Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fats, Carbs, Minerals
Uploaded by
HERRERA, ANGELAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fats, Carbs, Minerals
Uploaded by
HERRERA, ANGELACopyright:
Available Formats
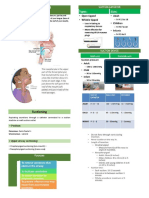
FATS
- Fat is so important for vision brain and nerve growth development
- provides half the calories in breast milk
Breast Milk
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an Omega-3 fatty acid
Linoleic acid
Arachidonic acid (ARA), an Omega-6 fatty acid
Deficiency of essential fatty acids in infants
- Dry scaly rash
(dermatitis)
- Decreased growth
- Increased susceptibility
to infection
- Poor wound healing
CARBOHYDRATE
- Lactose is the major carbohydrate in breast milk
It improves absorption of calcium & provides energy for brain growth
Lactose Intolerance
- common digestive problem where the body is unable to digest lactose
MINERALS
Calcium
for bone growth
Calcium is low in breast milk, but absorbed better than that in cows milk.
Iron
Term infants of a mother who had adequate iron intake during pregnancy will be born with
iron stores lasting for 3 months, until newborn begins to produce hemoglobin.
Iron helps move oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and helps muscles store and
use oxygen.
Iron deficiency.
Fluoride
Essential for building healthy teeth and for preventing tooth decay
Mother needs to drink fluoridated water during and after pregnancy to supply the baby
Fluoride supplement 0.25 mg/day may be given at 6 months of age.
You might also like
- Testosterone Supplement GuideDocument17 pagesTestosterone Supplement GuideStefan Ionascu67% (6)
- Pregnancy and LactationDocument62 pagesPregnancy and LactationFe Mina NisperosNo ratings yet
- 0417 Prenatalnutrition PDFDocument9 pages0417 Prenatalnutrition PDFPrakasha B GNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Needs of A Newborn: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNDocument32 pagesNutritional Needs of A Newborn: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNcoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- BREASTFEEDINGDocument49 pagesBREASTFEEDINGAurora Doris BatagaNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Areej Elhaj Naji M Elfatih Ghada OsmanDocument75 pagesPresented By: Areej Elhaj Naji M Elfatih Ghada OsmanNaji Mohamed AlfatihNo ratings yet
- 372 The Best Dyspraxia Program EverDocument1 page372 The Best Dyspraxia Program EverAnupama PouloseNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PregnancyDocument32 pagesNutrition in PregnancyErika Mae Capobrian PadayaoNo ratings yet
- Do's and Dont's During PregnancyDocument11 pagesDo's and Dont's During PregnancyNinoyz™100% (2)
- Understanding MilkDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Milkskills provider technological institue incNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Pregnancy Lactation - Infancy NotesDocument9 pagesNutrition in Pregnancy Lactation - Infancy NotesCorpus, Irene Zen P.No ratings yet
- Lactation ManagementDocument13 pagesLactation ManagementNadia Nur Salsabila50% (2)
- Exclusive BreastfeedingDocument6 pagesExclusive BreastfeedingDezttie IdEss Ndess100% (1)
- Chapter 14: Essentials in Infant Nutrition: Exclusive Breastfeeding (Ebf)Document11 pagesChapter 14: Essentials in Infant Nutrition: Exclusive Breastfeeding (Ebf)Rosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- Nactalia Marketing Presentation: Dadiah - NutribioDocument15 pagesNactalia Marketing Presentation: Dadiah - Nutribioعلاء البناءNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Laboratory Finals ReviewerDocument12 pagesNutrition Laboratory Finals ReviewerRettsu GamingNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Lecture Final (2023) - 20230915 - 102026 - 0000Document103 pagesBreastfeeding Lecture Final (2023) - 20230915 - 102026 - 0000ASHWINI JADAVNo ratings yet
- Components of Breast MilkDocument2 pagesComponents of Breast MilkAlya Putri KhairaniNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 2nd Yr RevisedaDocument90 pagesNutrition 2nd Yr Revisedaapi-3748748No ratings yet
- 10 Nutrients That Every Child NeedsDocument32 pages10 Nutrients That Every Child Needsps42166No ratings yet
- Nutri ReviewerDocument10 pagesNutri ReviewerkathleyaNo ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument17 pagesBreast FeedingАйгуль ТугелбаеваNo ratings yet
- Manajemen LaktasiDocument46 pagesManajemen LaktasiYona MarlinaNo ratings yet
- Nutritionist Ad 13Document1 pageNutritionist Ad 13Benjamin WeissNo ratings yet
- Breast Feedin New.Document78 pagesBreast Feedin New.Pranshu Prajyot 67No ratings yet
- Nutrico Sales PresentationDocument41 pagesNutrico Sales PresentationAngela LilicrinNo ratings yet
- OB MedicationsDocument32 pagesOB MedicationsCyndryl SampotonNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding: Growth of PathogensDocument5 pagesBreastfeeding: Growth of PathogensneutralmindNo ratings yet
