Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flutter Incremento y Decremento
Uploaded by
Peña FielOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flutter Incremento y Decremento
Uploaded by
Peña FielCopyright:
Available Formats
Reyes López Edwin Jaret
// ignore_for_file: no_leading_underscores_for_local_identifiers
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
//
// Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see the
// application has a blue toolbar. Then, without quitting the app,
try
// changing the primarySwatch below to Colors.green and then invoke
// "hot reload" (press "r" in the console where you ran "flutter
run",
// or simply save your changes to "hot reload" in a Flutter IDE).
// Notice that the counter didn't reset back to zero; the
application
// is not restarted.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: const MyHomePage(title: 'Incremento y decremento'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful,
meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that
affect
// how it looks.
Reyes López Edwin Jaret
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in
this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget)
and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something
has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method
below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would
not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
void _decrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something
has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method
below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would
not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter--;
});
}
@override
Reyes López Edwin Jaret
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as
done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build
methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating
rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was
created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions
it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit
its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in
Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio
Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself
and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the
vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
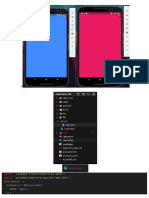
const Text(
'Contador:',
Reyes López Edwin Jaret
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headline4,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _decrementCounter,
tooltip: 'decrement',
child: const Icon(Icons.remove)),
]),
);
}
}
Reyes López Edwin Jaret
You might also like
- Build Flutter counter appDocument2 pagesBuild Flutter counter appWakaye AbbaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledMe CindyNo ratings yet
- Modul Praktikum 2021 Pemrograman Mobile Flutter: PetunjukDocument48 pagesModul Praktikum 2021 Pemrograman Mobile Flutter: PetunjukGanes Exwana DewiNo ratings yet
- Mainactivity - Java Package Com - Example.Alertdialog : Java Android Program To Demonstrate Alert Dialog BoxDocument32 pagesMainactivity - Java Package Com - Example.Alertdialog : Java Android Program To Demonstrate Alert Dialog BoxYasin PathanNo ratings yet
- Flutter Animate ColorDocument6 pagesFlutter Animate ColorTaoufik RachdiNo ratings yet
- Flutter Cheat Sheet 1Document8 pagesFlutter Cheat Sheet 1Slim AgentNo ratings yet
- 03 Advanced Mobile Programming Using FlutterDocument64 pages03 Advanced Mobile Programming Using FlutterDANIEL ABERANo ratings yet
- MIS304 Specialized 3Document19 pagesMIS304 Specialized 3amrrrefa3y74No ratings yet
- codeDocument11 pagescodemupendakimpulengegastonNo ratings yet
- Flutter Animation Basic Example - Animate Text Size ChangeDocument6 pagesFlutter Animation Basic Example - Animate Text Size ChangeTaoufik RachdiNo ratings yet
- Day - 5: Gestures: Gestures Are Primarily A Way For A User To Interact With A Mobile (Or Any Touch Based Device)Document3 pagesDay - 5: Gestures: Gestures Are Primarily A Way For A User To Interact With A Mobile (Or Any Touch Based Device)Kunal MehtaNo ratings yet
- FlutterDocument8 pagesFlutterbit20181210218No ratings yet
- Navigator Widget Flutter App RoutesDocument13 pagesNavigator Widget Flutter App RoutesAsad UllahNo ratings yet
- Android Progress Bar using ProgressDialog -Document6 pagesAndroid Progress Bar using ProgressDialog -html backupNo ratings yet
- Android Custom Toast ExampleDocument45 pagesAndroid Custom Toast ExampleSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Flutter Sqlite TutorialDocument10 pagesFlutter Sqlite TutorialTaoufik RachdiNo ratings yet
