Professional Documents
Culture Documents
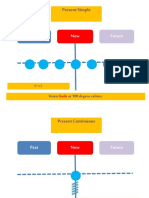
Simple Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
Uploaded by
maha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views11 pagessimple present
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsimple present
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views11 pagesSimple Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
Uploaded by
mahasimple present
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Use
. @)
1. Regular habits or daily routine: Use the Simple
Present to express the idea that an action is repeated
or usual. The action can be a habit, a hobby, a daily
event or something that often happens.
E.g. - | play soccer
- The school opens every morning at 7 AM.
- He always forgets her bag.
- Every twelve months, the Earth circles
the Sun.
Scanned with CamScanner
Use
O
| 2. Facts or generalizations: The Simple Present can also
indicate the speaker believes that a fact was true before,
is true now, and will be true in the future. It is not
important if the speaker is correct about the fact. It is also
used to make generalizations about people or things.
| E.g. - Cats like milk.
- Caracas is the capital of Venezuela
- Windows are not made of wood.
Scanned with CamScanner
3. Scheduled Events in the Near Future: Speakers
occasionally use Simple Present to talk about scheduled
events in the near future. This is most commonly done
when talking about public transportation, but it can be
used with other scheduled events as well.
E.g. —_- The bus leaves tonight at 6 PM.
- When do we board the plane?
- The party starts at 8 o'clock.
Scanned with CamScanner
[
| Use
| The simple present is used with adverbs like:
- Always : | always come to school by car
| - Often: | don’t come here very often
| - Usually: He usually eats breakfast at 7:00 AM
- Sometimes: Sometimes | go to party
| - Rarely: She rarely cooks
- Never: He is never late for class
- Every day: They sleep early every day
EE —— |
Scanned with CamScanner
Grammar rules
a O
1. To form the Simple Present we add -s to the
infinitive of the verb in the 3rd person singular (he,
she, it)
E.g. | live >He/she/it lives
| sing >He/she/it sings
Scanned with CamScanner
Grammar rules
hoe . _— O a
2. But when the verb ends in
a) -0, -ss, -sh, -ch, -x we add -es
E.g. |go > He/she/it goes
| kiss > He/she/it kisses
| watch > He/she/it watches
| wash > He/she/it washes
| fix > He/she/it fixes
Scanned with CamScanner
Grammar rules
oO
b) a consonant followed by -y, the -y changes into -
ie and we add -s
E.g. I study > He/she studies
c) a vowel followed by —y we just add -s
E.g. I play > He/she plays
Scanned with CamScanner
Grammar rules
O
3. To form the negative and the interrogative we need the
auxiliary verb to do in the present simple. This means we
have to add -es in the 3rd person singular (he, she, it)
while the main verb will be used in the infinitive.
E.g. I |
Do You like? You don't like
They They
She She
Does He like? He doesn't like
It It
Scanned with CamScanner
Affirmative
Subject + Verb (add -e, -es to the 3rd person singular)+ Complement
Negative
Subject + Aux. do/does + not + verb + complement
Interrogative
Aux. do/does + subject + verb + complement + ?
Scanned with CamScanner
Yaviiatr 1404 Interrogative
| live 1 don't live Do | live?
You live You don't live Do you live?
He lives He doesn't live Does he live?
She lives She doesn't live Does she live?
It lives It doesn't live Does it live?
We live We don't live Do we live?
You live You don't live Do you live?
They live They don't live Do they live?
Scanned with CamScanner
Grammar Structure
»
| Simple present Wh- Questions with the auxiliaries
“do” and “does”
do you |doon Saturday morning? —_-| have breakfast in
a restaurant.
What
-She does exercise.
does she] do on weekdays?
- We go to school on
weekdays.
- He plays soccer on
Wednesday.
do you | go to school?
When
does he | play
Scanned with CamScanner
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Be Verb Simple PresentDocument29 pagesBe Verb Simple PresentmahaNo ratings yet
- Imperative, SuggestionsDocument11 pagesImperative, SuggestionsmahaNo ratings yet
- Hwplusse2e Pi GPP 2.4Document4 pagesHwplusse2e Pi GPP 2.4mahaNo ratings yet
- Hwplusse2e Pi GPP 2.2Document2 pagesHwplusse2e Pi GPP 2.2mahaNo ratings yet
- Hwplusse2e Pi GPP 2.2Document2 pagesHwplusse2e Pi GPP 2.2mahaNo ratings yet
- Past Now Future: Present SimpleDocument34 pagesPast Now Future: Present SimplemahaNo ratings yet