Professional Documents
Culture Documents
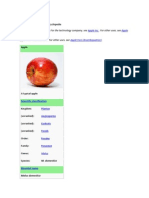
Apples
Uploaded by
Pip JohnsonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Apples
Uploaded by
Pip JohnsonCopyright:
Available Formats
Apples
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (Malus domestica). Apple trees are cultivated
worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus Malus. The tree originated in Central Asia,
where its wild ancestor, Malus sieversii, is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of
years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious
and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek, and European Christian tradition.
Apples grown from seed tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit
frequently lacks desired characteristics. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto
rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after
planting. Rootstocks are used to control the speed of growth and the size of the resulting tree, allowing
for easier harvesting.
There are more than 7,500 known cultivars of apples. Different cultivars are bred for various tastes and
uses, including cooking, eating raw, and cider production. Trees and fruit are prone to a number of fungal,
bacterial, and pest problems, which can be controlled by a number of organic and non-organic means. In
2010, the fruit's genome was sequenced as part of research on disease control and selective breeding in
apple production.
Worldwide production of apples in 2018 was 86 million tonnes, with China accounting for nearly half of
the total
Etymology
The word apple, formerly spelled æppel in Old English, is derived from the Proto-Germanic root *ap(a)laz,
which could also mean fruit in general. This is ultimately derived from Proto-Indo-European *ab(e)l-, but
the precise original meaning and the relationship between both words[clarification needed] is uncertain.
As late as the 17th century, the word also functioned as a generic term for all fruit other than berries but
including nuts—such as the 14th century Middle English word appel of paradis, meaning a banana.[4] This
use is analogous to the French language use of pomme.
You might also like
- Malus Malus SieversiiDocument1 pageMalus Malus SieversiiVinod NairNo ratings yet
- An Apple Is A SweetDocument1 pageAn Apple Is A SweetJOYCENo ratings yet
- Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaDocument1 pagePomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central Asiaelectronics0109No ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Apples: Planting - Growing - Harvesting - Preserving - PreparingFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Apples: Planting - Growing - Harvesting - Preserving - PreparingNo ratings yet
- Malus Malus Sieversii: Deciduous Tree Rose Family Pomaceous Fruit Cultivated Fruit Tree Genus Central AsiaDocument1 pageMalus Malus Sieversii: Deciduous Tree Rose Family Pomaceous Fruit Cultivated Fruit Tree Genus Central AsiarijoiNo ratings yet
- An Article Detailing Miscellaneous Tropical and Subtropical Fruits: Being the Durian, Santol, Carambola, Bilimbi, Tamarind, Carissa, Ramontchi, Ketembilla, Tuna, Pitaya, Tree-Tomato, and Genipa FruitsFrom EverandAn Article Detailing Miscellaneous Tropical and Subtropical Fruits: Being the Durian, Santol, Carambola, Bilimbi, Tamarind, Carissa, Ramontchi, Ketembilla, Tuna, Pitaya, Tree-Tomato, and Genipa FruitsNo ratings yet
- Apple: Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaDocument1 pageApple: Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaslyothersNo ratings yet
- Malus: Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaDocument1 pageMalus: Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaNamita GoyalNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Oranges: Growing Oranges for Pleasure and profitFrom EverandIntroduction to Oranges: Growing Oranges for Pleasure and profitNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument1 pageAppleharishNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument1 pageAppleAmaya AcelynNo ratings yet
- Monu Swence JumboDocument5 pagesMonu Swence JumboDeepak RameshNo ratings yet
- Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaDocument1 pagePomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaStephanieNo ratings yet
- Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaDocument1 pagePomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiarpkmidNo ratings yet
- Malus Malus Sieversii: Clarification NeededDocument1 pageMalus Malus Sieversii: Clarification NeededDilip Dhali, X B, 4223No ratings yet
- Apples Period 1Document25 pagesApples Period 1EllaNo ratings yet
