripheral NeuropathyDocument17 pages111 Peripheral NeuropathyjassbhanguNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument1 pageSpinal Cord Injurymaglangitjoannamarie1920No ratings yet
- Cerebral Concussion - PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesCerebral Concussion - PathophysiologyFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- RectalDocument2 pagesRectalanne laureNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Acute Ultrasound Emergencies On-Call Key Learning Points For The Radiology Registrar.Document1 pageTop Ten Acute Ultrasound Emergencies On-Call Key Learning Points For The Radiology Registrar.KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Shanz - PEDIA II 2.01 NEWDocument8 pagesShanz - PEDIA II 2.01 NEWPetrina XuNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument22 pagesLeprosyvisweswar030406No ratings yet
- Red Flags: Indications For Urgent ReferralDocument5 pagesRed Flags: Indications For Urgent ReferralEndah Novianti SoenarsinNo ratings yet
- DrugstudyHPV - AjimaDocument2 pagesDrugstudyHPV - Ajimaaisa baladjiNo ratings yet
- OC-Ischemia Heart DiseaseDocument1 pageOC-Ischemia Heart DiseaseCharlie LeeNo ratings yet
- Gynae HistoriesDocument2 pagesGynae HistoriesZahraa Al-SayedNo ratings yet
- Osce ChecklistDocument9 pagesOsce ChecklistXeric CedoNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Fourniers GangreneDocument13 pagesDrugstudy Fourniers GangrenemarinordNo ratings yet
- Assignment OrthoDocument3 pagesAssignment OrthoPeterNo ratings yet
- (S. Abbate) Ear Acupuncture Prescriptions and Techniques PDFDocument8 pages(S. Abbate) Ear Acupuncture Prescriptions and Techniques PDFVenom VerdinNo ratings yet
- History and PeDocument3 pagesHistory and PeMa. Isabel JamitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- Joint PainDocument11 pagesJoint PainSandarekha PereraNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Oxygenation Handouts 2007 Nclex 1232010737844931 1Document23 pagesMicrosoft Word Oxygenation Handouts 2007 Nclex 1232010737844931 1api-19824701100% (1)
- Oncology Nursing: A Sore That Does Not HealDocument2 pagesOncology Nursing: A Sore That Does Not HealAleandro DizonNo ratings yet
- Localisation in NeurologyDocument19 pagesLocalisation in NeurologyArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Localisation in NeurologyDocument19 pagesLocalisation in NeurologyArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Risk For HemorrhageDocument3 pagesRisk For HemorrhageJudith Arlie Eduarte PinedaNo ratings yet
- Lesion Localization in NeurologyDocument34 pagesLesion Localization in NeurologyValeria Leon AbadNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Neuropathy AidaDocument36 pagesPeripheral Neuropathy AidaAdlina ArifinNo ratings yet
- How To Diagnose VertigoDocument41 pagesHow To Diagnose VertigoHasbi Ash ShiddiqieNo ratings yet
- Degenerative in ShoulderDocument49 pagesDegenerative in Shoulderari rujatiNo ratings yet
- MRAT 211 - Lumbar Rehabilitation TransDocument11 pagesMRAT 211 - Lumbar Rehabilitation TransLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- MRAT 211 - Ankle & Foot TRANSDocument8 pagesMRAT 211 - Ankle & Foot TRANSLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- MRAT 211 - Thoracic Rehabilitation TRANSDocument10 pagesMRAT 211 - Thoracic Rehabilitation TRANSLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Crat 211 - Cardiovascular Rehabilitation & Intervention TransDocument12 pagesCrat 211 - Cardiovascular Rehabilitation & Intervention TransLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Crat 211 - Cardiac Pathology (Treatments)Document2 pagesCrat 211 - Cardiac Pathology (Treatments)Lovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Checklist Cardiac AssessmentDocument8 pagesChecklist Cardiac AssessmentLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Crat 211 - DM TransDocument4 pagesCrat 211 - DM TransLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Assessment TransDocument25 pagesCardiac Assessment TransLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Intenzifikator KC: Grinding Aid For Improvement of Cement GrindingDocument1 pageIntenzifikator KC: Grinding Aid For Improvement of Cement GrindingJohn GiannakopoulosNo ratings yet
