Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Efficient financial system objectives and flow of funds
Uploaded by
Jea Ann CariñozaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Efficient financial system objectives and flow of funds
Uploaded by
Jea Ann CariñozaCopyright:
Available Formats
Carinoza Jea Ann B.
BSA-3
A. Discuss the following items in 5 sentences per item. (5 pts.)
1. A Need for an efficient financial system for a country.
A vibrant and healthy economy requires a financial system that makes or
channels funds from people who save productive investment opportunities. The
financial system is complex in structure and functions throughout the world. A
developed economy relies in financial markets and institutions for efficient
transfer of funds. Every person’s life, family, business, and government are
affected by the financial system.
2. The Nature and Main objectives of the Financial System.
Financial system is a collection of agreements or conventions that govern the
lending and borrowing of funds by non-financial economic units and the
intermediation of this function by financial intermediaries in order to facilitate
the transfer of funds, to create additional money when necessary, and to create
markets for debt and equity instruments in order to efficiently determine the
price and allocation of funds. It enables an efficient transfer of funds between
entities with funds and those in need of funds. The financial system acts as a
reliable, timely, and cost-effective conduit between fund providers and fund
demanders. Additionally, it encourages savings among its stakeholders and
efficiently converts these resources into investment vehicles that help the
economy grow quicker.
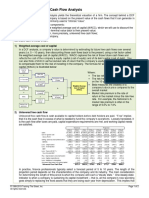
3. The Basic Flow of Funds through the Financial system.
The financial system consists of all financial intermediaries and financial
markets and their relations with respect to the flow of funds to and from
households, governments, business firms and foreigners, as well as the
financial infrastructure.
Now let’s look at the figure who are the lenders and borrowers in financial
markets. So, if you look at the lender-savers sides you find that households are
the main savers of the financial markets and then business firms then
governments and foreigners, also work as a savers or lenders in economy. Now
if you look at the borrowers side you find that business firm are the main
borrowers of the firm, so they are known as the number one power in an
economy of governments, households and foreigners. Now let’s look at the
segments of financial markets there are two broad segments namely direct
finance and indirect finance. If funds are transferred through financial markets
that means by selling financial instruments that called direct finance. Then if
funds are transferred through financial intermediaries like banks, insurance
companies or other financial institution then it well known as indirect finance.
4. Transaction and Information costs.
Transaction costs are expenses incurred when buying or selling a good or
service. Transaction costs represent the labor required to bring a good or
service to market, giving rise to entire industries dedicated to facilitating
exchanges. In a financial sense, transaction costs include brokers'
commissions and spreads, which are the differences between the price the
dealer paid for a security and the price the buyer pays. While Information costs
are costs incurred by an individual or a firm while amassing information to
help make a financial decision. If these costs are significant enough, it can
affect the profitability of a business enterprise or the soundness of a
consumer's purchase.
B. Define the following terms (5 pts.)
1. Risk sharing
Risk sharing is a contractual arrangement in which the buyer and seller
agree to “share” or split currency movement impacts on payments between
them.
2. Liquidity
Liquidity is the ease with which an asset can be exchanged for money
which savers view as a benefit.
3. Transaction costs
The cost of a trade or a financial transaction.
4. Moral Hazards
This is the problem investors experience in verifying that borrowers are
using their funds as intended.
5. Adverse Selection
This is the problem investors experience in distinguishing low-risk
borrowers from high-risk borrowers before making an investment.
