Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cryptography Primitives
Cryptography Primitives
Uploaded by
MohanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cryptography Primitives
Cryptography Primitives
Uploaded by
MohanCopyright:
Available Formats
4/15/2019 Modern Cryptography
Authentication
Authentication provides the identification of the originator. It confirms to the receiver that the data received
has been sent only by an identified and verified sender.
Authentication service has two variants −
Message authentication identifies the originator of the message without any regard router or system
that has sent the message.
Entity authentication is assurance that data has been received from a specific entity, say a particular
website.
Apart from the originator, authentication may also provide assurance about other parameters related to data
such as the date and time of creation/transmission.
Non-repudiation
It is a security service that ensures that an entity cannot refuse the ownership of a previous commitment or an
action. It is an assurance that the original creator of the data cannot deny the creation or transmission of the
said data to a recipient or third party.
Non-repudiation is a property that is most desirable in situations where there are chances of a dispute over the
exchange of data. For example, once an order is placed electronically, a purchaser cannot deny the purchase
order, if non-repudiation service was enabled in this transaction.
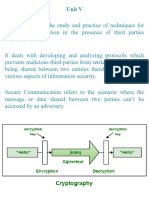
Cryptography Primitives
Cryptography primitives are nothing but the tools and techniques in Cryptography that can be selectively used
to provide a set of desired security services −
Encryption
Hash functions
Message Authentication codes M AC
Digital Signatures
The following table shows the primitives that can achieve a particular security service on their own.
Note − Cryptographic primitives are intricately related and they are often combined to achieve a set of desired
security services from a cryptosystem.
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cgi-bin/printpage.cgi 3/3
You might also like
- Project Report (Digital Signatures)Document33 pagesProject Report (Digital Signatures)Uzair Shakeel0% (1)
- John E. Hopcroft Rajeev Motwani Jeffrey D. Ullman Introduction To Automata Theory Languages and Computations Prentice Hall 2007Document7 pagesJohn E. Hopcroft Rajeev Motwani Jeffrey D. Ullman Introduction To Automata Theory Languages and Computations Prentice Hall 2007ashiful islamNo ratings yet
- 453 NS Tutorial 1Document5 pages453 NS Tutorial 1SHAMIMUL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument99 pagesUnit VYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- Network Security Paper2015 OriginalDocument6 pagesNetwork Security Paper2015 OriginalPriyanka BedekarNo ratings yet
- E&clDocument10 pagesE&clSBANo ratings yet
- Cs707 Current Past Viva Solved Questions1Document4 pagesCs707 Current Past Viva Solved Questions1Zahid Gulzar100% (1)
- Unit 1Document37 pagesUnit 1SutikshanNo ratings yet
- FirewallDocument16 pagesFirewallApoorva MahajanNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment (I, Ii, Iii, & Iv) of Cyber SecurityDocument15 pagesIndividual Assignment (I, Ii, Iii, & Iv) of Cyber SecurityjavedNo ratings yet
- Cryptographic Algo: Need For Data EncryptionDocument2 pagesCryptographic Algo: Need For Data EncryptionMunizza MehreenNo ratings yet
- Security Issues Unit 2Document10 pagesSecurity Issues Unit 2Richa GargNo ratings yet
- Authentication and Authorization in CryptographyDocument10 pagesAuthentication and Authorization in CryptographyVanshika KumarastogiNo ratings yet
- Message Authentication Code and Digital Signatures - Technical ReportDocument33 pagesMessage Authentication Code and Digital Signatures - Technical ReportRam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Introduction of E-CommerceDocument286 pagesModule-1: Introduction of E-Commercenidhi goelNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Introduction of E-CommerceDocument82 pagesModule-1: Introduction of E-Commercenidhi goelNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce Notes For BcomDocument115 pagesEcommerce Notes For BcomDrKrishna Priya ChakireddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Network Security and Public Key Infrastructure: Saujanya Raj Shrestha 017BSCIT041Document31 pagesUnit 6: Network Security and Public Key Infrastructure: Saujanya Raj Shrestha 017BSCIT041Saujanya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Non RepudiationDocument10 pagesNon RepudiationHarshithNo ratings yet
- VVFGC Cns Unit2 (Final)Document13 pagesVVFGC Cns Unit2 (Final)ArthiNo ratings yet