- Coduri Reactivi Pentra 400Document3 pagesCoduri Reactivi Pentra 400marianalinamihaelaNo ratings yet
- Reiki Crystal GridsDocument2 pagesReiki Crystal Gridsapi-270898792100% (1)
- Policy AnalysisDocument11 pagesPolicy Analysisapi-592404436No ratings yet
- Managing Insomnia Lesson 1Document22 pagesManaging Insomnia Lesson 1taurus_europe100% (2)
- Materi Policy Analysis TriangleDocument6 pagesMateri Policy Analysis TriangleRegina Marsha100% (1)
- Gad Plan 2022-2023Document6 pagesGad Plan 2022-2023Melvin AlmeriaNo ratings yet
- Bioprogressive Therapy: Overbite Reduction With The Lower Utility ArchDocument4 pagesBioprogressive Therapy: Overbite Reduction With The Lower Utility ArchMeguja jithinNo ratings yet
- Coles Medical 2011 - GeorgeDocument272 pagesColes Medical 2011 - GeorgeWong SterlingNo ratings yet
- Administration of Medication in SchoolsDocument8 pagesAdministration of Medication in SchoolsDavid KefferNo ratings yet
- Mirror GazingDocument1 pageMirror GazingNaranLoganNo ratings yet
- The Story of Blue Jeans: O'qish Va Yozish Amaliyoti Fanidan Oraliq Nazorat Savollari (2 Semestr)Document15 pagesThe Story of Blue Jeans: O'qish Va Yozish Amaliyoti Fanidan Oraliq Nazorat Savollari (2 Semestr)Sabrina ObidovaNo ratings yet
- BRC Food v6Document4 pagesBRC Food v6VanifsmsNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy For Primary Frozen Shoulder in Secondary Care Hanchard 2019Document11 pagesPhysiotherapy For Primary Frozen Shoulder in Secondary Care Hanchard 2019patinoomar67No ratings yet
- Lic DocsDocument11 pagesLic DocsRahul ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 6th FDI-IDA Joint Meeting 2010 Program & AbstractsDocument82 pages6th FDI-IDA Joint Meeting 2010 Program & AbstractsJosep AtmadjajaNo ratings yet
- Siddha InstituteDocument10 pagesSiddha InstituteBala GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Malaria Chart June 2012Document8 pagesMalaria Chart June 2012H!TNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Culture Module BrochureDocument8 pagesFood Safety Culture Module Brochurejamil voraNo ratings yet
- Vibrio & Aeromonas & PlesiomonasDocument48 pagesVibrio & Aeromonas & PlesiomonasOscar PeñaNo ratings yet
- Fresh Air Camp Application 2010Document13 pagesFresh Air Camp Application 2010Morgan Memorial Goodwill IndustriesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For A Certificate of Fitness For High-Pressure Gas and Liquids Transmission PipelinesDocument35 pagesGuidelines For A Certificate of Fitness For High-Pressure Gas and Liquids Transmission Pipelineshesam_ab2002100% (4)
- Wins Monitoring System - Dagumbaan Integrated SchoolDocument17 pagesWins Monitoring System - Dagumbaan Integrated SchoolAnonymous tfXHIRnNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument3,216 pagesRevisionRylie RuuNo ratings yet
- How To Maintain Throat HygieneDocument9 pagesHow To Maintain Throat Hygieneankita singhNo ratings yet
- Health and Social Care UkDocument5 pagesHealth and Social Care UkAkular AyramNo ratings yet
- Kualitas Hidup Pasien GoutDocument10 pagesKualitas Hidup Pasien GoutShared LifeNo ratings yet
- SR 90Document2 pagesSR 90Aeron John GallaNo ratings yet
- Solicitation Restroom MaintenanceDocument10 pagesSolicitation Restroom MaintenanceDarnel CayogNo ratings yet
- A Study On Psoriasis of Nails Severity Scoring SystemDocument4 pagesA Study On Psoriasis of Nails Severity Scoring SystemKhilyatul MufidaNo ratings yet