Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FM Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Glenda PaezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FM Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Glenda PaezCopyright:
Available Formats
• They are the
cornerstones of the
Introduction to Why study overall financial system
in which financial
Financial Markets Financial managers operate
• Individuals use both for
Markets and investing
• Corporations and
Prepared by: Ms. Ida
Institutions? governments use both
for financing
OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL MARKETS Primary Markets versus Secondary Markets
Primary Markets Secondary Markets
markets in which users of markets where financial
PRIMARY MARKETS SECONDARY MARKETS
VS funds (e.g. corporations, instruments are traded
MONEY MARKETS CAPITAL MARKETS governments) raise funds among investors (e.g.
FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKETS by issuing financial NYSE, NASDAQ)
instruments (e.g. stocks
and bonds)
Money Markets versus Capital Markets Foreign Exchange Markets
Money Markets Capital Markets • “FX” markets deal in trading one currency for
markets that trade debt markets that trade debt another (e.g. dollar for yen)
securities with maturities (bonds) and equity (stock) • The “spot” FX transaction involves the immediate
of one year or less (e.g. instruments with exchange of currencies at the current exchange rate
CD’s, U.S. Treasury bills) maturities of more than • The “forward” FX transaction involves the
one year exchange of currencies at a specified date in the
future and at a specified exchange rate
Derivative Security Markets Overview of Financial Institutions
• The markets in which derivative securities Institutions that perform the essential function
trade. of channeling funds from those with surplus
funds to those with shortages of funds
• Derivative Security (e.g. banks, thrifts, insurance companies,
– An agreement between two parties to exchange a securities firms and investment banks, finance
standard quantity of an asset at a predetermined price companies, mutual funds, pension funds).
on a specified date in the future.
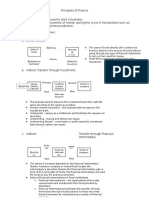
Flow of Funds in a World without FIs: Flow of Funds in a World without FIs:
Direct Transfer Direct Transfer
Users of Funds FI Suppliers of Funds
Financial Claims (Brokers)
(Equity and debt
instruments)
Suppliers of
Users of Funds
Funds FI
(Corporations) Cash Cash
(Households) (Asset
Cash transformers)
Financial Claims Financial Claims
Example: A firm sells shares directly to investors without (Equity and debt securities) (Deposits and insurance policies)
going through a financial institution.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin 10
Types of Financial Institutions Types of Financial Institutions
• Commercial banks • Insurance companies
– depository institutions whose major assets are loans – financial institutions that protect individuals and
and major liabilities are deposits corporations from adverse events
• Thrifts • Securities firms and investment banks
– depository institutions in the form of savings and – financial institutions that underwrite securities and
loans, credit unions engage in securities brokerage and trading
Types of Financial Institutions Types of Financial Institutions
• Finance companies • Pension Funds
– financial institutions that make loans to individuals – financial institutions that offer savings plans for
and businesses retirement
• Mutual Funds
– financial institutions that pool financial resources
and invest in diversified portfolios
Services Performed by Financial Services Provided by FIs Benefiting the Overall
Intermediaries Economy
• Monitoring Costs • Money Supply Transmission
• Liquidity and Price Risk • Credit Allocation
• Transaction Cost Services
• Maturity Intermediation • Intergenerational Wealth Transfers
• Denomination Intermediation • Payment Services
Risks Faced by Financial Institutions Regulation of Financial Institutions
• Interest Rate Risk • Off-Balance-Sheet Risk • FIs provide vital financial services to all
• Foreign Exchange Risk • Technology Risk sectors of the economy; therefore, their
• Market Risk • Operational Risk regulation is in the public interest
• Credit Risk • Country or Sovereign
Risk • In an attempt to prevent their failure and the
• Liquidity Risk • Insolvency Risk failure of financial markets overall
Factors Leading to Significant Growth in
Regulation of Financial Institutions
Foreign Markets
• Financial Markets became more global as the • The pool of savings from foreign investors has
value of stocks traded in foreign markets soared increased
• Foreign bond markets have served as a major • International investors have turned to U.S. and other
source of international capital markets to expand their investment opportunities
• Globalization also evident in the derivative • Information on foreign investments and markets is
securities market now more accessible (e.g. internet)
You might also like
- FMI Lecture 1Document13 pagesFMI Lecture 1shakirNo ratings yet
- 1-Marketing Financial Products - An IntroductionDocument43 pages1-Marketing Financial Products - An IntroductionKartik BhartiaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Role and Overview PDFDocument30 pages1.1 Role and Overview PDFRedNo ratings yet
- Financial Environment: An OverviewDocument26 pagesFinancial Environment: An OverviewLaiba KhanNo ratings yet
- Fin EnvDocument35 pagesFin Envbisma9681No ratings yet
- Finance An OverviewDocument15 pagesFinance An OverviewramanpushkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Financial MarketsDocument18 pagesChapter 1-Financial Marketskim cheNo ratings yet
- CH1 Market Organization and Structure 2021Document37 pagesCH1 Market Organization and Structure 2021Arbi ChaimaNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Role of Financial SystemDocument58 pagesThe Nature and Role of Financial SystemMadhu BabuNo ratings yet
- FINMAN7 - W2 - Capital MarketsDocument33 pagesFINMAN7 - W2 - Capital MarketsCADAGO, Erica P.No ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument32 pagesFinancial MarketsEmil BabiloniaNo ratings yet
- Finance Part 2 PDFDocument5 pagesFinance Part 2 PDFJustine PascualNo ratings yet
- Role of financial markets and institutionsDocument3 pagesRole of financial markets and institutionsMeilin Denise MEDRANANo ratings yet
- Financial Market Chapter 1Document20 pagesFinancial Market Chapter 1Karylle EntinoNo ratings yet
- FINA 3780 Chapter 1Document27 pagesFINA 3780 Chapter 1roBinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1shraddha amatyaNo ratings yet
- What Are Financial MarketsDocument5 pagesWhat Are Financial MarketsJasmine FalibleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document99 pagesChapter 5firdausismadi100% (1)
- AE18.1 Financial Markets and Financial SystemDocument23 pagesAE18.1 Financial Markets and Financial SystemTrishia Mae OliverosNo ratings yet
- Managerial Finance: An Overview of Financial Systems and MarketsDocument116 pagesManagerial Finance: An Overview of Financial Systems and MarketsJaja SutejaNo ratings yet
- INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM EXPLAINEDDocument24 pagesINDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM EXPLAINEDAlinaNo ratings yet
- Great Learning - Session 1 - Overview of Indian Financial SytemDocument14 pagesGreat Learning - Session 1 - Overview of Indian Financial Sytemsudnandini86No ratings yet
- KCV49 PJYC4 M0 DJ PJ 827Document26 pagesKCV49 PJYC4 M0 DJ PJ 827GybcNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument41 pagesIndian Financial SystemKaneNo ratings yet
- Ch1.Introduction and Overview of Financial MarketsDocument17 pagesCh1.Introduction and Overview of Financial MarketsHazell DNo ratings yet
- Financial System - Introduction ExplainedDocument31 pagesFinancial System - Introduction ExplainedVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM OVERVIEWDocument35 pagesINDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM OVERVIEWRitesh RamanNo ratings yet
- Business Financial EnvironmentDocument198 pagesBusiness Financial EnvironmentAmitava MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Financial Assets, Money, Financial Transactions, and Financial InstitutionsDocument24 pagesFinancial Assets, Money, Financial Transactions, and Financial InstitutionsJeremy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- BINTY FMDocument13 pagesBINTY FMPatralekha DeNo ratings yet
- Finance Part 2Document6 pagesFinance Part 2Justine PascualNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Financial Markets and InstitutionsAisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Financial System and MarketsDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Indian Financial System and MarketstayaisgreatNo ratings yet
- FIN200 Introduction To Finance and Financial Environment 2019-20Document35 pagesFIN200 Introduction To Finance and Financial Environment 2019-20Lone MasiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Introduction To Banking and Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesLecture - Introduction To Banking and Financial InstitutionsJessalyn Cabael100% (1)
- Structure of Fin SysDocument80 pagesStructure of Fin SysharishNo ratings yet
- Abm BFLDocument22 pagesAbm BFLGiann Lorrenze Famisan RagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter - OneDocument30 pagesChapter - OneMagix SmithNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument8 pagesFinancial MarketRegin MagpiliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Financial MarketsDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Financial MarketsHoy HoyNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions OverviewDocument31 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions OverviewBUBOYNo ratings yet
- 6-Financial Environment System LDocument27 pages6-Financial Environment System LerolcanNo ratings yet
- EFB201 Introduction To Financial Markets SlidesDocument14 pagesEFB201 Introduction To Financial Markets Slideshowunfung0705No ratings yet
- Role of financial markets and institutions lectureDocument13 pagesRole of financial markets and institutions lectureJohanna Nina UyNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System: PGDM 4 TrimesterDocument15 pagesIndian Financial System: PGDM 4 TrimesterAshok PaikraNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Overview of the Indian Financial SystemDocument35 pagesModule 1: Overview of the Indian Financial SystemSibika GadiaNo ratings yet
- Raising Capital in The Financial MarketsDocument18 pagesRaising Capital in The Financial Markets22GayeonNo ratings yet
- PrernaDocument23 pagesPrernaNil SenNo ratings yet
- FM - 2Document14 pagesFM - 2akesingsNo ratings yet
- Eco 531 - Chapter 2Document53 pagesEco 531 - Chapter 2Nurul Aina IzzatiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Unit I - Introduction To Financial Systems and Financial MarketDocument41 pages3 - Unit I - Introduction To Financial Systems and Financial MarketAlexis Ann Angan AnganNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Islamic Financial Principles and SystemsDocument20 pagesThe Importance of Islamic Financial Principles and SystemsNouf ANo ratings yet
- Some Basic Definitions: Fintmed Session 1 Second Term Academic Year 2013 - 2014Document2 pagesSome Basic Definitions: Fintmed Session 1 Second Term Academic Year 2013 - 2014Mikka Ella ÜNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Financial System: Group1: Michelle Santiago ReighlynroseteDocument23 pagesOverview of The Financial System: Group1: Michelle Santiago ReighlynroseteJoan Pearl SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Lec 01Document22 pagesLec 01Hamid KhurshidNo ratings yet
- Cab PDFDocument35 pagesCab PDFhgcgfNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets & Institutions: Chapter 1Document305 pagesFinancial Markets & Institutions: Chapter 1Ase Sharew100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Basics of Financial MarketsDocument46 pagesLecture 1 - Basics of Financial MarketsNitesh BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Module 1.1 Financial MarketsDocument60 pagesModule 1.1 Financial MarketssateeshjorliNo ratings yet
- Belbin Team Roles QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesBelbin Team Roles Questionnaireapi-248119294No ratings yet
- CLAT Preparation by OpusDocument11 pagesCLAT Preparation by Opustheopusway100% (1)
- Understanding Plural and Singular Forms of NounsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Plural and Singular Forms of NounsCristine Igama ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Release Notes For Licensing Mentor Graphics SoftwareDocument8 pagesRelease Notes For Licensing Mentor Graphics SoftwareMentorNo ratings yet
- KCSE History Marking SchemeDocument61 pagesKCSE History Marking SchemeDavid Musila ToywaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources in TamilnaduDocument4 pagesWater Resources in TamilnaduVignesh AngelNo ratings yet
- Abc Ved 1227686577805956 8Document21 pagesAbc Ved 1227686577805956 8Sathiya Soruban ElangovanNo ratings yet
- 5 Pillars of IslamDocument4 pages5 Pillars of IslamTapiwa Asher MoyoNo ratings yet
- BISE MultanDocument617 pagesBISE MultanZubair NadeemNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Religion Summative TestDocument5 pagesGrade 11 Religion Summative TestEngelbert TejadaNo ratings yet
- Open Group Guide: Business CapabilitiesDocument25 pagesOpen Group Guide: Business Capabilitieshanan100% (1)
- USAID Conference - Beyond The Usual Suspects-EdDocument4 pagesUSAID Conference - Beyond The Usual Suspects-EdInterActionNo ratings yet
- Humanitarian Affairs Officer Interview Questions and Answers GuideDocument12 pagesHumanitarian Affairs Officer Interview Questions and Answers GuidemohmedNo ratings yet
- Humantrafficking Logic ModelDocument1 pageHumantrafficking Logic Modelapi-341131818100% (1)
- The Historical Development of Teaching as a Profession in the PhilippinesDocument5 pagesThe Historical Development of Teaching as a Profession in the PhilippinesRichel Leola SumagangNo ratings yet
- People Vs MalimitDocument2 pagesPeople Vs MalimitAya Baclao100% (2)
- ISO 9001 Quality Objectives - What They Are and How To Write ThemDocument7 pagesISO 9001 Quality Objectives - What They Are and How To Write ThemankitNo ratings yet
- Understanding Diverse LearnersDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Diverse LearnersMerry Grace Aballe Abella100% (2)
- No Man Is An Island Introduction HICHAM OUAZENEDocument1 pageNo Man Is An Island Introduction HICHAM OUAZENEسدن آرما0% (1)
- Kentucky Gun Co Black Friday Page 1 2022Document1 pageKentucky Gun Co Black Friday Page 1 2022AmmoLand Shooting Sports NewsNo ratings yet
- Maulik Shah ResumeDocument1 pageMaulik Shah ResumeDeepak SantNo ratings yet
- CIT Vs Ople Digest For PrintingDocument4 pagesCIT Vs Ople Digest For PrintingJaniceNo ratings yet
- Chart of AccountsDocument2 pagesChart of AccountsailihengNo ratings yet
- Shaking Hands With Other Peoples PainDocument19 pagesShaking Hands With Other Peoples PainGimonjoNo ratings yet
- Ciril Report 2019Document44 pagesCiril Report 2019Aloka MajumderNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Research Reflection PaperDocument9 pagesAssignment 3: Research Reflection PaperDang HuynhNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Read and Circle The Correct AnswerDocument5 pagesExercise 1: Read and Circle The Correct AnswerDiệu HườngNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Business Plan: Barbara MasciocchiDocument20 pagesHow To Make A Business Plan: Barbara MasciocchiFabianNo ratings yet
- General TermsDocument8 pagesGeneral TermsSyahmi GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Nord Pool - The Nordic Power MarketDocument30 pagesNord Pool - The Nordic Power MarketVanádio Yakovlev FaindaNo ratings yet