Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci-117 Waves
Uploaded by
yennaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sci-117 Waves
Uploaded by
yennaCopyright:
Available Formats
SCI-117 WAVES AND OPTICS
MODULE 2
YENNA R. LUMBA BSED SCI-3
LEARNING CHECK
I. WORD BANK
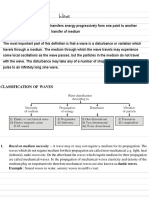
Mechanical wave - refers to waves that needs to travel through a medium in order to transfer energy. Waves that
pass through rope and springs, sound waves, and water waves are all example of this type of waves.
Longitudinal wave -are waves in which the medium particle flows back and forth horizontally in a direction that is
parallel to the propagation line.
Transverse wave - refers to waves in which the medium particle goes up and down while travelling horizontally
and perpendicular to the waves motion direction.
Doppler effect - is a phenomenon in which an observer̀ hears a high pitched sound from an approaching source
than from a stationary source . The observer can also hear a lower pitched sound from a source that is moving
away.
Sound intensity - the quantity of energy per unit of time through a unit are perpendicular to the direction in which
sound travels is referred.
II. QUESTIONS
1. What is the evidence that sound travels as a wave?
Sound has various features that are identical to those of any other waves, which provesthat it travels as a waves.
Sound causes interference, which is a wave phenomena, and it can also be refracted. Most imporantly, sound
travels through a medium like any other wave.
2. Children sometimes play with a homemade `̀telephone´'by attaching a string to the bottoms of two paper
cups. When the string is stretch and a child speaks to one cup, the sound can be heard at the other cup. Explain
clearly how the sound wave travels from one cup to the other.
The string that connects the cups acts as a medium for energy transmission, allowing the wave to flow through. As
the person at one end of the string produces sound through speaking, it produces sound waves. Particle vibration
travels from one end of the strings to the other. This is why the person at the other end of the line can hear what
the other is saying.
3. Is there Doppler shift if the source and observer move in the same direction, with the same velocity? Explain.
There will be no change in frequency if the source and the observer is travelling at the same speed and in the same
time and in the same direction. However, I believe that his is not relevant if the source abd the receiver are
travelling at a rapid rate, as there will be some element that change the frequency of the sound.
III. THINK & SOLVE
You might also like
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Waves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalDocument11 pagesWaves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalMaha Letchumy BalakeristananNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument6 pagesWave NotesVittorio ApidosNo ratings yet
- Vakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodDocument21 pagesVakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodvigiraneza0No ratings yet
- I.I.T Foundation Programme: Class: VIII Sound PhysicsDocument10 pagesI.I.T Foundation Programme: Class: VIII Sound PhysicsSesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY 12 Observing Sound WavesDocument2 pagesLABORATORY 12 Observing Sound WavesKelseyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A WaveDocument28 pagesAnatomy of A WaveAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: WavesDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: WavesKyera LovesNo ratings yet
- RT101-1-Intro To AudioDocument77 pagesRT101-1-Intro To AudiozealxonlineNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument21 pagesWavesTintinententen Christine TintinNo ratings yet
- Ar 1328 Building Utilities O3: Saint Louis CollegeDocument9 pagesAr 1328 Building Utilities O3: Saint Louis CollegeGreen ArcNo ratings yet
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajNo ratings yet
- Waves and SoundDocument17 pagesWaves and SoundMUHAMMAD DANIYAL KANDANo ratings yet
- Physics FPRM Four NotesDocument122 pagesPhysics FPRM Four NotesCharles GhatiNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument41 pagesWavesMimi CiervaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument8 pagesSoundHagen SeahNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document37 pagesScience 2Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument14 pagesWaveLitiaMikoNo ratings yet
- Sound Theory KMAE Ref MaterialDocument24 pagesSound Theory KMAE Ref Materialvishwa NNo ratings yet
- Physics 4 PDFDocument122 pagesPhysics 4 PDFBABU JOHNNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves and MusicDocument24 pagesSound Waves and Musicravikant6No ratings yet
- Doppler Effect For Sound: and Review of WaveDocument25 pagesDoppler Effect For Sound: and Review of WaveSHEENA MAE DALGUNTASNo ratings yet
- Oscillation: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsDocument0 pagesOscillation: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsJia HuiNo ratings yet
- " Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueDocument12 pages" Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueMaria ClarissaNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves - An EssayDocument8 pagesSound Waves - An EssayAshley RoyNo ratings yet
- Physics Module 3Document36 pagesPhysics Module 3Euann MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 3: Acoustics and Lighting SystemsDocument5 pagesBuilding Utilities 3: Acoustics and Lighting SystemsDennis Roel T. DulayNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument27 pagesWavesBrianna MalcolmNo ratings yet
- BuDocument15 pagesBubreycariganNo ratings yet
- Wave 25 November 2021Document41 pagesWave 25 November 2021Ulfa Mahfudli FadliNo ratings yet
- Phy Topic 1 F4Document41 pagesPhy Topic 1 F4Kandrossy GlassNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument6 pagesPhysics NotesLegend RR3No ratings yet
- 4.2 Travelling WavesDocument5 pages4.2 Travelling WavesEesha SajidNo ratings yet
- ch11 2Document90 pagesch11 2tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatNo ratings yet
- Waves, Sound & Music: (In One-Dimension, Mainly)Document30 pagesWaves, Sound & Music: (In One-Dimension, Mainly)Adal GanisNo ratings yet
- Report - Lights, Camera, ActionDocument7 pagesReport - Lights, Camera, Actionrajkrishna03No ratings yet
- SoundDocument25 pagesSoundsubashini silvaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Revision RSG 2015 - WavesDocument5 pagesYear 10 Revision RSG 2015 - Waves이다은No ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument31 pagesSound Wavesvirginiajuma812No ratings yet
- Sound Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSound Worksheet 1drz0m100% (1)
- Sound Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSound Worksheet 1drz0mNo ratings yet
- Sound IXDocument35 pagesSound IXarpankrishna739No ratings yet
- Unit 1. Module 5: Sounds: Longitudinal WaveDocument1 pageUnit 1. Module 5: Sounds: Longitudinal WaveMaristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Investigation 2.0Document12 pagesInvestigation 2.0GnalixNo ratings yet
- Pintuan Joshua MoisesDocument7 pagesPintuan Joshua MoisesKate Winslet Love Galan FazonNo ratings yet
- Waves: Presented By: Ms. Evalyn Suyat-CapindingDocument72 pagesWaves: Presented By: Ms. Evalyn Suyat-CapindingKristina C IbonNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Sound and LightDocument68 pagesWeek 8 - Sound and LightGenel Yutuc100% (1)
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocument24 pages1.6 Sound WavessfwongNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade - WavesDocument21 pages6th Grade - Wavesleojohn2No ratings yet
- Waves - Lecture 1Document45 pagesWaves - Lecture 1Hisham MohamedNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument15 pagesMotionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties AND InteractionsDocument40 pagesWave Properties AND InteractionsRachelleOiguelShakiraNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument21 pagesWavesKavya BNo ratings yet
- Topic 36 Waves - Introduction To Sound WavesDocument8 pagesTopic 36 Waves - Introduction To Sound WavesMarcus GohNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To WaveDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To WaveOyeladun IdrisNo ratings yet
- P22 1 Sound and ResonanceDocument12 pagesP22 1 Sound and ResonanceSantiago GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Wave On String (IITian Notes - Kota)Document106 pagesWave On String (IITian Notes - Kota)hola cholaNo ratings yet
- Activity For 3rd LessonDocument5 pagesActivity For 3rd LessonyennaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesCell Structure-WPS OfficeyennaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnswerDocument2 pagesChapter 7 AnsweryennaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Answer.Document1 pageChapter 8 Answer.yennaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-6 Questions and AnswersDocument13 pagesModule 1-6 Questions and AnswersyennaNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (553)
- The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameFrom EverandThe Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (88)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (147)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Step By Step Mixing: How to Create Great Mixes Using Only 5 Plug-insFrom EverandStep By Step Mixing: How to Create Great Mixes Using Only 5 Plug-insRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)