Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Corrosion
Uploaded by
Carlos ChirindzaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Corrosion
Uploaded by
Carlos ChirindzaCopyright:
Available Formats
CORROSION CHEMISTRY
INTRODUCTION:
The process of destruction or deterloration of metals or its alloys by chemical or
electrochemical attack through Its environment starting at its surface is called corrosion.
EX.: 1. Rusting of iron (Fe2O3.2H2O)
2. Formation of blue green film on copper or bronze (CuCO3 Cu (OH)2.)
3. Tarnishing of silver.
With the exception of noble metals Pt, Au, Ag etc., most of the metals exist in nature
in combined form of oxides, hydroxides, carbonates, chlorides, sulphides and silicates.
These are known as ores and minerals of the metals. During extraction, metal ores reduced
to their metallic states. The metals have a natural tendency to revert back to combined state.
The process by which the metals have a tendency to go back their combined state is known
as corrosion. Corrosion is thus exactly the reverse of extraction of metals and also known as
weeping of metals.
Cause of corrosion: Metals are stable only in the compound state. So, the metals always
try to get back to the original state by means of corrosion. Less energy states (Metallic
compound) are more stable than the higher energy states (Metals)
Cost of Corrosion: Enormous losses occur due to corrosion every year in all countries of
the world. These losses are made up of direct losses (Which include shut down losses in the
form of cost production, losses due to Inefficiency etc.). The cost of replacement of materials
and equipment loss through corrosion has been currently estimated to be Rs. 13000 crores
per year on account of replacement of pipes, building products, auto parts, water heater and
other materials subjected to corrosion. In addition, the life of equipment, plant, and bridge
etc. is very much reduced, which may cause explosions and severe adverse effects,
including possible loss of life. In fact, It is very difficult to assess exactly the losses incurred
due to corrosion, because the losses cannot be measured in terms of the cost of metals
alone, but the high cost of fabrication Into machine tools /structures/equipment should also
be taken Into account.
it is estimated that 40% of failures in electronic equipment, like computers, tele
communication equipment, television equipment is due to metallic corrosion. (Loss of
contact). In India, the corrosion problems are more, serious than the cold countries because
of its tropical climate. According to rough estimate direct losses due to corrosion is 250 cores
per year. The money spent on its prevention la about 50-70 cores per year. The indirect
losses due to corrosion cannot be estimated in terms of money. Taking all the factors into
consideration, therefore, it is extremely important to know the mechanism of corrosion. So
that it can be minimized to a greater extent and the heavy losses incurred due to corrosion
may be greatly reduced.
You might also like
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Oil and Gas Corrosion Prevention: From Surface Facilities to RefineriesFrom EverandOil and Gas Corrosion Prevention: From Surface Facilities to RefineriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- AWS D1.1 GuidesDocument6 pagesAWS D1.1 GuidesBiju_Pottayil100% (6)
- UNIT-I CorrDocument42 pagesUNIT-I CorrArthi SelvaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Corrosion and Its PreventionDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Corrosion and Its PreventionEsaKhanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Corrosion ControlDocument9 pagesBasics of Corrosion ControlSenad Senna MuratovicNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 CorrosionDocument26 pagesUnit 3 CorrosionVasudev GuptaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Inhibitors PDFDocument184 pagesCorrosion Inhibitors PDFNgoVietCuong100% (2)
- Corrosion Engineering Chapter 1Document30 pagesCorrosion Engineering Chapter 1Man DjunNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument20 pagesCorrosionndesigngmailNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Lecture 1Document32 pagesCorrosion Lecture 1PrakashVeerasekarNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Inhibitors-1Document24 pagesCorrosion Inhibitors-1Guilherme Dos Santos MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Prevention and ControlDocument10 pagesCorrosion Prevention and ControlBensoyNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Prevention and Control: By: Patick James Pallo Ram Jun RegaladoDocument10 pagesCorrosion Prevention and Control: By: Patick James Pallo Ram Jun RegaladoBensoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To CorrosionDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Corrosionmotasem100% (2)
- Electrochemistry and CorrosionDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry and CorrosionAkshith SriramNo ratings yet
- Industrial Materials and ProcessesDocument24 pagesIndustrial Materials and ProcessesJamie Christine0% (1)
- Project P 1 CLGG AhsbhDocument16 pagesProject P 1 CLGG Ahsbhpranav mahajanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Corrosion 2022Document31 pagesUnit 3. Corrosion 2022Rohit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Albofera PaintingDocument12 pagesAlbofera PaintingALBOFERA, PRAISE GEE L.No ratings yet
- Unit 2 (B) CorrosionDocument98 pagesUnit 2 (B) CorrosionpkNo ratings yet
- Cat 2 Complete Tapas GhatakDocument213 pagesCat 2 Complete Tapas Ghatakmir zainNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument5 pagesCorrosionsamyuldarosaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Lecture Notes For 1st Cycle Test 07022016Document17 pages1 - Lecture Notes For 1st Cycle Test 07022016SaiPraneethNo ratings yet
- CHY1701 ETH VL2021220503815 Reference Material I 21-02-2022 Module 3Document69 pagesCHY1701 ETH VL2021220503815 Reference Material I 21-02-2022 Module 3Kilari RohithNo ratings yet
- CAP2Document58 pagesCAP2ChriaAkaleziNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Control TechnologyDocument10 pagesCorrosion Control TechnologyMouayed ZeadanNo ratings yet
- 12 - Corrosion and Its Control - (I)Document32 pages12 - Corrosion and Its Control - (I)Anushka SahuNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Its Prevention CHANGDDocument24 pagesCorrosion and Its Prevention CHANGDRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Corrosion - 2019Document31 pagesUnit 2 Corrosion - 2019Abhay hNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 CorrosionDocument37 pagesUnit 2 CorrosionRohan PolNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CorrosionDocument17 pagesIntroduction To CorrosionAli MadridNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument159 pagesCorrosionLearning-Key for SUCCESS YadavNo ratings yet
- Aircraft CorrosionsDocument33 pagesAircraft Corrosionsheruizhe06No ratings yet
- CorosionDocument15 pagesCorosionHazel PiniliNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument3 pagesCorrosionAnsuman SamalNo ratings yet
- Material Science: Prof. Satish V. KailasDocument8 pagesMaterial Science: Prof. Satish V. KailasMilan D SaintNo ratings yet
- 3.2. CorrosionDocument46 pages3.2. Corrosionbroadbazaar3819845No ratings yet
- Notes-2015 Corrosion PDFDocument11 pagesNotes-2015 Corrosion PDFHerculesriderNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of MetalsDocument18 pagesCorrosion of Metalsvdmoorthy123No ratings yet
- Expose CorrosionDocument5 pagesExpose CorrosionFa TehNo ratings yet
- Taboada Chapter 17Document3 pagesTaboada Chapter 17Carl Vincent TaboadaNo ratings yet
- VTG 2012 Vol. LX, No. 1Document14 pagesVTG 2012 Vol. LX, No. 1Ana AlilNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Metals and Its PreventionDocument11 pagesCorrosion of Metals and Its PreventionAli BasheerNo ratings yet
- Environmental Degradation PDFDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Degradation PDFMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument93 pagesCorrosionJessy JamesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Chemistry of Pipes in SeawaterDocument18 pagesIntroduction To The Chemistry of Pipes in SeawaterNarvis RinconNo ratings yet
- Effect of Corrosion in StructuresDocument32 pagesEffect of Corrosion in StructuresasvihariNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: EngineeringDocument149 pagesCorrosion: EngineeringarielNo ratings yet
- Chloride Attack and Sulfate AttackDocument22 pagesChloride Attack and Sulfate AttackMohammed FaseehullaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Basics of Surface PropertiesDocument54 pagesUNIT 1 Basics of Surface PropertiesArthi SelvaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry B - Lecture 6Document64 pagesIndustrial Chemistry B - Lecture 6Daniel Rsix CornwallNo ratings yet