- 21 23 AnswerDocument16 pages21 23 Answers2187022No ratings yet
- Samara UniversityDocument7 pagesSamara Universityfentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- INS - Assignment 3 (TCS2223033)Document5 pagesINS - Assignment 3 (TCS2223033)Kavinesh 123No ratings yet
- Information Security Assignement: Public Key InfrastructureDocument5 pagesInformation Security Assignement: Public Key InfrastructureJoel J JoyNo ratings yet
- 1602505091unit 3 Cyber Security Tools & TechniquesDocument27 pages1602505091unit 3 Cyber Security Tools & TechniquesMuhammad MalikNo ratings yet
- PROTECT - Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (October 2021)Document8 pagesPROTECT - Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (October 2021)asdd111asNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Lesson1to9 IAaS1Document62 pagesTopic1 Lesson1to9 IAaS1Kervi Sanares BacuelNo ratings yet
- Communication System Security: - Lidong Chen, Guang GongDocument27 pagesCommunication System Security: - Lidong Chen, Guang Gongswathi bnNo ratings yet
- Digital Signatures and Authentication ProtocolsDocument19 pagesDigital Signatures and Authentication ProtocolsMerryl Lorraine GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Security Attack: Any Action That Compromises The Security of Information Owned by AnDocument9 pagesSecurity Attack: Any Action That Compromises The Security of Information Owned by AnAnjiNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing 7700: Fall 2005 Lecture 16: Grid SecurityDocument32 pagesGrid Computing 7700: Fall 2005 Lecture 16: Grid SecurityJaswanth RoyalNo ratings yet
- Ques On 2: Common Types of User Authentication IncludeDocument16 pagesQues On 2: Common Types of User Authentication Includeshruti.exe03No ratings yet
- X 800 Security ServicesDocument6 pagesX 800 Security ServicesSourav DebnathNo ratings yet
- Web Service SecureDocument67 pagesWeb Service SecureMessaraNo ratings yet
- Nis 1Document13 pagesNis 1badg15594No ratings yet
- Ass5 ICCDocument4 pagesAss5 ICCAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Network Security Unit 2Document45 pagesNetwork Security Unit 2Satyam PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2020BCS 076 IT CryptographyDocument27 pages2020BCS 076 IT CryptographyPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- CNS U1Document16 pagesCNS U1Pooja ReddyNo ratings yet
- 22 Itt Project On Digital SignaturesDocument27 pages22 Itt Project On Digital SignaturesAvinash Dutta100% (1)
- Computer SecurityDocument39 pagesComputer SecurityMuhaamadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document27 pagesUnit 119wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Data Security &integrityDocument18 pagesChapter 3 - Data Security &integrityGetnete degemuNo ratings yet
- Manav Rachna International Institute of Research and StudiesDocument12 pagesManav Rachna International Institute of Research and StudiesRajiv ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cyber Law Notes - 2022Document34 pagesUnit 2 Cyber Law Notes - 2022Akash RajaNo ratings yet
- CNS - Unit 1Document25 pagesCNS - Unit 1alameenNo ratings yet
- 9-Site Security, Access Control-25-Feb-2021material I 25-Feb-2021 Access ControlDocument12 pages9-Site Security, Access Control-25-Feb-2021material I 25-Feb-2021 Access ControlSharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Authenticity & Integrity of CertificateDocument9 pagesAuthenticity & Integrity of CertificatesurajNo ratings yet
- Bbit 443Document3 pagesBbit 443Kiki KymsNo ratings yet
- Network Security (Sami)Document11 pagesNetwork Security (Sami)black smithNo ratings yet
- Is CH6Document9 pagesIs CH6Dhruv SojitraNo ratings yet
- Study-Materials CSE 6th Cryptography-Network-Security S.-DalaiDocument63 pagesStudy-Materials CSE 6th Cryptography-Network-Security S.-DalaiKedar nath NayakNo ratings yet
- HCI711s Week 3Document21 pagesHCI711s Week 3gabrieljohannes233No ratings yet
- CSCL 1 MarksDocument4 pagesCSCL 1 MarksSurendra DawadiNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Data Security: A Review of Cryptography and Steganography TechniquesDocument9 pagesHybrid Data Security: A Review of Cryptography and Steganography TechniquesMichaelNo ratings yet
- Security Attacks, Services and MechanismsDocument3 pagesSecurity Attacks, Services and Mechanismsrel786No ratings yet
- CSS Unit-1Document18 pagesCSS Unit-1Aryan DixitNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce SecurityDocument60 pagesEcommerce SecurityHarshithNo ratings yet
- MyfileDocument10 pagesMyfileHaroon KhanNo ratings yet
- AZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500From EverandAZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500No ratings yet