- Apple The Tasty FruitDocument2 pagesApple The Tasty FruitlololoNo ratings yet
- Apple TreeDocument4 pagesApple TreeIoana GrayNo ratings yet
- Apple FruitDocument2 pagesApple Fruitrajeshjain90No ratings yet
- Apple: Apple Inc. Apple (Disambiguation)Document2 pagesApple: Apple Inc. Apple (Disambiguation)Anonymous MqF7u3uNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument28 pagesApplekierdalf.binNo ratings yet
- Apple FruitDocument5 pagesApple FruitTanvi PawarNo ratings yet
- Berry: For Botanical Usage, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument13 pagesBerry: For Botanical Usage, See - For Other Uses, SeeEirojram MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Malus Malus Sieversii: Apple BlossomDocument1 pageMalus Malus Sieversii: Apple BlossomRaluNo ratings yet
- Apple 123Document25 pagesApple 123Vijay BhagavatulaNo ratings yet
- Botanical Information: Apple Apple TreeDocument6 pagesBotanical Information: Apple Apple TreeadamNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument2 pagesAppletamilseo1856No ratings yet
- Malus Malus Sieversii: - The Tree Originated inDocument26 pagesMalus Malus Sieversii: - The Tree Originated inKangLimNo ratings yet
- Apple: Navigation SearchDocument12 pagesApple: Navigation SearchFrancisco CabreraNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument16 pagesApplethippliNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument24 pagesApplesiddharthchoudhary.eisNo ratings yet
- Fruits: School: Degree: Subject: Teacher: StudentsDocument5 pagesFruits: School: Degree: Subject: Teacher: StudentsMelissa ZarcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, Apples, Jules, Fruit BreedDocument77 pagesChapter 1, Apples, Jules, Fruit BreedMayu FaicanNo ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument46 pagesFruits and Vegetablesshireeshmishra79No ratings yet
- Berries Are GowingDocument1 pageBerries Are GowingidkNo ratings yet
- Strawberry: For Other Species of Strawberry, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument8 pagesStrawberry: For Other Species of Strawberry, See - For Other Uses, SeeIrene Joy GomezNo ratings yet
- Garden StrawberryDocument18 pagesGarden StrawberryAshNo ratings yet
- Garden Strawberry: Fragaria × AnanassaDocument5 pagesGarden Strawberry: Fragaria × AnanassaLakshanmayaNo ratings yet
- Factual ReportDocument7 pagesFactual ReportSep AhmadNo ratings yet
- Free, Professional Scriptwriting SoftwareDocument10 pagesFree, Professional Scriptwriting SoftwaremadyNo ratings yet
- History: Wild AncestorsDocument2 pagesHistory: Wild AncestorspriyankaNo ratings yet
- Botanical Information: Wild AncestorsDocument2 pagesBotanical Information: Wild AncestorsAnnabelle ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Study On Modern Horticulture, Evaluation of Fruit CultivarsDocument210 pages2011 Study On Modern Horticulture, Evaluation of Fruit CultivarsTomada KlaraNo ratings yet
- Description StrawberryDocument7 pagesDescription StrawberryEgi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Apple: For The Technology Company, See For Other Uses, See - "Apple Tree" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument5 pagesApple: For The Technology Company, See For Other Uses, See - "Apple Tree" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeelathaprabhuNo ratings yet
- Watermelon: For Other Uses, SeeDocument16 pagesWatermelon: For Other Uses, SeeJeans PearlyNo ratings yet
- APPLEDocument2 pagesAPPLEAiman ZafarNo ratings yet
- StrawberryDocument3 pagesStrawberryTanvi PawarNo ratings yet
- BlackberryDocument2 pagesBlackberryGina FelyaNo ratings yet
- FruitsDocument10 pagesFruitsHarshika BhagourNo ratings yet
- Citrus FruitsDocument11 pagesCitrus FruitsymonnlopezNo ratings yet
- Essay About ApplesDocument2 pagesEssay About Apples•Enkeei•No ratings yet
- Kadapa BananaDocument21 pagesKadapa BananaChandrasekhar ReddypemmakaNo ratings yet
- ApplesDocument2 pagesApplesFunny FunnyNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument10 pagesChapter IISHeen100% (1)
- Name: Irwan Febriyansah 16150061Document1 pageName: Irwan Febriyansah 16150061briyanNo ratings yet
- Flood ControlDocument5 pagesFlood ControlPip Johnson100% (1)
- Western HanDocument4 pagesWestern HanPip JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Lunar New YearDocument3 pagesLunar New YearPip JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 12physics - Module 5 GuideDocument19 pages12physics - Module 5 GuidePip JohnsonNo ratings yet
- The BatmanDocument1 pageThe BatmanPip JohnsonNo ratings yet
- George Tawlon Manneh Oppong Ousman WeahDocument1 pageGeorge Tawlon Manneh Oppong Ousman WeahPip JohnsonNo ratings yet
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)