- KUIS III WORKSHOP PEMROGRAMAN APLIKASIDocument15 pagesKUIS III WORKSHOP PEMROGRAMAN APLIKASIyoiki yakitoriNo ratings yet
- State Managements in Flutter and Making Network RequestsDocument90 pagesState Managements in Flutter and Making Network RequestsDaniel .WNo ratings yet
- Laravel New Apicloudx GitDocument12 pagesLaravel New Apicloudx GitCalakmul CBTANo ratings yet
- Android GridView Zoom Images Animation TutorialDocument7 pagesAndroid GridView Zoom Images Animation TutorialKurniawan PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Javafx Database OperationsDocument51 pagesGetting Started With Javafx Database OperationsTri Yani Fatchur RahmanNo ratings yet
- MAD 1 - 7 RECORDDocument38 pagesMAD 1 - 7 RECORDShyam ShyamNo ratings yet
- TUTORIALDocument61 pagesTUTORIALMD ASIF ALAMNo ratings yet
- Flutter for Android devs: Apply Android skills to build mobile appsDocument40 pagesFlutter for Android devs: Apply Android skills to build mobile appsHABTAMUNo ratings yet
- Stateful Widget Lifecycle MethodsDocument6 pagesStateful Widget Lifecycle MethodsAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- REACTDocument22 pagesREACTPrathapNo ratings yet
- Modul 1:: Tujuan: Mengenal Java Net Beans Java 2 Di Bagi Atas Tiga Paket, YaituDocument6 pagesModul 1:: Tujuan: Mengenal Java Net Beans Java 2 Di Bagi Atas Tiga Paket, YaituRizka ArdinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of JAVA: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument16 pagesAssignment of JAVA: Submitted To: Submitted byHarish UpmanyuNo ratings yet
- Flutter Prefinal ReviewerDocument59 pagesFlutter Prefinal Reviewerjeric del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Android FragADocument7 pagesAndroid FragAsantosh sanjyalNo ratings yet
- MA - 3 Widget Every WhereDocument15 pagesMA - 3 Widget Every Whereasiamohamed1909No ratings yet
- I Made Deon Virgananta - ProjectUTSDocument28 pagesI Made Deon Virgananta - ProjectUTSI Made Deon VirganantaNo ratings yet
- Airline Reservation System ProjectDocument139 pagesAirline Reservation System ProjectDharitri DeviNo ratings yet
- Getting Started XFire Web Service With Spring and Hibernate Using Netbeans and TomcatDocument8 pagesGetting Started XFire Web Service With Spring and Hibernate Using Netbeans and TomcatilhamiarieNo ratings yet
- 'Package:flutter/material - Dart' 'Package:pageview - App/src/app - Dart'Document93 pages'Package:flutter/material - Dart' 'Package:pageview - App/src/app - Dart'Juan Fernando Córdova ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Add and Subtract button to increment and decrement counter in FlutterDocument3 pagesAdd and Subtract button to increment and decrement counter in FlutterMuhammad Shehzad Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Java 2 For BeginnersDocument40 pagesJava 2 For BeginnerssudhircarpenterNo ratings yet
- Gand Mara Le 3. Chutiya 4. Madar Chod 5. Fuddu: Stateful Widget LifecycleDocument6 pagesGand Mara Le 3. Chutiya 4. Madar Chod 5. Fuddu: Stateful Widget LifecycleAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- RunApp function in FlutterDocument16 pagesRunApp function in FlutterAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- MAD Notes - R18!4!6 UnitsDocument86 pagesMAD Notes - R18!4!6 Unitssai chanduNo ratings yet
- Create A Matching Game Using Visual StudioDocument15 pagesCreate A Matching Game Using Visual StudioAnkit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Pratical ListDocument42 pagesPratical Listdiwaja8050No ratings yet
- Tugas WEBHOSTING MK Mobile TechnologyDocument15 pagesTugas WEBHOSTING MK Mobile TechnologyedoNo ratings yet
- Mad SolnsDocument26 pagesMad SolnsSharan M ANo ratings yet
- Navigation Drawer MenuDocument14 pagesNavigation Drawer MenuRana ArslanNo ratings yet
- Android Expandable ListviewDocument13 pagesAndroid Expandable ListviewtoarnabchNo ratings yet
- Flutter Apprentice - Complete GuideDocument5 pagesFlutter Apprentice - Complete GuideAsad UllahNo ratings yet
- Extra Flutter 3Document9 pagesExtra Flutter 3Amit VermaNo ratings yet
- React Native For DummiesDocument25 pagesReact Native For DummiesWbx WbxNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledSubiksha ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- AppletDocument6 pagesAppletTHIRUMALAXEROX INTERNETNo ratings yet
- 'Dart:Math' 'Package:Flutter/Widgets - Dart': Mycustomclipper Customclipper Path Double Mycustomclipper Path SizeDocument5 pages'Dart:Math' 'Package:Flutter/Widgets - Dart': Mycustomclipper Customclipper Path Double Mycustomclipper Path SizeMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Flutter SederhanaDocument11 pagesFlutter SederhanaKeny Kirana WanazianaNo ratings yet
- SpinnerDocument6 pagesSpinnercervantes.greciaanelis.2021No ratings yet