You might also like
- Capital Happens When Funds Are Invested in Productive Investments That Yield Returns ForDocument3 pagesCapital Happens When Funds Are Invested in Productive Investments That Yield Returns ForPerbielyn BasinilloNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic Developmentrevathi alekhya80% (10)
- Financial Markets, Institutions and InstrumentsDocument9 pagesFinancial Markets, Institutions and InstrumentsPaula Rodalyn MateoNo ratings yet
- Components of IFS NotesDocument6 pagesComponents of IFS NotesPrasad IngoleNo ratings yet
- Financial Market CH 1Document13 pagesFinancial Market CH 1mohammadfoziya354No ratings yet
- Gabriel Adegite BUAD 811 Individual AssignmentDocument5 pagesGabriel Adegite BUAD 811 Individual AssignmentSheila OdorNo ratings yet
- FINMARDocument37 pagesFINMARMichelle Angela DiesmaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledJhianne EstacojaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 ReportDocument7 pagesGroup 5 ReportSonam Peldon (Business) [Cohort2020 RTC]No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Overview of the Financial SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Overview of the Financial Systemshai santiagoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Financial SystemDocument14 pagesPhilippine Financial SystemMarie Sheryl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Module in Financial Management - 02Document9 pagesModule in Financial Management - 02Karen DammogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Financial System OverviewDocument44 pagesChapter 1 Financial System OverviewTamrat KindeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Financial System OverviewDocument44 pagesChapter 1 Financial System OverviewLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument3 pagesFinancial MarketChristian FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Features of The Financial System of DevelpoedDocument35 pagesFeatures of The Financial System of DevelpoedChahat PartapNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets ExplainedDocument7 pagesFinancial Markets ExplainedJarell Carven NicaveraNo ratings yet
- Nature and Importance of Financial SystemsDocument11 pagesNature and Importance of Financial SystemsAuie Eugene Frae SalameraNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Financial SystemDocument7 pagesThe Philippine Financial SystemKhyell PayasNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Market: (ACFN, 2 Credit Hour)Document25 pagesFinancial Institutions and Market: (ACFN, 2 Credit Hour)Mikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document3 pagesUntitled 1cesar_mayonte_montaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Prelim 10-19-21Document2 pagesFinancial Markets Prelim 10-19-21Ash kaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1tamirat tadeseNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Financial System PDFDocument33 pagesOverview of The Financial System PDFFlorence Joy AbkilanNo ratings yet
- Financial System OverviewDocument10 pagesFinancial System OverviewYonas N IsayasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-An Overview of Financial SystemDocument15 pagesChapter 1-An Overview of Financial SystemKalkayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-One 1. An Overview of The Financial Sysyem 1.1. Financial System in GeneralDocument18 pagesChapter-One 1. An Overview of The Financial Sysyem 1.1. Financial System in Generalyared haftuNo ratings yet
- MTH103 Notes Lec1Document5 pagesMTH103 Notes Lec1stanleyNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument36 pagesLecture NotesAmritNo ratings yet
- Financial Systems and Markets ExplainedDocument11 pagesFinancial Systems and Markets ExplainedFaheem Ahmed0% (1)
- Hide 1 Financial Controls and Monitoring 2 Financial Services 3 See Also 4 References EditDocument21 pagesHide 1 Financial Controls and Monitoring 2 Financial Services 3 See Also 4 References EditPankaj GautamNo ratings yet
