Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Java Enums
Uploaded by
Jaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Java Enums
Uploaded by
Jaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoCopyright:
Available Formats
Java Enums
The Enum in Java is a data type which contains a fixed set of constants.
It can be used for days of the week (SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY,
THURSDAY, FRIDAY, and SATURDAY) , directions (NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, and WEST),
season (SPRING, SUMMER, WINTER, and AUTUMN or FALL), colors (RED, YELLOW, BLUE,
GREEN, WHITE, and BLACK) etc. According to the Java naming conventions, we should
have all constants in capital letters. So, we have enum constants in capital letters.
Java Enums can be thought of as classes which have a fixed set of constants (a variable
that does not change). The Java enum constants are static and final implicitly. It is
available since JDK 1.5.
Enums are used to create our own data type like classes. The enum data type (also
known as Enumerated Data Type) is used to define an enum in Java. Unlike C/C++,
enum in Java is more powerful. Here, we can define an enum either inside the class or
outside the class.
Java Enum internally inherits the Enum class, so it cannot inherit any other class, but it
can implement many interfaces. We can have fields, constructors, methods, and main
methods in Java enum.
Points to remember for Java Enum
o Enum improves type safety
o Enum can be easily used in switch
o Enum can be traversed
o Enum can have fields, constructors and methods
o Enum may implement many interfaces but cannot extend any class because it
internally extends Enum class
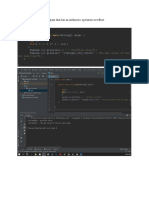
Simple Example of Java Enum
You might also like
- Enum Types JavaDocument3 pagesEnum Types JavaAmandeep PuniaNo ratings yet
- Java Enums: Points To Remember For Java EnumDocument6 pagesJava Enums: Points To Remember For Java EnumBrothers CreationNo ratings yet
- 13 Enums and AnnotationsDocument16 pages13 Enums and AnnotationsSebastian RomaniucNo ratings yet
- Derived Syntactical Constructs in Java: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Document10 pagesDerived Syntactical Constructs in Java: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Shobhit KumarNo ratings yet
- Enum TypesDocument2 pagesEnum TypesmanoharNo ratings yet
- Derived Syntactical Constructs in Java: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Document13 pagesDerived Syntactical Constructs in Java: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Shobhit KumarNo ratings yet
- Sains KomputerDocument2 pagesSains KomputerRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Kannada Class - Session I Handout: Kannada Word English Word Simple SentenceDocument1 pageKannada Class - Session I Handout: Kannada Word English Word Simple SentenceIrene BooneNo ratings yet
- Java EnumDocument6 pagesJava EnumRahul Singh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Java - Basic SyntaxDocument12 pagesJava - Basic Syntaxfathima camangianNo ratings yet
- Naming ConventionDocument1 pageNaming ConventionsuhasNo ratings yet
- Union and Enum: Md. Ja K A Ria Lectu Rer de Pt. O F Cse, MistDocument11 pagesUnion and Enum: Md. Ja K A Ria Lectu Rer de Pt. O F Cse, MistSakib RafeeNo ratings yet
- One-to-One Letter Sound CorrespondencesDocument4 pagesOne-to-One Letter Sound CorrespondencesjohannasannNo ratings yet
- Session-5 List in PythonDocument51 pagesSession-5 List in PythonSahithNo ratings yet
- Java TutorialDocument17 pagesJava TutorialTelika RamuNo ratings yet
- Catastrophic BacktrackingDocument15 pagesCatastrophic BacktrackingMark ArmNo ratings yet
- ARRAYS PresentationDocument9 pagesARRAYS PresentationshyannNo ratings yet
- PLP 24Document43 pagesPLP 24ashokmohan87No ratings yet
- EP2 Ladybird Week6Document1 pageEP2 Ladybird Week6Adam ShawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 1 PDFCha TagataNo ratings yet
- SLANT Spelling Week 13Document1 pageSLANT Spelling Week 13kwhitley3No ratings yet
- Contempo IntruzoDocument1 pageContempo IntruzoJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Inheritance - Programming Activity (Intruzo, Jaymarc P.)Document11 pagesInheritance - Programming Activity (Intruzo, Jaymarc P.)Jaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 PlatformDocument1 pageActivity #1 PlatformJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Selection SortDocument5 pagesSelection SortJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 PlatformDocument1 pageActivity #1 PlatformJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Platform AsignmentDocument2 pagesPlatform AsignmentJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Database Summary IntruzoDocument1 pageDatabase Summary IntruzoJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Selection Sort SourceCodeDocument1 pageSelection Sort SourceCodeJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Activity #2 OOP Intruzo, Jaymarc P.Document7 pagesActivity #2 OOP Intruzo, Jaymarc P.Jaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Web Summary IntruzoDocument1 pageWeb Summary IntruzoJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet
- Integration Summary IntruzoDocument1 pageIntegration Summary IntruzoJaymarc “Drummer jAyZ” IntruzoNo ratings yet