- Android Studio: Alt + Insert Override MethodsDocument18 pagesAndroid Studio: Alt + Insert Override MethodsAngelica SutawijayaNo ratings yet
- TM Teknologi MobileDocument13 pagesTM Teknologi MobileINDAH LISANTINo ratings yet
- Simple Calculator - JavaDocument12 pagesSimple Calculator - JavaMichelin FernandezNo ratings yet
- FastRefreshDevToolsIntegration TestDocument5 pagesFastRefreshDevToolsIntegration TestmahoragaNo ratings yet
- Agilent 7890GC Firmware Bulletin B.02.05.03 and A.01.16Document35 pagesAgilent 7890GC Firmware Bulletin B.02.05.03 and A.01.16infinity1200No ratings yet
- Literature Review in Social Science Research PDFDocument6 pagesLiterature Review in Social Science Research PDFc5ha8c7g100% (1)
- Consumer Perception Towards Online Food DeliveryDocument49 pagesConsumer Perception Towards Online Food DeliveryGokul krishnanNo ratings yet
- Kumulative Dissertation Uni WienDocument8 pagesKumulative Dissertation Uni WienWebsitesThatWritePapersForYouSingapore100% (1)
- What Are Your Children Watching On Youtube?: December 2011Document11 pagesWhat Are Your Children Watching On Youtube?: December 2011Quỳnh nhiNo ratings yet
- Cv-Anglaishager Ben FradjDocument5 pagesCv-Anglaishager Ben FradjAmira BououdNo ratings yet
- Norfolk SlidesCarnivalDocument39 pagesNorfolk SlidesCarnivalFarah Soufana0% (1)
- Adjusted School Reading Program of Buneg EsDocument7 pagesAdjusted School Reading Program of Buneg EsGener Taña AntonioNo ratings yet
- RER615 DNP3 Point List ManualDocument136 pagesRER615 DNP3 Point List ManualРоман ВоеводаNo ratings yet
- Amplitude ModulationDocument89 pagesAmplitude Modulationelyk herreraNo ratings yet
- Finance Management SystemDocument83 pagesFinance Management SystemAbel tejuNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - Attempt ReviewDocument16 pagesMidterm Exam - Attempt ReviewErick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ads 512 Chap 1Document30 pagesAds 512 Chap 1Airin SamuelNo ratings yet
- Micon Ic Check SheetDocument3 pagesMicon Ic Check SheetVenkatesh Subramanya0% (1)
- GRADUS Catalogue - Stair Edgings & Floor TrimsDocument164 pagesGRADUS Catalogue - Stair Edgings & Floor TrimsHarsha V. PriyaNo ratings yet
- Paper Zinnia Flower Template PDF by JenniferCarrollDocument2 pagesPaper Zinnia Flower Template PDF by JenniferCarrollmariaNo ratings yet
- Crs Robotics Thermo Crs Robots PresentationDocument17 pagesCrs Robotics Thermo Crs Robots PresentationRogelio NavarroNo ratings yet
- Wireless remote controller guide for round flow cassette air conditionerDocument23 pagesWireless remote controller guide for round flow cassette air conditionerSicologo CimeNo ratings yet
- Manual WinREG 4.1 EN 2017 09 06Document46 pagesManual WinREG 4.1 EN 2017 09 06MD. AL MUZAHIDNo ratings yet
- UART Implementation Using FPGA: December 2019Document50 pagesUART Implementation Using FPGA: December 2019V.ASHISH REDDYNo ratings yet
- Dos Windows 95 Fat Fat12 Fat16 Windows 98 Windows Me Fat32 Windows 2000 Logical Disk Manager DiskpartDocument1 pageDos Windows 95 Fat Fat12 Fat16 Windows 98 Windows Me Fat32 Windows 2000 Logical Disk Manager Diskpartgagandhawan31No ratings yet
- Monitoring and Evaluation FinalDocument20 pagesMonitoring and Evaluation FinalNational Child Health Resource Centre (NCHRC)No ratings yet
- 4th International European Conference On Interdisciplinary Scientific ResearchesDocument843 pages4th International European Conference On Interdisciplinary Scientific ResearchesDouglas Mesadri GewehrNo ratings yet
- Fee Structure Btech CseDocument1 pageFee Structure Btech Cseankit panwarNo ratings yet
- 3 Installing The Product: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument41 pages3 Installing The Product: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineHyacinthe KOSSINo ratings yet
- The Android Arsenal - Dialogs - Spots Progress DialogDocument8 pagesThe Android Arsenal - Dialogs - Spots Progress DialogRudolfNo ratings yet
- Training Report ON Study of Marketing Strategies at Hyndai Bachelor of Business AdministrationDocument71 pagesTraining Report ON Study of Marketing Strategies at Hyndai Bachelor of Business AdministrationBhola ThNo ratings yet
- Braking Resistor SAFUR180F460 Braking Resistor 460V 180kW 2.4 OhmDocument2 pagesBraking Resistor SAFUR180F460 Braking Resistor 460V 180kW 2.4 OhmmanthuNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Project Management Processes Methodologies and Economics 2 e 2nd Edition 0130413313Document24 pagesSolution Manual For Project Management Processes Methodologies and Economics 2 e 2nd Edition 0130413313JohnValenciaajgq100% (36)
- Promoting Digital InclusivityDocument12 pagesPromoting Digital InclusivityFrench Mariee P. EdangNo ratings yet