- The Financial System Provides The Intermediation Between Savers and Investors and Promoters Faster Economic DevelopmentDocument3 pagesThe Financial System Provides The Intermediation Between Savers and Investors and Promoters Faster Economic DevelopmentsanskritiNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System ComponentsDocument8 pagesIndian Financial System ComponentsSteffin JosephNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument31 pagesFinancial MarketsCheesca Macabanti - 12 Euclid-Digital ModularNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets ReflectionDocument4 pagesFinancial Markets ReflectionMENESES, Trixie Ann TrapaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - OverviewDocument6 pagesFinancial Markets - OverviewCharmaine Klaire Agan AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument13 pagesFinancial MarketschidanandckmNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial SystemsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Financial SystemsVinay ArtwaniNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Financial MarketsDocument9 pagesCase Study - Financial Marketsbtsvt1307 phNo ratings yet
- Introduction FINANCEDocument9 pagesIntroduction FINANCEBOL AKETCHNo ratings yet
- Financial System ComponentsDocument14 pagesFinancial System Componentsnirshan rajNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL SYSTEMS AND MARKETS CHAPTER 1Document67 pagesFINANCIAL SYSTEMS AND MARKETS CHAPTER 1Gabrielle Anne MagsanocNo ratings yet
- CH1@FI&M Final EditedDocument7 pagesCH1@FI&M Final Editedtamiratg24No ratings yet
- Key Financial System RolesDocument2 pagesKey Financial System RolesLinusChinNo ratings yet
- Financial System in Ethiopia: 4 Institutional Finance: Advantages and Limitations of Institutional FinanceDocument12 pagesFinancial System in Ethiopia: 4 Institutional Finance: Advantages and Limitations of Institutional FinanceRas DawitNo ratings yet
- FIM-revision-2Document116 pagesFIM-revision-2Bao Khanh HaNo ratings yet
- Essay Questions Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument5 pagesEssay Questions Chapter 1 QuestionsHelen Joan Bui100% (2)
- ABIYDocument9 pagesABIYEyob HaylemariamNo ratings yet
- Fin Mkts Unit I Lec NotesDocument6 pagesFin Mkts Unit I Lec Notesprakash.pNo ratings yet
- ULOa - Efficient Financial System-SIM - 0Document8 pagesULOa - Efficient Financial System-SIM - 0lilienesieraNo ratings yet
- Financia Institutions and Markets Chapter 1Document12 pagesFinancia Institutions and Markets Chapter 1Surafel BefekaduNo ratings yet
- Financial IntermediationDocument41 pagesFinancial IntermediationRphdd100% (4)
- Financial Markets (Chapter 5)Document3 pagesFinancial Markets (Chapter 5)Kyla DayawonNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System: Prepared by Jinesh A. ShahDocument42 pagesIndian Financial System: Prepared by Jinesh A. ShahSai charan Reddy CHINTHALAPALLINo ratings yet
- 1 The Problem That Arises For A Buyer of GoodsDocument14 pages1 The Problem That Arises For A Buyer of GoodsGETAHUN ASSEFA ALEMUNo ratings yet
- Notes - Financial Markets - OverviewDocument10 pagesNotes - Financial Markets - OverviewNaman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Financial Markets and Their RoleDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Financial Markets and Their RoleRenda QiutiNo ratings yet
- How Money Flows Through Financial MarketsDocument4 pagesHow Money Flows Through Financial MarketsMinh NguyệtNo ratings yet
- Report in MTH of IntDocument6 pagesReport in MTH of IntAngie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Types of mortgage loans and institutionsDocument2 pagesTypes of mortgage loans and institutionsJea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Function of Financial IntermediariesDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 - Function of Financial IntermediariesJea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Ass. Partnership DissolutionDocument8 pagesAss. Partnership DissolutionJea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Ass.1 Acctng. For Special TransactionDocument17 pagesAss.1 Acctng. For Special TransactionJea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Ass. Cost Chapter 8Document4 pagesAss. Cost Chapter 8Jea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Ass. CAC Chapter 9Document3 pagesAss. CAC Chapter 9Jea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Ass. Chapter 11 Shareholders Equity (Part 2)Document12 pagesAss. Chapter 11 Shareholders Equity (Part 2)Jea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- History of Money PhilippinesDocument3 pagesHistory of Money PhilippinesJea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Definitions of MoneyDocument2 pagesFunctions and Definitions of MoneyJea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document40 pagesChapter 4prashantgargindia_93No ratings yet
