0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesActivity 1
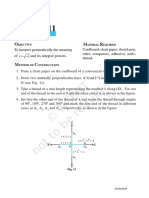
The document describes an activity to verify the distributive law of sets, which states that A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C). Five figures are drawn on a board with circles representing sets A, B, and C within rectangles representing a universal set U. The figures show different set operations like intersections and unions. By observing which areas are shaded in each figure, it demonstrates that the shaded area is the same in the figures representing each side of the distributive law equality, verifying that the law holds true for the given sets A, B, and C.
Uploaded by
Ajay AroraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesActivity 1
The document describes an activity to verify the distributive law of sets, which states that A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C). Five figures are drawn on a board with circles representing sets A, B, and C within rectangles representing a universal set U. The figures show different set operations like intersections and unions. By observing which areas are shaded in each figure, it demonstrates that the shaded area is the same in the figures representing each side of the distributive law equality, verifying that the law holds true for the given sets A, B, and C.
Uploaded by
Ajay AroraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd