Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FCPS Part 1 Medicine Syllabus Final
Uploaded by
Md. Afraem Hossain SeamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FCPS Part 1 Medicine Syllabus Final
Uploaded by
Md. Afraem Hossain SeamCopyright:
Available Formats
SYLLABUS FOR
FCPS (MEDICINE) PART-1
BANGLADESH COLLEGE
OF
PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS
67, SHAHEED TAJUDDIN AHMED SARANI
MOHAKHALI, DHAKA-1212, BANGLADESH
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
CONTENTS
Page No.
A. Introduction 1
B. Entry requirements 1
C. Purpose and academic aims 1
D. Content of the examination 2
E. Syllabus 4
1. Genetics 1
2. Immunology 5
2.1 Immunology and Immunological Tests
2.2 Clinical Conditions 6
2.3 Management 7
3. General aspects of medical practice 7
4. Infectious diseases and tropical medicine 7
4.1 Microbiology 7
4.2 Immunology of Infectious Diseases 8
4.3 Pathophysiology 8
4.4 Epidemiology 8
4.5 Treatment 8
4.6 Specific Infections 9
5. Cardiology 10
5.1 Anatomy and Physiology 10
5.2 Pathophysiology and Pathology 10
5.3 Cell Biology 10
5.4 Clinical Pharmacology 11
5.5 Clinical Cardiology 11
6. Respiratory Medicine 12
6.1 Anatomy and Physiology 12
6.2 Pathophysiology and Pathology 12
6.3 Cell Biology and Genetics 13
6.4 Clinical Pharmacology 13
6.5 Clinical conditions 13
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
7. Gastroenterology 14
7.1 Clinical Science 14
7.2 Disorders of the mouth, tongue and salivary glands 15
7.3 Disorders of the esophagus and stomach 15
7.4 Functional Disorders 15
7. 5 Disorders of the small intestine 15
7.6 Disorders of the liver, biliary tree and pancreas 16
7.7 Inflammatory bowel diseases and gut infections 16
7.8 Colorectal disorders 16
8. Neurology 16
8.1 Neuroanatomy 16
8.2 Neurophysiology 17
8.3 Cell Biology 17
8.4 Neuropharmacology 17
8.5 Neuropathology 18
8.6 Clinical Neurology 18
9. Clinical Hematology 19
9.1 Iron Metabolism 19
9.2 Megaloblastic Anemias 19
9.3 Haemolytic Anemias 19
9.4 Other Anemias
9.5 Polycythemia and Meyloproliferative disorders 19
9.6 White Cell disorders 19
9.7 Disorders of Hemostasis 20
10. Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorders 20
10.1 Hypothalamus/Pituitary 21
10.2 Thyroid 21
10.3 Adrenal 21
10.4 Testis 22
10.5 Parathyroici / Bone 22
10.6 Diabetes Mellitus 22
10.7 Disorders of lipid metabolism 23
11. Nephrology 23
11.1 Renal Physiology 23
11.2 Glornerular and Tubular 23
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
11.3 Infections of the kidney 24
11.4 Acute and chronic renal failure 24
11.5 Hypertension and kidney 25
11.6 Drug and the kidney 25
11.7 Renal problems in pregnancy 25
11.8 Renal replacement therapy 25
12. Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Imbalance 25
13. Rheumatology 25
13.1 Clinical Science 26
13.2 Clinical Conditions 26
13.3 Investigations 27
13.4 Management 27
14. Clinical nutrition 28
15. Principles of medical oncology 28
16. Clinical toxicology 28
17. Principles of geriatric medicine 29
18. Psychiatry 29
Mental state 29
Etiological factors in psychiatric illness 29
Investigations 30
Syndromes of psychiatric disorders and their treatment 30
Psychiatric aspects of physical disease 30
Mental retardation 30
19. Dermatology 31
Basic Science 31
Clinical Dermatology 31
Investigation 32
Drugs and Therapy 32
20. Climatic and environmental factors in disease 32
21. Statistics, epidemiology and evidence-based medicine 33
Descriptive Statistics 33
Graphical Techniques 33
Inferential Techniques 34
Evidence-Based Medicine 34
Clinical Trials 34
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
A. INTRODUCTION
Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons (BCPS) was formed by Order of
Honorable President of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh (No. 63 of 1972). It
is founded as the highest body for conferring postgraduate qualifications in
various disciplines of medical science. The ultimate goal is to bring about an
improvement in the health and nutritional status of the people in the country. The
College runs its Fellowship examinations twice a year. At present, the College
runs FCPS exams in 21 disciplines. FCPS (Medicine) is one of them. The
Fellowship exam is taken in two parts. Although divided into two parts, the FCPS
(Medicine) is a single examination. FCPS (Medicine) Part 1 is not in itself a
diploma, nor does it carry Membership status. The part I examination assesses
mainly core knowledge pertinent to the particular clinical discipline. Three
written papers of MCQs are used as tools for evaluation. A candidate may appear
in the part I exam 18 months after graduation. Requisites for appearing in the part
II exam are successful crossing of the part I exam, completion of a semi-
structured three-year training in accredited centers and production of a research
report of acceptable quality in the form of dissertation. The final exam comprises
written, clinical and oral components. The following sections deal with the
syllabus of FOPS (Medicine) Part 1 examination.
B. Entry Requirements
To meet the entry requirements for the Part 1 Examination, one must hold medical
qualification that is recognized by the Bangladesh Medical & Dental Council. No
one will be admitted to the Examination before the expiry of 18 months from the
date of graduation.
C. Purpose and Academic Aims
The FCPS (Medicine) has three main academic aims:
• To test a wide range of up-to-date medical knowledge so that physicians
are encouraged to develop their full clinical and academic potential;
• To maintain and improve the practice of clinical Medicine;
• To provide a sound basis for Continuing Professional Development.
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
The Practice of high quality Medicine necessitates that you have knowledge of
important new advances in disease mechanism, an understanding of evidence-
based Medicine, and an ability to apply this knowledge and understanding in the
management of patients. Preparation for the Examination will encourage you to
acquire relevant knowledge and understanding. It is important that you develop
skills and acquire professional habits that will enable you to keep abreast of
current medical knowledge and new developments. Preparation for the
Examination will help you to develop such skills and professional habits. Hence,
reading the should be a normal part of your professional life.
The Part 1 Examination is set at a level that is appropriate for medical graduates.
The FCPS (Medicine) Part 1 Examination is designed to identify physicians who
have a broad knowledge and understanding of common or important disorders as
well as of basic sciences relevant to medical practice.