- A. Birth History: Birth Weight 3200 G, Body Length 46 CMDocument6 pagesA. Birth History: Birth Weight 3200 G, Body Length 46 CMAnonymous H08GQfGAWNo ratings yet
- PCBF KpjrawangDocument48 pagesPCBF KpjrawangDr Puteri Nur Sabrina Binti Mohd HanapiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: Nutritional Needs of A NewbornDocument13 pagesChapter 19: Nutritional Needs of A NewbornAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Kinds of Vitamin .: Vitamins Are Only Needed in Very Small AmountsDocument8 pagesUnit 1: Kinds of Vitamin .: Vitamins Are Only Needed in Very Small AmountsNguyễn Thoại NamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document54 pagesTutorial 6ShenariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Milk Activity MaterialDocument3 pagesChemistry Milk Activity MaterialRishan GobseNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument18 pagesVitaminsAbdul QuddusNo ratings yet
- Nutrition BreastfeedingDocument44 pagesNutrition BreastfeedingDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Chemistry Project Report (ST Josephs HSS Trivandrum, Year 2009-2010)Document25 pagesVitamins Chemistry Project Report (ST Josephs HSS Trivandrum, Year 2009-2010)kidilamvivek88% (26)
- OBSTETRICSDocument12 pagesOBSTETRICSmanasa gandikotaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Lactation: Current Breast-Feeding RatesDocument5 pagesLecture 9 - Lactation: Current Breast-Feeding Ratesrachel oNo ratings yet
- BreastfeedingDocument40 pagesBreastfeedingAdwaitha KrNo ratings yet
- 7th Lecture - Pregnancy-1Document3 pages7th Lecture - Pregnancy-1Pornillosa, Jenaehl Mikhail S.No ratings yet
- Nutrition NotesDocument7 pagesNutrition NotesThyataira chuaNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Scan Report: Plagiarism Unique Plagiarized Sentences Unique SentencesDocument2 pagesPlagiarism Scan Report: Plagiarism Unique Plagiarized Sentences Unique SentencesBhavin MehtaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of BreastfeedingDocument2 pagesBenefits of BreastfeedingESPINOSA JHANNANo ratings yet
- 5 Reasons Why You ShouldnDocument2 pages5 Reasons Why You ShouldnazrafasriNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nutrition and Nutritional Disorders: PediatricsDocument4 pagesPediatric Nutrition and Nutritional Disorders: Pediatricsapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Breast Feeding and Its AdvantagesDocument45 pagesBreast Feeding and Its AdvantagesRajeev NepalNo ratings yet
- Read, Translate Into Indonesia, and Make A ConclusionDocument4 pagesRead, Translate Into Indonesia, and Make A ConclusionWahyu Kusuma DewiNo ratings yet
- Dietetic Guidelines Short VersionDocument22 pagesDietetic Guidelines Short VersionIsela Menjivar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Quiz NDTDocument1 pageQuiz NDTchristinejeancenabreNo ratings yet
- Women's Health Booklet 1-10Document16 pagesWomen's Health Booklet 1-10Komala SariNo ratings yet
- Take Health SupplementDocument5 pagesTake Health Supplementkavya shreeNo ratings yet
- PBL 1Document29 pagesPBL 1Aulia SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Fat (Lemak) - 1Document6 pagesFat (Lemak) - 1Eva SihalohoNo ratings yet
- Sorghum Foods Book EN - CompressedDocument16 pagesSorghum Foods Book EN - CompressedSorghum FoodsNo ratings yet
- Dietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarDocument27 pagesDietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarIsela Menjivar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Projectchem 200428051734Document21 pagesProjectchem 200428051734sm2524363No ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Nutritional Needs of A NewbornDocument8 pagesChapter 19 - Nutritional Needs of A NewbornMerenisa LiminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document7 pagesChapter 10HERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Why Is Practicing Being TRUTHFULDocument1 pageWhy Is Practicing Being TRUTHFULHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- What Is The Value of LifeDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Value of LifeHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Wambui ImciDocument1 pageWambui ImciHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Head Skull and FaceDocument2 pagesAssessment of The Head Skull and FaceHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- SuctioningDocument2 pagesSuctioningHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Ranking of Health ProblemsDocument1 pageRanking of Health ProblemsHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Patient PositioningDocument2 pagesPatient PositioningHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Rubrics Perilight TherapyDocument1 pageRubrics Perilight TherapyHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Rubrics PositioningDocument3 pagesRubrics PositioningHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion TherapyDocument2 pagesBlood Transfusion TherapyHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAPHDocument2 pagesPARTOGRAPHHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet