Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Key To Long 42 Question Review
Answer Key To Long 42 Question Review
Uploaded by
Gabriel Parks0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Answer Key to Long 42 Question Review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesAnswer Key To Long 42 Question Review
Answer Key To Long 42 Question Review
Uploaded by
Gabriel ParksCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
‘When it says “Type E” you have to look at the other answer key which has pictures of
graphs and see what it should look like.
1. ‘Type E (2 curves have anything answer)
Inc Dem =(P up Q up) + Inc Supply (P Do Qup) = IncD & IncS = P Anything QUp
2. ‘Type H (2 curves have anything answer)
up Qup) + Dec Supply (P Up Q do)= IncD& DecS = P Up QAnything
3. TypeA
Inc Dem = (P up Qup) since supply stayed same.
4, ‘Type G (2 curves have anything answer)
Dec Dem= (P do Qdo) + Inc Supply (P Do Qup) = DecD& IncS = P do Q Anything
5. Type F (2 curves have anything answer)
DecDem= (P do Q do) + DecSupply (P up Q do)= DecD& DecS = PAnything QDo
6. TypeB
Dec Dem = (P do Qdo) since supply stayed same.
7. Type
Inc Supply = (P down Q up) since demand stayed the same
8. TypeD
Dec Supply = (P up Q down) since demand stayed the same
9, Obviously nothing changed
10. Notice in problems 1 & 4 if you move both Supply and Demand SAME direction
(either inc or dec) than they fight over price and price is Anything
U1. Notice in problems 2 & 5 where if Supply and Demand move OPPOSITE directions
(one inc while other dec) than they fight over quantity and quantity is Anything
12 Since supply steyed the same, demand would have had to decrease to make EQ go
down, The graph looks like Type B (Price down and Quantity down)
13 Since demand stayed the same, supply would have had to decrease to make EQ go
own, The graph looks like Type D (Price up and Quantity down)
14 Since supply stayed the same, demand would have had to decrease to make EP go
down, The graph looks like Type B. (Price down and Quantity down)
15 Since demand stayed the same, supply would have had to increase to make EP go
down. The graph looks like Type C (Price down and Quantity up)
All of 16-23 only directly shift one curve and only one curve.
16 Less Supply Looks Like ‘Type D EP Inc EQ Dec
17 More Supply Looks Like Type C EP Dec EQ Inc
18 More Demand Looks Like Type A EP Ine EQ Inc
19 More Supply Looks Like Type C EP Dec EQ Inc
20 More Supply Looks Like Type C EP Dec EQ Inc
21 Less Demand Looks Like Type B EP Dec EQ Dec
22 More Demand Looks Like Type A EP Ine EQ Inc
23 Less Demand Looks Like Type B EP Dec EQ Dec
24) 5 Factors that Shift Demand (all listed on page 17 in your packet)
1) Income —_2) Preferences 3) Substitutes (Related Good)
4) Compliment (Related Good) 5) Expectations (in future)
25. 7 Factors for Supply (all listed on page 19 in your packet)
1)) Resource Prices 2) Productivity (like Nature) 3) Producing Technology
4) Govt taxes 5) Govt Régulation like Quota 6) Expectation 7) # of Sellers
26) Secret Trick is if it mentions:
Price and Supply of Same Product = No Shift Supply
Price and Demand of Same Product = No Shift Demand
27) Compliments like Milk&Cereal or bread&butter or peanut butter&jelly or etc
28) Substitutes like Coke&ePepsi, or Ford&GM or Nike&Addias
29) Because no one would buy at high prices (or less demand)
30) Because no one would sell at low prices (low supply)
31) We divide up resources by Price & Money
32) Any altemate method like appearance, first/come first serve wouldn't be better for
everyone as there are always “winners’ and “losers”
33) Since we have to divide up resources because of scarcity.
34) Any price below equilibrium makes a shortage
35) Any price above equilibrium makes a surplus
36) QS > QD is a surplus
37838) Make any Supply/Demand Graph.