D. Content of the Examination
The Examination currently consists of three papers, each consisting of 50
multiple-choice questions (MCQs), which are designed to test your knowledge of
a wide range of topics in General Medicine including the scientific basis of
clinical practice. The topics are arbitrarily distributed among the three papers in
following manner:
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
Topic-wise Distribution of Questions
Paper I
Topic Number
General Aspects of Medical Practice 5
Genetics 5
Neurology 15
Gastroenterology 10
Hepatology 05
Haematology 8
Principles of oncology 1-2
Climatic & Environmental factors in diseases 1-2
Paper II
Topic Number
Cardiology 15
Endocrinology and Metabolic disorders 15
Clinical Nutrition 3
Toxicology 3
Dermatology 4
Psychiatry 5
Medical Statistics 5
Paper III
Topic Number
Immunology 5
Respiratory Medicine 10
Infectious diseases and Tropical Medicine 15
Disturbances in Water, Electrolyte and Acid-Base balance 3
Nephrology 8
Principles of Geriatric Medicine 1
Rheumatology 8
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
The questions on a particular body system should be divided in following three
categories:
1. Clinically relevant basic information on the particular system, i.e.,
Anatomic, Physiological and Pathological basis of diseases pertaining to
the system. Some standard textbook of Medicine (for example, Harrison's
Principles of Internal Medicine) may be followed for preparing such
questions. Wherever appropriate, 20 to 30% of question from a particular
system should belong to this category. For example, out of 15 questions on
Neurology 4 to 5 questions should cover
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Neurophysiology Standard textbooks of
Medicine should also be used as guides for constructing questions on Genetics
and Immunology.
2. Clinical Assessment related to the particular system. 'These questions should
relate to history taking and principles and procedure of examination. Standard
textbooks of Clinical Methods (e.g., ID Hutchison's or McLeod's ones) should,
utilized for developing such questions. 10 to 20% of questions from a particular
system should belong to this category. For example, out of 15 questions on
Neurology 2 to 3 questions should cover neurological history taking and
examination.
3. Cardinal clinical and laboratory features and classification of diseases. Some
simple textbook of Medicine (e.g., Davidson's) may be used for developing
questions on this aspect. 30 to 50% of questions from a particular system should
belong to this category. For example, out of 15 questions on Neurology 5 to 7
questions should cover Clinical and diagnostic Neurology.
4. Clinical Pharmacology of drugs used for treatment of diseases belonging to the
particular system. Some standard textbook of Medicine should be followed for
preparing such questions. 10 to 20% of questions from a particular system should
below: to this category. For example, out of 15 questions on Neurology 2 to 3
questions should cover Neuropharmacology.
E. Syllabus
No syllabus can be comprehensive. Hence, this syllabus is indicative of those
areas of knowledge with which you are expected to be familiar, but is not intended
to be exhaustive or to exclude other items of knowledge, which are of similar
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
relevance. You can expect, however, that the majority of questions Will test
knowledge in the broad areas specified.
I. GENETICS
You should have an understanding of the structure and function of chromosomes
and genes and knowledge of the principles of inheritance of chromosomal and
genetic disorders.
Examples of topics that might be included
• Chromosomal basis of inheritance
• Chemical basis of inheritance
• Manipulating and tracking genes
• Single gene disorders
• Chromosomal disorders
• Multifactorial disorders o Genetic counseling
• Perinatal diagnosis e Gene therapy
2. IMMUNOLOGY
Although a detailed knowledge of basic immunology and immunological diseases
is not required, you should have a sound working knowledge of the principles of
immunomechanisms.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Humoral and cell-mediated immunity
• Immunodeficiency syndromes
• Phagocytic dysfunction diseases
• Complement deficiencies
• Hypersensitivities including allergies and autoimmune diseases
Immunology and immunological tests
You should have a basic knowledge of the immune system in health and diseases.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Common immunological laboratory tests
• Evaluation of patients with immune disease
• Intercellular communication and signal transduction
• Lymphocyte and phagocytic cell biology
• Antigen presentation
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Humoral, cellular and mucosal immunity including TH1 and TH2
responses
• Inflammation
• Complement system and cytokines
• Hypersensitivity and autoimmunity
Clinical conditions:
You should be able to answer questions on the various immunodeficiency
syndromes.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Mechanisms of immunodeficiency
• Antibody immunodeficiency disorders
• T-cell immunodeficiency disorders
• Combined antibody and cellular immunodeficiency disorders
• Phagocytic dysfunction diseases 6 Complement deficiencies
You should know the main clinical characteristics and immediate management
of acute allergic emergencies.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Anaphylaxis
• Angio-oedema
• Urticaria
You should be familiar with immunology as applied to other medical
diseases.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Rheumatic disease (connective tissue diseases)
• Endocrine diseases (thyroid autoimmune diseases, di mellitus, Addison's
disease) abetes
• Haematological diseases (pernicious anaemia, autoimmune haemolytic
anaemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura)
• Gastrointestinal diseases (Coeliac disease, inflammatory bowel disease,
hepatobiliary disease)
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Renal diseases (Goodpasture's Syndrome, immune-complex
glomerulonephritis)
• Dermatological diseases (discoid lupus, pemphigus pemphigoid)
• Neurological disease syndromes) demyelinating diseases, myasthenic
syndromes.
Management
You should be able to answer questions on the principles of immunosuppressive
therapy including major indications and side effects.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Immunosuppressive drug therapy (corticosteroids, cytotoxic agents, and
cyclosporin)
• Intravenous immunoglobulin
• Monoclonal antibodies
• Bone marrow transplantation
You should know about the principles of immunisation and be familiar with
vaccines currently in use.
3. GENERAL ASPECTS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE
You should have a sound understanding of attributes of a good physician.
Examples of topics that might be included
• Doctor-patient relationship
• General aspects of history taking
• General physical examination
• Medical ethics
• Socio-demographic influences on pathogenesis and management of
diseases
• Cost awareness in Medicine
4. Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine
Microbiology
You should understand the major taxonomy of bacteria in terms of Gram-staining
and aerobic/anaerobic metabolism. Virus classification is not important except
for members and characteristics of the herpes group. Virus replication with
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
reference to retroviruses should be understood. Major pathogenic protozoa and
helminths should be known.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Aerobic or anaerobic bacteria
• Gram-staining characteristics of bacteria
Immunology of infectious diseases
You should understand immune deficiency states linked with types of
opportunistic infections. Principles of immunization and knowledge of vaccines
currently used should also be known.
Examples of topics that might be included
• Opportunistic infections
• Inununization policy
Pathophysiology
You should have a basic understanding of:
• Sepsis
• ARDS
Epidemiology
You should have knowledge of the principles of epidemiolo relevant to infectious
diseases.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Mechanisms of transmission of pathogens
• How epidemics happen
• Knowledge of carrier states reservoirs, vectors and zoonoses
• Elementary concepts of the control of communicable diseases tracing,
chemoprophylaxis of close contacts)
Treatment
You should know the broad indications for, and major advers effects of,
commonly employed antimicrobial agents.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• B-lactarnas
• Tetracyclones
• Macrolides
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Aminoglycosides
• Quinolines
• Trimethoprim
• Metronidazole
• Antituberculous drugs
• Antimalarial drugs
• Antiviral agents
• Antifungal drug
• Antiparasitic drugs
Specific infection
Knowledge of the characteristics, recognition, prevention, eradication and
pathological effects of all commonly encountered bacteria, viruses, rickettsia,
fungi, protozoa, parasites and toxins, including and understanding of the
principles of infection control, will be required. Special attention to differential
diagnosis, appropriate investigations and awareness of when presumptive therapy
is indicated is essential.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Tuberculosis
• Cholera and other infective diarrheas
• Pneumococcal infections
• Meningitis
• Typhoid fever
• Sexually transmitted diseases
• Influenza
• Mumps
• Dengue
• AIDS
• Malaria
• Visceral leishmaniasis
• Amebiasis
• Candidiasis
• Tineas
• Subcutaneous and deep mycoses
• Scabies
• Leprosy
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
4.7 Envenomation - Snakebite, scorpion & other stingers. Biological basis,
pathophysiology of envenomation.
Example of topic that might be included:
• Venomous snakes
• Mode of action of venoms
• Anti snake venins
Clinical Pharmacology
You should know the indication for drug therapy in cardiac disease and
understand h actions, interactions and side effects of the drugs used. The ein
phasis will often be on new drugs or on novel applications or newly
observed side effects of established drugs. Details of drug dosage are asked
only rarely.
Clinical Cardiology-
You must know the clinical features and management of the cardiac
disorders encountered in hospital practice by the general physician, though
detailed specialist knowledge is not expected. You should have knowledge
of risk factors.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Clinical features of constrictive pericarditis, cardiac temponade,
endocariditis, valvular heart disease
• Management of coronary syndromes
• Management of cardiac failure
• Management issues in atrial fibrillation
• Indications for, and types of, permanent pacemaker
Knowledge of important changes in clinical practice, following the
publication of major clinical trials, is likely to be tested.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Use of ACE inhibitors after myocardial infarction
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Use of HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in primary and secondary
prevention of coronary morbidity and mortality
• Use of beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs in left ventricular dysfunction
You should know:
• Indications for invasive and non-invasive cardiac investigation
• Principles of these investigative methods, their limitations and the
clinical relevance of the results
Knowledge of the practical aspects of the investigative technique is not required.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Common ECG abnormalities aphic abnormalities such as hypert
• Basic echocardiographic obstructive cardiomyopathy or pericardial
effusion
• Indications for coronary angiography
6. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
Anatomy and Physiology
You could understand clinically relevant anatomy of the upper and lower
respiratory tract and thorax including radiological anatomy.
You should have knowledge of the principles of respiratory physiology
including:
• How respiration is controlled
• Principles of gas exchange and oxygen transport
• Ventilation -perfusion relationship
• Lung volumes and transfer factor, a Respiratory aspects of sleep and
exercise physiology
You should understand the:
• Physical, humoral and cellular aspects of respiratory defense
mechanisms
• Physiology of the proteinase inhibitors and pulmonary surfactant
Pathophysiology and Pathology
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
You should understand the effects of disease on pulmonary physiology and
anatomy including.
• The pulmonary and bronchial circulations and gas exchange
• Adaptations to chronic hypoxemia
• Pleural fluid production and reabsorption
You should understand the application of the basic immunological process to
pulmonary pathology including:
• Asthma
• Tuberculosis
You should possess knowledge of humoral and cellular immunodeficiency states
and sequelae. The microbiology of acute and chronic respiratory infections
should be known.
Cell Biology and Genetics
You should have knowledge of:
• Lung inflammation and repair
• Vasculitis
• Cystic fibrosis, Anti-protease deficiency
Clinical Pharmacology
The indications for, and mechanisms of action of, drugs used in respiratory
disease together with their interactions and side effects should be known.
Important respiratory complications of other drugs, e.g., NSAIDs and beta
blockers, should also be understood.
Clinical conditions
The clinical features, investigation and management of respiratory disease likely
to be encountered by a general physician must be known. Examples of topics that
might be included:
. Pleural effusion
• Chest pain
• Haemoptysis
• Breathlessness
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
The impact of systemic disease on the respiratory system should be known.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Vasculitis
• Neuromuscular diseases
• HIV infection
You should know how to assess respiratory malignant condition and understand
the general principles of oncological management including the indications for
surgery.
The indications for specialized investigations, including bronchoscopy, CT
scanning lung biopsy, lung volumes and exercise testing should be known.
You should have knowledge on the control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection.
Exclusions
Knowledge of detailed pulmonary mechanics, oncology drug regimens, drug
therapy of environmental mycobacterial infection, inhalation drug kinetics and
detailed histological descriptions not required.
7. GASTROENTEROLOGY
Clinical Science
You should understand the:
• Structure and function of the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary tract
• Neurohormonal control of gut motility
• Secretory and absorptive functions of the gastro-intestinal tract and liver
• Symptoms and signs of gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary and pancreatic
diseases
• Genetics of the more common gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary and
pancreatic diseases
• Genetic of the more common gastrointestinal and liver disorders
• Clinical pharmacology of drugs used in gastrointestinal disorders including
their actions. Interactions and adverse effects
Examples of topic that might be included:
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Control of gastric acid secretion
• Autonomic control of gut function
• Effects of cholinergic, adrenergic and serotonergic agents on gut function
Disorders of the mouth, tongue and salivary glands
You should have an understanding of:
• Mouth ulcers, periodontal and salivary disorders
• Oral manifestations of systemic and dermatological disorders
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Causes of mouth ulcers and their management.
• Skin disorders commonly involving the buccal mucosa
Disorders of the esophagus and stomach
You should be familiar with the following disorders:
• Achalasia
• Carcinomas
• Gastrointestinal hemorrhage
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Control of HCI, secretion by the parietal cells
• Role of Helicobacter-associated gastritis in peptic ulcer disease
• Management of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding
Functional disorders
You should have knowledge of:
• Functional chest pain and functional dyspepsia
• Irritable bowel syndrome and functional abdominal pain
• Functional constipation and diarrhoea
• Neural control of visceral nociception and gut motility
• Role of emotional and psychosocial factors in illness
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Management of chronic pain and the use pain-modifying drug therapy
Disorders of the small intestine
You should have knowledge of:
• 'Malabsorption syndromes
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Investigations commonly used in the assessment of suspected
malabsorption
Disorders of the liver, biliary tree and pancreas
You should have knowledge of:
• Bilirubin metabolism and the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids
• Causes of jaundice and cholestasis
• Common pancreatic disorders including carcinoma
• Fulminant liver failure
• Acute and chronic hepatitis
• Drugs, toxins, alcohol and the liver
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Aetiology, clinical and histopathological features of acute and chronic
parenchymal disorders of the liver
• Aetiology, presentation and management of acute and chronic pancreatitis
Inflammatory bowel diseases and gut infections
You should be familiar with:
• Infective gastroenteritis
• Parasitic and protozoal gut infections
• Ulcerative colitis
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Causes, investigation and management of acute and chronic enteric
disorders
Colorectal disorders
You should have knowledge of
• Polyps
• Carcinomas
• Anorectal disorders
8. NEUROLOGY
Neuroanatomy
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
You are not expected to have detailed knowledge of neuroanatomy. Questions
with an anatomical bias will be confined to circumstances where an
understanding of anatomical structure is of critical importance in appreciating the
localization of a particular neurological problem.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• The clinical features of a lesion in different parts of the brain
• The manifestations of a particular nerve root or peripheral nerve disorder
• The organization of pathways within the spinal cord
Neurophysiology
Detailed knowledge of neurophysiology is not expected but, as with
neuroanatomy, certain aspects of the subject are particularly relevant to the
understanding of neurological disease and may be tested.
Examples of topic that might be included:
The formation, circulation, absorption and content of the cerebrospinal fluid
• Aspects of cerebral blood flow
• Functions of basal ganglia, hypothalamus, cerebellum
• Muscle tone, reflexes
Cell Biology
Questions in this area will relate to advances in the cellular mechanisms of certain
neurological disease process which have provided better understanding of disease
mechanisms and which might, in the future, lead to more rational therapy.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• The role of the dopaminergic and cholinergic systems in various disorders
• The role of other neurotransmitters in certain diseases, for example, in
Alzheimer's disease
Neuropharmacology
You are expected to have some knowledge of new drug developments in
neurology, as well as the established drug therapies.
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
Examples of topic that might be included:
• The role of some recently introduced anticonvulsants
• The present status of immunosuppressant therapy in multiple sclerosis
Neuropathology
You are not expected to have a detailed knowledge of Neuropathology. You will
be expected to have outline knowledge of the pathological aspects of some
common diseases, for example, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and
Alzheimer’s disease, CNS tuberculosis, peripheral neuropathies, Neuromuscular
junction failure.
Clinical Neurology
Questions in the field of clinical neurology will test your knowledge of the more
common disorders. There will be emphasis on clinical features, which have been
shown to be of diagnostic value. The choice of subject matter will be influenced
by areas of recent advance, particularly those which have either led to better
definition of disease entities, or have led to their improved management.
In the field of cerebrovascular Medicine, examples of topic that might be
included:
• Epidemiological aspects, in particular the risk factors for stroke
• The evidence for the role of anti-platelet agents in transient, ischemic
attacks
9. CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY
You will be expected to have knowledge of the following:
• Physiology, control and function of formed blood elements
• Bone marrow structure and function
• Applications of biochemistry, genetics, immunology, and virology to
blood disorders
• Effects of age and pregnancy on blood disease
• Splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, and their causes
• Principles and hazards of blood and blood product replacement therapy
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Principles of marrow transplantation
• Adverse effects of drugs on the blood and marrow
Iron metabolism
You should have an understanding of:
• Physiology of iron, including its absorption
• Iron overload
• Iron deficiency states including diagnosis, causes and treatment
• Iron metabolism, including anaemias of chronic disorders and sideroblastic
anaemias
Megaloblastic anaemias
You should understand the physiology of vitamin B12 and folic acid and the
mechanisms and investigation of deficiencies and their management.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• B12 deficiency
• Folate deficiency
Haemolytic anaemias
You should understand:
• Mechanisms of shortened red cell survival
• Features and management of congenital and acquired haemolytic states
• Molecular pathology of thalassaemia and common haemoglobinopathies
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Causes of haemolysis
• Diagnosis of haemolytic anaemia
Other anaemias
• Anaemias complicating systemic disease
• Aplastic anaemia
• Myelodysplastic syndromes
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
Polycythaemia and myeloproliferative disorders
You should know the causes, investigation and management of polycythaemia
and myeloproliferative disorders.
White cell disorders
You should understand the:
• Physiology of leucocytes
• Leucocytosis and leucopenia.
• Acute and chronic leukaemias, including diagnosis, management and
prognosis
• Lymphoproliferative diseases including Hodgkins disease, non-Hodgkin's
lymphomas, and plasma cell dyscrasias
Disorders of haemostasis
You should possess knowledge of
• Platelet function and coagulation
• Thrombocytopenia and impaired platelet function
• Thrombocytosis
• Common congenital and acquired disorders of coagulation (especially
anticoagulant therapy and disseminated intravascular coagulation)
10. ENDOCRINOLOGY
Although you are not expected to have a detailed knowledge of biochemistry, it
is anticipated that you will have an insight into the mechanisms of hormone action
and the importance of receptors and substances involved in control of intracellular
metabolism. You should have knowledge of the clinically relevant anatomical
aspects of this specialty.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Factors involved in cell signaling
• Anatomical relationships of the pituitary gland
• The cell types in the pancreatic islets
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• A broad understanding of the pathways of carbohydrate, protein and fat
metabolism
• Endocrine tests in routine clinical use
Hypothalamus / Pituitary
Detailed knowledge of the structure of hypothalamic hormones is unnecessary.
Knowledge of the endocrine system.
Examples of topic that might be included
• The physiology and pathophysiology of control of pituitary hormone
secretion
• The mechanisms of maintaining plasma osmolality
• Tests of pituitary hormone secretion
• Pituitary diseases such as acromegaly, prolactinoma and Cushing's
syndrome
• Drugs used in the treatment of pituitary disease
• Pituitary replacement therapy
Thyroid
Since thyroid disease is common you are expected to have a broad knowledge of
the mechanisms of thyroid disease, its clinical presentation and treatment.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Thyroid hormone biosynthesis and its control
• Important drugs interfering with thyroid function
• Indications for use of various types of thyroid function tests
• Autoimmunity and the thyroid
• Clinical features of thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism
• Goiter and its management
• Thyroid neoplasia
Adrenal
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
A detailed knowledge of mechanisms of steroid biosynthesis is not required, but
you are expected to have some knowledge of those parts, which are clinically
important.
Examples of question topic might include:
• Tests for adrenocortical function
• Endocrine causes of hypertension and their differential diagnosis
• Clinical features and management of adrenal hyper and hypofunction
• Complications of steroid therapy
Testis
You are not expected to have a detailed knowledge of the urological investigation
of infertility but some concept or relevant investigations and of the endocrine
aspects of testicular function is required.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• The aetiology of hypogonadism both primary and secondary
• Causes of male infertility related to general medical diseases and its
treatment
• Causes of erectile dysfunction and its investigation
• Androgen replacement therapy
Parathyroid / bone
Detailed knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of bone metabolism is not
required. You are expected however to have some broad concept of the control
of bone turnover and the disorders which can result in its failure.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Control of calcium metabolism
• Laboratory tests of parathyroid function
• The causes of hypercalcaemia
• The mechanisms of osteomalacia
• Hyperparathyroidism, both primary and secondary
• The prophylaxis and treatment of osteoporosis
Diabetes mellitus
You are expected to have detailed knowledge of this very common condition.
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Control of carbohydrate metabolism
• Aetiology of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes
• Insulin resistance
• Management of diabetic emergencies
Disorders of lipid metabolism
Although a detailed knowledge of lipid metabolism is not required, you are
expected to have an understanding of the importance of this group of disorders.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Control of cholesterol metabolism
• Etiology of different types of hyperlipidemias including both cholesterol
and triglyceride disorders
• Indications for lipid lowering agents and their complications
11. NEPHROLOGY
Physiology
You should have knowledge of:
• Discrete functions of glomerular ultrafiltration and tubular function
• Proximal and distal parts of the nephron, with particular reference to
control of water and electrolyte balance.
• Renal tubular acidosis
• Fluid, electrolyte, and acid-balance disturbances
Glomerular and tubular disorders
You are expected to have some knowledge of glomerular ultrastructure based
upon techniques of light microscopy, electron microscopy and
immunofluorescence as applied to renal biopsy. These techniques form the basis
of current understanding of primary glomerular disorder as in idiopathic
glomerulonephritis, and nephropathies of systemic diseases.
Examples of topic that might be included:
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Primary glomerular disorders
• Diabetic nephropathy
• Lupus nephritis
• Hypertensive nephrosclerosis
You should be acquainted with the metabolic sequelae of acute nephritis and
nephrotic syndromes. You should be aware of the investigation and assessment
of glomerular and tubular disorders, including ultrasonic studies and nuclear
Medicine. You should have an understanding of disturbed renal and
metabolic functions in nephrotic syndrome from a variety of causes.
Knowledge of internal nephritis (especially those cases with reversible
etiology such as drugs, heavy metals and analgesics) is expected.
Infections of the kidney
You should be familiar with the management of urinary tract infections
including their detection, predisposing factors, prevention and treatment.
A knowledge of anatomical abnormalities leading to repeated urinary
tract infection is expected.
Examples of topic that might be included.
• UTIs
You should be aware of other infections that could affect the kidney by
direct invasion or by immune-complex deposition. Examples of topic that
might be included in infection of the urinary tract with:
• Mycobacteria
• HIV
• CMV
• HBV
• HCV
Acute and chronic renal failure
Knowledge of the management of acute and chronic renal failure and of the
disturbed physiology involved is expected. You should be familiar with
pathophysiological changes and non-dialytic treatment in different stages
of progressive renal failure. Knowledge of the principles of nutritional
requirements and dietary intervention for patients with chronic renal failure
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
is required. Other therapeutic means to slow down the progression renal
failure should be understood.
Hypertension and renal problems in pregnancy
You are expected to be familiar with renal adaptation to pregnancy, the
management and prophylaxis of renal disease and hypertension in
pregnancy. Drugs and the kidney knowledge of the role of the kidney in the
normal elimination of drugs is expected and you should understand the
mechanisms by which drugs cause nephrotoxic damage. The principles of
dose adjustment according to residual renal function should he known.
Renal replacement therapy Knowledge of different dialysis modalities and
their complications is expected. You should know the complications related
to immunosuppressive therapy following renal transplantation.
12. FLUID, ELECTROLYTE AND ACID-BASE IMBALANCE
You should have knowledge of Physiology of Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-
Base balance, and pathophysiology of its imbalances so that you may handle
such disturbances in an appropriate manner.
Examples of topics that might be included:
Hypo- or hyper kalemia
Hypo- or hyper natremia
Acidosis and alkalosis
SIADH
13. RHEUMATOLOGY Detailed knowledge of all the rheumatic
conditions is not required. However, you should have a sound working
knowledge of the basic principles of the common musculoskeletal
conditions. Examples of topics that might be included:
• Inflammatory arthritis
• Back pain
• Periarticular disorder
• Osteoarthritis
• Connective tissue diseases
• Bone diseases
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
Clinical Science
Basic physiology, biochemistry, anatomy and pathology relating to
musculoskeletal disease should be known.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Physiology of pain
• Physiology of inflammation
• Urate metabolism
• Bone metabolism
• Applied anatomy, particularly of cervical and lumbar nerve roots, and of
peripheral nerves commonly involved in disease
The pathology of the common rheumatic conditions should be known.
Examples of topics that might be included in pathological findings:
• Rheumatoid arthritis
• Osteoarthritis
• Connective tissue diseases
• Bone diseases
Clinical conditions
You should know the relative prevalence and major associations of the common
rheumatological conditions. Examples of topics that might be included the
relationship to:
• Age
• Gender
• Genetic influences
• Environmental influences
• Occupational influences
You should be able to answer questions on the symptoms and signs of the
rheumatic diseases.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Rheumatoid arthritis and associated syndromes
• Seronegative spondyloarthirits (ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis,
reactive arthritis, enteropathic arthritis)
• Osteoarthritis
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Crystal arthritis (gout, pyrophosphate arthritis)
• Connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's
syndrome, scleroderma, polymyositis/ dermatomyositis)
• polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis
• Systemic vasculitic syndromes
• Bone disorders (osteoporosis, osteomalacia)
You should be familiar with arthritis associated with other medical conditions.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Sarcoidosis
• Erythema nodosum
• Infections and arthritis (e.g Parvovirus B 19)
Investigations
You should have knowledge of the investigations relevant to the diagnosis and
assessment of rheumatic diseases.
Examples of the topics that might be included:
• Acute phase proteins
• Immunological tests relating to the connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid
factor, ANA, anti-dsDNA, ANCAs, etc.)