- FINANCE FOR MARKETING ASSIGNMENT- FULL TIMEDocument5 pagesFINANCE FOR MARKETING ASSIGNMENT- FULL TIMEBNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Drivers and Metrics - Key Financial Measrues of Firm PerformanceDocument10 pagesSupply Chain Drivers and Metrics - Key Financial Measrues of Firm PerformanceGovis HippiosaNo ratings yet
- FM2 Concept DiaryDocument15 pagesFM2 Concept Diarydev guptaNo ratings yet
- Simpl Is Cahier Des Charges Edi v18Document42 pagesSimpl Is Cahier Des Charges Edi v18Oussama RamboukNo ratings yet
- Investment HomeworkDocument26 pagesInvestment HomeworkĐức HoàngNo ratings yet
- Factor Investing in Fixed-Income - Cross-Sectional and Time-Series Momentum in Sovereign Bond MarketsDocument48 pagesFactor Investing in Fixed-Income - Cross-Sectional and Time-Series Momentum in Sovereign Bond Marketspietro silvestriNo ratings yet
- Reading 42 Risk Management An IntroductionDocument8 pagesReading 42 Risk Management An IntroductionFundamental researchersNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis and Portfolio Management Prof: C.S. Mishra Department of VGSOM Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument29 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio Management Prof: C.S. Mishra Department of VGSOM Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurviswanathNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting in An Economic Context 8th Edition Pratt Test BankDocument19 pagesFinancial Accounting in An Economic Context 8th Edition Pratt Test BankKatrinaYounggmqsy100% (57)
- Full Download Essentials of Investments 8th Edition Bodie Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Essentials of Investments 8th Edition Bodie Solutions Manualsultryjuliformykka100% (26)
- Lahore School of Economics Financial Management II Cash Flow Estimation and Risk Analysis - 2Document2 pagesLahore School of Economics Financial Management II Cash Flow Estimation and Risk Analysis - 2IIBRAHIM 245No ratings yet
- 1 PhototecDocument3 pages1 Phototecalice horanNo ratings yet
- History of Accounting Rex VillanuevaDocument3 pagesHistory of Accounting Rex Villanuevalgucabugao treasuryNo ratings yet
- 50 Multiple Choice, T/F, & Essay QuestionsDocument24 pages50 Multiple Choice, T/F, & Essay QuestionsManal Elkhoshkhany100% (1)
- Homework 2 MGMT 41150 Key PDFDocument6 pagesHomework 2 MGMT 41150 Key PDFLaxus DreyerNo ratings yet
- Total Unit To Be Accounted For 90Document6 pagesTotal Unit To Be Accounted For 90Harsh KSNo ratings yet
- MBA FF Group Project Assignment Fall 2020 - Group B3 (Indus Motor)Document23 pagesMBA FF Group Project Assignment Fall 2020 - Group B3 (Indus Motor)Aliza RizviNo ratings yet
- MGT 101Document4 pagesMGT 101Taiba ShehzadiNo ratings yet
- Common Stock Valuation TechniquesDocument84 pagesCommon Stock Valuation TechniquesBushra JavedNo ratings yet
- TTS - DCF PrimerDocument2 pagesTTS - DCF PrimerKrystleNo ratings yet
- WEYGANDT Planning For Capital InvestmentsDocument43 pagesWEYGANDT Planning For Capital InvestmentsPaula Merriles100% (1)
- IFRS Statement of Financial Position PDFDocument36 pagesIFRS Statement of Financial Position PDFmonneNo ratings yet
- Costs That Stay The Same, Regardless of Which Alternative Is Chosen, Are Irrelevant To The Decision Being MadeDocument1 pageCosts That Stay The Same, Regardless of Which Alternative Is Chosen, Are Irrelevant To The Decision Being MadeKARL PASCUANo ratings yet
- SOLVED - IAS 7 Statement of Cash FlowsDocument16 pagesSOLVED - IAS 7 Statement of Cash FlowsMadu maduNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Receivable FinancingDocument5 pagesLecture Notes On Receivable Financingjudel ArielNo ratings yet
- PT Astra Agro Lestari Tbk Financial Summary 2010Document2 pagesPT Astra Agro Lestari Tbk Financial Summary 2010Intan Maulida SuryaningsihNo ratings yet
- The Dividend Policy in Europe - The Cases of The UK, Germany, France and ItalyDocument285 pagesThe Dividend Policy in Europe - The Cases of The UK, Germany, France and ItalyOre.ANo ratings yet
- Section C - BOTH Questions Are Compulsory and MUST Be AttemptedDocument6 pagesSection C - BOTH Questions Are Compulsory and MUST Be AttemptedAliNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) by Towhidul AlamDocument11 pagesSecurities and Exchange Commission (SEC) by Towhidul AlamTowhidul Alam Pavel0% (1)