- Unit-2. Corrosion Science and Engineering - 2023Document18 pagesUnit-2. Corrosion Science and Engineering - 2023bxkyfhzw8hNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Protection 7.1 Causes of Corrosion:: (2) Combined StateDocument10 pagesCorrosion Protection 7.1 Causes of Corrosion:: (2) Combined Stateحاتم غيدان خلفNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document114 pagesUnit 3pthangarasu sctengNo ratings yet
- Dry Corrosion and Wet CorrosionDocument17 pagesDry Corrosion and Wet Corrosionasal0032100% (1)
- CorrosionDocument17 pagesCorrosionElon MuskNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument59 pagesCorrosionsparkshock100% (1)
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ClenAir by Nu-Calgon CatalogDocument12 pagesClenAir by Nu-Calgon CatalogornotNo ratings yet
- C40 Nitro Blade: Grind ThruputDocument2 pagesC40 Nitro Blade: Grind ThruputarnoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Proteins and EnzymesDocument4 pagesExercise Proteins and EnzymesBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
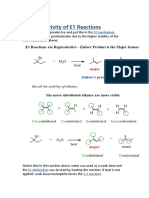
- Elimination RegioselectivityDocument11 pagesElimination RegioselectivitysarahNo ratings yet
- Fired Heater - 2013 FW TalkDocument38 pagesFired Heater - 2013 FW TalkSong Hoe100% (2)
- Kinetics 2022 (Student) PDFDocument62 pagesKinetics 2022 (Student) PDFSundaravadivel Prabhav (Njc)No ratings yet
- Dragon City GuideDocument11 pagesDragon City GuideHardiansyah Ilga RizkiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Basics of UV/EB Chemistry and FormulationsDocument64 pagesIntroduction To The Basics of UV/EB Chemistry and FormulationsdamiendamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology-Science Concerned With History, Sources and Physical and Chemical Property ofDocument6 pagesPharmacology-Science Concerned With History, Sources and Physical and Chemical Property ofRobbie PalceNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Standard2021Document52 pagesThermodynamic Standard2021jesus_manrique2753No ratings yet
- Biochem PDFDocument53 pagesBiochem PDFMiriam JonesNo ratings yet
- Pipe Process JcoeDocument21 pagesPipe Process JcoeValentinoNo ratings yet
- Risk Evaluation Method For Natural GasDocument10 pagesRisk Evaluation Method For Natural GasDave CNo ratings yet
- Industrijski Izmenjivaci Toplote GEA, Tip VCIDocument16 pagesIndustrijski Izmenjivaci Toplote GEA, Tip VCIAleksandarAndric100% (1)
- Geogrid ReinforcementDocument5 pagesGeogrid ReinforcementphilipyapNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Exporters and ImportersDocument7 pagesAluminium Exporters and ImportersChaitu Un PrediCtble0% (1)
- Agricultural PollutionDocument3 pagesAgricultural PollutionOlukunle AlabetutuNo ratings yet
- TDS Byk-037 enDocument2 pagesTDS Byk-037 enwtwilightwNo ratings yet
- Seta Verification Materials: STVM MTVMDocument2 pagesSeta Verification Materials: STVM MTVMdchyNo ratings yet
- Sample Cleaning Validation ProtocolDocument9 pagesSample Cleaning Validation ProtocolOryza SativaNo ratings yet
- Ejection Temperature RequiredDocument4 pagesEjection Temperature RequiredAnonymous fCp1HRwpNo ratings yet
- Epdm Roofing Handbook 0408Document36 pagesEpdm Roofing Handbook 0408Masi Uddin50% (2)
- Classification of Steel PDFDocument11 pagesClassification of Steel PDFkart_rl100% (2)
- 2022 Validation of A Rapid and Economical RP-HPLC Method For Simultaneous Determination of Metformin Hydrochloride and Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Greenness Evaluation Using AGREE ScoreDocument7 pages2022 Validation of A Rapid and Economical RP-HPLC Method For Simultaneous Determination of Metformin Hydrochloride and Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Greenness Evaluation Using AGREE ScoreMuhammad Ali SyedNo ratings yet
- Ale75wv 3e40zs1200p1Document29 pagesAle75wv 3e40zs1200p1Thanh BarcaNo ratings yet
- Energies 06 04607Document33 pagesEnergies 06 04607Sangita MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Silvering ActivatorDocument11 pagesSilvering ActivatorIwan Tejasukmana100% (1)
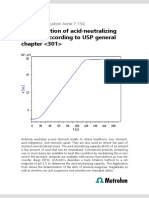
- Determination of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity According To USP General ChapterDocument3 pagesDetermination of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity According To USP General Chapterivanbenavides07No ratings yet
- Sentence Completion Advanced Level Test - Quiz (Online Exercise With Answers) 2Document5 pagesSentence Completion Advanced Level Test - Quiz (Online Exercise With Answers) 2Alvi ElvamaNo ratings yet