• Contemporary imaging techniques in rheumatology (x-ray, ultrasound,
MR imaging)
Management
You should be able to answer questions on the management of rheumatic disease.
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Drug related therapies (indications and contra-indications, adverse effects,
drug interactions.
• Simple analgesics
• Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
• Corticosteroids
• Allopurinol
• Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs
• Immunosuppressive drugs
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
l4. CLINICAL NUTRITION
You should be familiar with:
• Nutritional requirements in health
• Assessment of nutritional status
• Nutritional deficiency states
• Primary nutritional disorders
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Calorific requirements
• Body water distribution
• Derivation of the body mass index
• Protein calorie malnutrition
• Essential dietary constituents
• Vitamin requirements
• Pathogenesis and management of obesity
15. PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL ONCOLOGY
You should have a good understanding of pathogenesis of neoplasia, behavior of
the cancer cells and principles of management of neoplastic disorders.
Examples of topic that might be included:
• Etiology of neoplasms
• Staging of neoplasms
• Paraneoplastic syndromes
• Principles of chemotherapy
• Principles of endocrine therapy
• Management of cancer pain
16. CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
You should understand the principles of management of patients who have been
poisoned with drugs or other toxic substances. This should include assessment,
recognition of common symptom patterns, principles of removal of toxic
substances, and their antidotes where these approaches may be appropriate.
Examples of topic that might be included:
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
. Organophosphorus poisoning
• Atropine/datura poisoning
• Ethanol poisoning
• Methanol poisoning
• Benzodiazepine poisoning
• Tetrodotoxin poisoning
• Snake bite
17. PRINCIPLES OF GERIATRIC MEDICINE
In your clinical practice, you must be aware of anatomic and physiological
changes with aging, common age-related disorders and drug pharmacokinetics in
the elderly. You should have knowledge of:
• Physiological effects of aging
• Immobility
• Falls
• Stroke rehabilitation
• Drug treatment in the elderly
18. PSYCHIATRY
Mental state
You should understand the conduct and scope of a mental state examination. You
are expected to be familiar with features of abnormal mental states and
particularly those that present commonly to physicians and to Accident and
Emergency Departments.
Etiological factors in psychiatric illness
You should understand the primary etiological factors in psychiatric areas
including
• Genetic factors
• Environmental factors
• Life events
Investigations
You should be familiar with the potential value of, and indications for common
laboratory' procedures used in psychiatric illness including:
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Psychometric testing
• EEG
• Brain imaging
Syndromes of psychiatric disorders and their treatment
You should have knowledge of:
• Organic brain syndromes (delirium, dementia, focal brain syndromes, head
injury)
• Schizophrenia and related syndromes
• Paranoid disorders and related syndromes
• Affective disorders (anxiety states, phobic disorders, bipolar affective
disorders)
• Grief and bereavement
• Self-harm, attempted suicide, suicide
• Substance misuse (including alcohol dependence)
• Eating disorders
• Obsessive compulsive disorder
• Abnormal illness behavior
Syndromes associated with medically explained physical symptoms (including
somatization and somatoform disorders)
Psychiatric aspects of physical disease you should be aware of the psychiatric
presentations of physical disease including:
• Endocrine and metabolic disorders
• Toxic states
• AIDS
• Neurological disease
• Epilepsy
• Pain
Mental retardation
You should know the features of the commoner syndromes.
19. DERMATOLOGY
Basic Science
You will be expected to have a working knowledge of the structure and
function of the epidermis and dermis. Clinical Dermatology Knowledge of
the clinical features of the following skin diseases is required:
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Psoriasis
• Eczema
• Urticaria
• Superficial fungal infections (dermatophytosis, pityriasis versicolor)
• Common skin cancers such as melanoma
• Vitiligo and alopecia areata
• Pemphigus and pemphigoid
• Cutaneous herpes virus infections (herpes simplex, varicella zoster)
• Cutaneous staphylococcal and streptococcal infections
• Leprosy
Many diseases affecting internal organs will present with skin signs or
symptoms. You should know the differential diagnosis and plan of
investigation of patients who present with the following cutaneous signs or
symptoms which may indicate internal disease:
• Itch
• Hyperpigmentation
• Generalized erythema
• Loss of hair
• Increased hair growth
• Common patterns of nail dystrophy such as clubbing
• Erythema nodusum
• Erythema multiforme
• Purpura
• Ulceration
• Vasculitis
You are expected to be able to recognize the cutaneous symptoms and signs of
systemic diseases.
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
Examples of topic that might be included
• Collagen vascular disease such as SLE, systemic sclerosis
• Metabolic and endocrine disorders
• Infectious diseases
• Cancers
• Leukaemias
• Respiratory and cardiovascular diseases
• Common inherited diseases such as neurofibromatosis
You should have knowledge of the main dermatological complications of
therapeutic immunosuppression (for example, systemic corticosteroid therapy,
cyclosporine etc.) or of diseases such as HIV which cause immunosuppression.
Investigation you should know the principles but not details of dermatological
investigation such as patch testing.
Drugs and therapy
You will not be expected to have a detailed knowledge of the treatment of skin
diseases or dermatoses. However you should know the drugs, which cause life-
threatening skin conditions such as erythroderma or Stevens-Johnson syndrome,
angio-oedema and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
20. CLIMATIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN DISEASE
• Global warming
• Disasters
• Arsenicosis/lathyrism
• IDG
• Drowning, Electrocution etc.
Example (s) of topic that might be included
• Effect of global warming
• Pathophysiology of arsenicosis
• Effect of electrocution
• Effect of drowning
21. STATISTICS, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE
you should have a basic understanding of the usage and limitations of the
common statistical tests used in reporting the results of research in clinical
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
journals. The following lists of terms give some idea of the range of terms and
techniques which you should understand, all of which can be found regularly in
journals such as The Lancet, British Medical Journal and New England Journal
of Medicine. You are not expected to have any knowledge of computer packages
for carrying out statistical calculations. You may be expected to carry out simple
calculations that do not require the use of calculator. You are not expected to
memorise formulae for statistical tests, but should understand their conceptual
basis. The following lists are not intended to be inclusive but as illustrative of the
type of knowledge that you need to inclusive but as illustrative of the type of
knowledge that you need to possess.
Descriptive Statistics
Examples of topics that might he included:
• Mean, median, mode
• Standard deviation, standard error
• Confidence interval
• Variance
• Range, quartile, inter-quartile range
• Percentile
• Skewness
• Contingency table
• Population
• Missing values
• Outliers
Graphical techniques
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Histogram
• Box-plot
• Scattergram
Inferential techniques
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Null hypothesis
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
• Alternative hypothesis
• Parametric and non-parametric tests
• Normal distribution
• Type 1 and Type 2 errors
• Fa1se positive and false negative
• Statistical power
• One and two-tailed tests
• Statistical significance, P value
• T-test
• Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon test
• Chi-square test for 2 x 2 contingency table
• Correlation (Pearson's and spearman's)
• Linear regression
• Study design
Clinical trials
Examples of topics that might be included:
• Interpretation of simple clinical trial data
• Randomization
• Placebo-controlled trial
• Open trial
• Single-blind trial
• Double-blind trial
• Intention-to-treat
• Bias
Evidence-based Medicine
You are expected to have an understanding of evidence-based Medicine and an
ability to apply this understanding in the management of patients.
SYNAPSE MEDICAL ACADEMY
You might also like
- Medical Books Reference ListDocument6 pagesMedical Books Reference ListKarl CNo ratings yet
- Cns PhysiologyDocument152 pagesCns PhysiologyDr. Niyati Patel100% (1)
- Embryology of The Renal SystemDocument8 pagesEmbryology of The Renal SystemStd DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Thrombolytic TherapyDocument37 pagesThrombolytic TherapySani sunilNo ratings yet
- Membership of the Royal Colleges of Physicians UK Exam ResultsDocument129 pagesMembership of the Royal Colleges of Physicians UK Exam ResultsA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Medico-Legal Aspects of Physical InjuriesDocument9 pagesMedico-Legal Aspects of Physical InjuriesRhem Rick Corpuz100% (1)
- The Nervous System: by Janelle Liane V. TabaldoDocument68 pagesThe Nervous System: by Janelle Liane V. Tabaldojanelle liane tabaldoNo ratings yet
- MRCPUK Part 1 SyllabusDocument62 pagesMRCPUK Part 1 Syllabusthargyikyaw100% (5)
- Practice GI QuestionsDocument14 pagesPractice GI QuestionsJenna DantNo ratings yet
- VALVULAR HEART DISEASE GUIDEDocument69 pagesVALVULAR HEART DISEASE GUIDEAbanoub AwadallaNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument40 pagesBasal GangliaEnkefalos KardiaNo ratings yet
- ECHO MASTERCLASS: A GUIDE TO ACCURATELY ASSESSING HEART VALVE DISEASEDocument136 pagesECHO MASTERCLASS: A GUIDE TO ACCURATELY ASSESSING HEART VALVE DISEASEVladlena Cucoș-CaraimanNo ratings yet
- Neurology Work BookDocument73 pagesNeurology Work BookCastleKGNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesIntroduction to Anatomy & Physiology Nervous SystemJacia’s SpaceshipNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Sample Questions MRCPDocument33 pagesPart 1 Sample Questions MRCParvindNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Document64 pagesAnatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Batot EvaNo ratings yet
- 2 ThoraxDocument7 pages2 Thoraxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Craniotomy Techniques for Head TraumaDocument14 pagesCraniotomy Techniques for Head Traumapemetaan dokumen aktreditasi100% (1)
- Cross-Sectional Anatomy of The Thorax-BleinDocument355 pagesCross-Sectional Anatomy of The Thorax-BleinNatnael GetahunNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Vascular Diseases ExplainedDocument115 pagesCerebral Vascular Diseases ExplainedUbaidillah Romadlon AlfairuziNo ratings yet
- Questions From Exam 08.09.22Document12 pagesQuestions From Exam 08.09.22Ismo SNo ratings yet
- QQ - GG: AdrenalDocument84 pagesQQ - GG: AdrenalbnvjNo ratings yet
- Survival Rad 15 - Lung HandoutDocument41 pagesSurvival Rad 15 - Lung HandoutLorraineYongNo ratings yet
- WHO TRS 816 EngDocument68 pagesWHO TRS 816 EngSina MnaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Spa TreatmentDocument35 pagesBenefits of Spa TreatmentMercy Zonio100% (1)
- 4 5866212804146498341Document36 pages4 5866212804146498341Faris FirasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lower Extremity - Hirsch TextbookDocument546 pagesAnatomy of The Lower Extremity - Hirsch TextbookAkash ShahNo ratings yet
- Review of Pharmacology (PGMEE) Paperback - 2018 (PDFDrive)Document660 pagesReview of Pharmacology (PGMEE) Paperback - 2018 (PDFDrive)xwendnla russiaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease From EEG Signals Where Are We StandingDocument43 pagesDiagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease From EEG Signals Where Are We StandingElvis Josip EspinozaNo ratings yet
- The autonomic nervous system (ANS) and its role in regulating the sympathetic responseDocument28 pagesThe autonomic nervous system (ANS) and its role in regulating the sympathetic responseG4min6 M45t3rNo ratings yet
- FomaDocument1,218 pagesFomaosamaeNo ratings yet
- January 2023 Article Questions - Practice Q PDFDocument19 pagesJanuary 2023 Article Questions - Practice Q PDFbody fayez100% (1)
- SK Golden 11: 500 Important Points in Surgery, Medicine, Gynaecology, Radiology and AnaesthesiaDocument480 pagesSK Golden 11: 500 Important Points in Surgery, Medicine, Gynaecology, Radiology and AnaesthesiaEXE 3100% (1)
- OSPE DU MedicineDocument101 pagesOSPE DU MedicinesaifNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeuroanatomyDocument33 pagesIntroduction To NeuroanatomyAsad Osman100% (1)
- Suggested Topic For Neet PG of All 19 Subjects..Document23 pagesSuggested Topic For Neet PG of All 19 Subjects..Vipul Khajuria100% (1)
- Interpreting arterial blood gas resultsDocument38 pagesInterpreting arterial blood gas resultsroopaNo ratings yet
- QweqDocument7 pagesQweqJackieNo ratings yet
- Neurology Study Guide Oral Board Exam ReviewDocument1 pageNeurology Study Guide Oral Board Exam Reviewxmc5505No ratings yet
- DR Saleh Course fainalSEPT 20Document103 pagesDR Saleh Course fainalSEPT 20JehanzebNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia From HarrisonDocument3 pagesHypernatremia From HarrisonNobel LaureateNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For PhysiciansDocument40 pagesGuidelines For PhysiciansS.M. Shahriar islam ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Level of Pain During Office Hysteroscopy According To Menopausal Status, Parity, and Size of InstrumentDocument4 pagesEvaluating The Level of Pain During Office Hysteroscopy According To Menopausal Status, Parity, and Size of InstrumentMaqsoodUlHassanChaudharyNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument21 pagesNeurophysiologyKeya PatelNo ratings yet
- Chorea - A Practical Approach To Movement Disorders Diagnosis and ManagementDocument16 pagesChorea - A Practical Approach To Movement Disorders Diagnosis and ManagementNathasia SuryawijayaNo ratings yet
- CXR Interpretation: by Dr. Iqbal TariqDocument19 pagesCXR Interpretation: by Dr. Iqbal TariqSalman Khan100% (1)
- UntitledDocument135 pagesUntitledDr.younes95 RekaaneyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisNo ratings yet
- Higher Mental Function Examination Dementia, Altered MentalDocument37 pagesHigher Mental Function Examination Dementia, Altered MentalCamille DoamanNo ratings yet
- Abg CasesDocument22 pagesAbg CasesNehal ElsaidNo ratings yet
- MICRO FALCON (Latest Edition)Document19 pagesMICRO FALCON (Latest Edition)Nikhil kumar Sangam.No ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Fever?: 1 DR - Shamol /inter/feverDocument28 pagesApproach To A Patient With Fever?: 1 DR - Shamol /inter/feverkiloNo ratings yet
- One Shot RevisionDocument171 pagesOne Shot RevisionKuldip PatelNo ratings yet
- CVS II Tutorials Apr 12-17Document7 pagesCVS II Tutorials Apr 12-17rishitNo ratings yet
- Deepak Marwah Medicine Mcqs-Compressed - CompressedDocument265 pagesDeepak Marwah Medicine Mcqs-Compressed - CompressedyagnavinikhithaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEWDocument7 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEWFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Venous congestion in the liverDocument135 pagesVenous congestion in the liverJustin JannatiNo ratings yet
- Stroke Program Orientation Medical StaffDocument22 pagesStroke Program Orientation Medical StaffLaura VelaNo ratings yet
- FAST PACES CLINICAL MEDICINE - CDRDocument30 pagesFAST PACES CLINICAL MEDICINE - CDRTaniaNo ratings yet
- OSPE AnswersDocument4 pagesOSPE AnswersLiyana SulaimanNo ratings yet
- 1 Stroke NeuroanatomyDocument47 pages1 Stroke NeuroanatomySherief MansourNo ratings yet
- 20 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Ophthamology PDFDocument46 pages20 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Ophthamology PDFSisterzzShopDua0% (1)
- Mousab Kibreet Notes of Internal Medicine 2ed EditionDocument253 pagesMousab Kibreet Notes of Internal Medicine 2ed EditionAbdulltif AliNo ratings yet
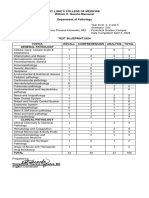
- GP Test Blueprint 2024Document1 pageGP Test Blueprint 2024Immah PinedaNo ratings yet
- Synovial ChondromatosisDocument4 pagesSynovial ChondromatosisNadia Bordaş100% (1)
- Dr. G. M. Taori: Curriculum VitaeDocument12 pagesDr. G. M. Taori: Curriculum Vitaesrajan sahuNo ratings yet
- Case Based Discussion Astma Bronchiale, Hypertension: Chusna Helmia 01.209.5853Document26 pagesCase Based Discussion Astma Bronchiale, Hypertension: Chusna Helmia 01.209.5853helmiaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Ragging Committee For The Academic Year 2015 - 16: Ug Wing, Afmc PuneDocument4 pagesAnti-Ragging Committee For The Academic Year 2015 - 16: Ug Wing, Afmc PuneDeepak RanjanNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument6 pagesHematologyRian CopperNo ratings yet
- Effective and Practical Complete Blood Count DeltaDocument7 pagesEffective and Practical Complete Blood Count Deltarince noveliaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga Ethical Per April'22 (Khus Riau)Document8 pagesDaftar Harga Ethical Per April'22 (Khus Riau)iraNo ratings yet
- Pleno Skenario A TB Dewasa-1Document58 pagesPleno Skenario A TB Dewasa-1ninja sanjeninNo ratings yet
- Stool Exam Guide - Key Tests, Colors, Consistencies in 40 CharactersDocument8 pagesStool Exam Guide - Key Tests, Colors, Consistencies in 40 CharactersLester John HilarioNo ratings yet
- Stop The Bleed Booklet FinalDocument16 pagesStop The Bleed Booklet FinalUrsula MalauNo ratings yet
- EMR Implementation Readiness Assessment and Patient Satisfaction ReportDocument20 pagesEMR Implementation Readiness Assessment and Patient Satisfaction ReportAbidi HichemNo ratings yet
- Strabismus Prevalence and Associated Factors Among Pediatric Patients in Southern Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional StudyDocument10 pagesStrabismus Prevalence and Associated Factors Among Pediatric Patients in Southern Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional StudyDenise MacieNo ratings yet
- Villanueva 2016Document4 pagesVillanueva 2016OleOhhNo ratings yet
- E01 AeromedicalDocument28 pagesE01 AeromedicalRumahorbo Hinsa JulianNo ratings yet
- ppl10 - WebsiteDocument14 pagesppl10 - Websiteapi-270774299No ratings yet
- EFIC2015 Poster AbstractsDocument1,066 pagesEFIC2015 Poster AbstractsszscribdNo ratings yet
- Cucms Rheumatology Questions PDFDocument3 pagesCucms Rheumatology Questions PDFMaisara JhsNo ratings yet
- Doctor's OrderDocument2 pagesDoctor's OrderWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Manage Expired and Slow Moving InventoryDocument7 pagesManage Expired and Slow Moving InventoryIdan RidwanNo ratings yet
- Reimplantation of Avulsed Primary IncisorsDocument4 pagesReimplantation of Avulsed Primary IncisorsDilmohit SinghNo ratings yet
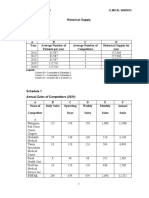
- Historical SupplyDocument5 pagesHistorical Supplylara torricoNo ratings yet
- Download Clinical Psychopharmacology Principles And Practice 1St Edition S Nassir Ghaemi full chapterDocument67 pagesDownload Clinical Psychopharmacology Principles And Practice 1St Edition S Nassir Ghaemi full chapterdoug.wiggins940100% (4)
- AlopeciaDocument2 pagesAlopeciaAldrich ArquizaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Sars-Cov-2Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Sars-Cov-2sandeep yadav0% (2)
- Septal Hematoma 1Document3 pagesSeptal Hematoma 1Anonymous 2y6ycCSNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacovigilance Interview Questions For FRESHERSDocument8 pagesBasic Pharmacovigilance Interview Questions For FRESHERSPrakash MishraNo ratings yet