Draw a Horizontal Price Line above the Equilibrium Price this will be a SURPLUS
Draw a Horizontal Price Line below the Equilibrium Price this will be a SHORTAGE,
39 F (Willing and able)
40 F (those are compliments)
ALT. P Juice Dec people buy more juice so they buy less of a substitute (so the substitute
demand shifts left)
42: If asked how supply and demand work together to form price mention all of the
following (Would need all 3 for full credit)
A) Supply tries to sell high
B) Demand tries to buy cheap
©) This forces a compromise at equilibrium
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Rubric, Mini-Q Writing Assignment - The CRUCIBLEDocument2 pagesRubric, Mini-Q Writing Assignment - The CRUCIBLEGabriel Parks0% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Extra Credit Career ExplorationDocument4 pagesExtra Credit Career ExplorationGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- SW Exam Practice DrawingsDocument51 pagesSW Exam Practice DrawingsGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Annotated Binary Molecular NotesDocument1 pageAnnotated Binary Molecular NotesGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Significant Figures NotesDocument2 pagesSignificant Figures NotesGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Build An Atom GuidedInquiry StudentHandout With ProtonsDocument4 pagesBuild An Atom GuidedInquiry StudentHandout With ProtonsGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
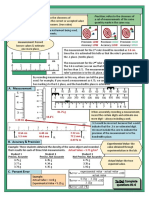
- Measurement Unit Study Guide Review CardsDocument3 pagesMeasurement Unit Study Guide Review CardsGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Installing A Floor, PB3 RES U04 CH03Document33 pagesInstalling A Floor, PB3 RES U04 CH03Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Floor Plan Reading Guide WorksheetDocument1 pageFloor Plan Reading Guide WorksheetGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
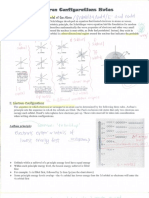
- Annotated Electron Configuration NotesDocument2 pagesAnnotated Electron Configuration NotesGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Corner Wall PlansDocument7 pagesCorner Wall PlansGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Pretest (65 Questions)Document5 pagesAnswer Key To Pretest (65 Questions)Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Full Unit 4 PacketDocument38 pagesFull Unit 4 PacketGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Floor Plan Reading Guide WorksheetDocument1 pageKami Export - Floor Plan Reading Guide WorksheetGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature ReviewDocument1 pageNomenclature ReviewGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- VideosDocument1 pageVideosGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Foundations, PB3 RES U03 CH01Document14 pagesFoundations, PB3 RES U03 CH01Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Progressivism Graph AnalysisDocument36 pagesProgressivism Graph AnalysisGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Practice Test, Lynch Economics Unit 2 (Trivia Version) - QuizletDocument14 pagesPractice Test, Lynch Economics Unit 2 (Trivia Version) - QuizletGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Wall Layout, Pb3 Res U05 Ch01Document14 pagesWall Layout, Pb3 Res U05 Ch01Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Project Instructons - Due 11 - 18Document1 pageProject Instructons - Due 11 - 18Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Unit 2, Quizlet TermsDocument4 pagesUnit 2, Quizlet TermsGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
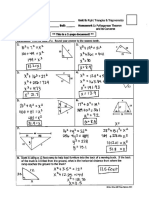
- Pythagorean Theorem Assignment Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPythagorean Theorem Assignment Answer KeyGabriel Parks80% (5)
- Answer Key For The Long Review AssignmentDocument2 pagesAnswer Key For The Long Review AssignmentGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Unit 1, Quizlet TermsDocument3 pagesUnit 1, Quizlet TermsGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Lynch Economics Unit 4 (Trivia Version)Document4 pagesLynch Economics Unit 4 (Trivia Version)Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Lynch Economics Unit 3Document4 pagesLynch Economics Unit 3Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Lynch Economics Unit 3 (Trivia Version)Document4 pagesLynch Economics Unit 3 (Trivia Version)Gabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Rubric, About Me Paper Plate IntroductionsDocument2 pagesRubric, About Me Paper Plate IntroductionsGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- The Way To Rainy Mountain - Reading SkillDocument1 pageThe Way To Rainy Mountain - Reading SkillGabriel ParksNo ratings yet