Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Detail Pengertian CPU
Detail Pengertian CPU
Uploaded by
IT Rsud BatangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Detail Pengertian CPU
Detail Pengertian CPU
Uploaded by
IT Rsud BatangCopyright:
Available Formats
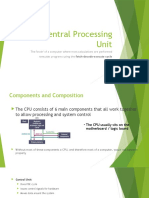
A CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the primary component of a computer that
performs most of the processing and control functions. It is also known as the "brain"
of the computer, as it is responsible for executing instructions and performing
calculations.
The CPU is typically a small, square-shaped chip that is located on the motherboard
of the computer. It consists of one or more processing cores, each of which can
execute a set of instructions simultaneously. The speed and performance of the CPU
are determined by several factors, including the number of cores, clock speed, cache
size, and architecture.
The clock speed of the CPU is measured in GHz (gigahertz) and represents the
number of clock cycles the CPU can perform in one second. The higher the clock
speed, the more instructions the CPU can execute in a given amount of time. The
cache size is the amount of memory that the CPU uses to store frequently accessed
data, which helps improve performance by reducing the time it takes to access this
data.
The architecture of the CPU refers to the way in which it is designed and organized.
Different CPU architectures are optimized for different types of applications, such as
gaming, video editing, or data processing. Some of the most common CPU
architectures include x86, ARM, and PowerPC.
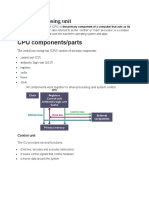
In addition to executing instructions, the CPU also communicates with other
components of the computer, such as memory, storage devices, and input/output
devices. It uses a variety of bus interfaces and protocols to exchange data with these
components, enabling the computer to perform a wide range of tasks.
Overall, the CPU is a critical component of a computer, responsible for executing
instructions and performing calculations that enable the computer to function. The
speed and performance of the CPU can have a significant impact on the overall
performance and usability of the computer.
You might also like
- CC101 Chapter 4Document54 pagesCC101 Chapter 4Randy FinNo ratings yet
- Coa - Lecture 3 - BNCDocument5 pagesCoa - Lecture 3 - BNCShizz denariNo ratings yet
- Architecture CPU, GPU & ClustersDocument11 pagesArchitecture CPU, GPU & ClusterswindtreaterNo ratings yet
- Document Xyz5Document1 pageDocument Xyz5AceNo ratings yet
- ProcessorDocument12 pagesProcessorvinayikartNo ratings yet
- CPU - Central Processing UnitDocument10 pagesCPU - Central Processing UnitJay Ambadkar100% (5)
- Lecture 3Document21 pagesLecture 3Priyam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- The Different Parts of A CPU and Their FunctionsDocument33 pagesThe Different Parts of A CPU and Their Functionsigiz starkleNo ratings yet
- Hardware Function - CpuDocument42 pagesHardware Function - CpumyzalNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument3 pagesComputer ArchitectureRao BehramNo ratings yet
- Basic Hardware Familirization - Introduction To Computer HardwareDocument10 pagesBasic Hardware Familirization - Introduction To Computer Hardwaredghelp1234No ratings yet
- Components of Computer: Hardware Software HardwareDocument9 pagesComponents of Computer: Hardware Software Hardwarerashidqureshi6944No ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Computer System HardwareDocument17 pagesUNIT 2 - Computer System HardwareComputer75% (4)
- Compiled byDocument33 pagesCompiled byprashantnikuNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Paper - 6Document12 pagesInformation Technology Paper - 6Aamin singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Processor FundamentalsDocument16 pagesChapter-5 Processor FundamentalsVimal VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Part 2 - Central Processing UnitDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Part 2 - Central Processing UnitmeshNo ratings yet
- The Central Processing Unit (CPU) .: Transfer of Data Among DevicesDocument4 pagesThe Central Processing Unit (CPU) .: Transfer of Data Among DevicesSarmad Salih Jawad AlkodaryNo ratings yet
- L-9 Processor and MemoryDocument27 pagesL-9 Processor and MemoryDiganta MondalNo ratings yet
- CPU Fetch-Execute CycleDocument5 pagesCPU Fetch-Execute CycleDivaNo ratings yet
- Os by Harsh YadavDocument9 pagesOs by Harsh YadavHarsh YadavNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Computer Hardware (Faridi S.) (Z-Library)Document136 pagesBeginners Guide To Computer Hardware (Faridi S.) (Z-Library)Dikerson CarlosNo ratings yet
- CpuDocument1 pageCpuMiggy VelasquezNo ratings yet
- COA Complete NotesDocument60 pagesCOA Complete Notesbittukamble0No ratings yet
- Cpu Final NotesDocument6 pagesCpu Final NotesSonu zehen001No ratings yet
- A CpuDocument3 pagesA CpuEllen VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 7Document1 page7Sahoo DipaliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information & Communication Technology: CPU Central Processing UnitDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Information & Communication Technology: CPU Central Processing UnitalikdsaNo ratings yet
- RamadhanAbdulBarryDocument8 pagesRamadhanAbdulBarryNckyNo ratings yet
- TO Computers: Neo BaDocument186 pagesTO Computers: Neo BaNaïGa UmutesiNo ratings yet
- Processing System: Processing System, Which Includes The Primary Memory, The Central Processing Unit (CPU), ExpansionDocument10 pagesProcessing System: Processing System, Which Includes The Primary Memory, The Central Processing Unit (CPU), ExpansionAregawi GebreyesusNo ratings yet
- System UnitDocument19 pagesSystem Unitapi-304500968No ratings yet
- System Unit LessonDocument10 pagesSystem Unit LessonUnknown TototNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 PDFDocument3 pagesLesson 3 PDFcharimaine hernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - CPUDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - CPUapi-3750451No ratings yet
- The CPU May Also Be Called The Microprocessor or The Computer ProcessorDocument6 pagesThe CPU May Also Be Called The Microprocessor or The Computer ProcessorWan Nur FathihahNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument64 pagesComputer HardwareAbishek NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Cpu WorkingDocument2 pagesCpu WorkingNouman RiazNo ratings yet
- Makalah CPU Dan StorageDocument9 pagesMakalah CPU Dan StorageAdi SuripiyantoNo ratings yet
- Hardware (CH#3)Document6 pagesHardware (CH#3)itslilyjulesssNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument5 pagesComputer Architectureapi-417400228No ratings yet
- HANDOUTSDocument2 pagesHANDOUTSMichael Ramin Vargas AlidoNo ratings yet
- Cpu and Its Working MechanismDocument9 pagesCpu and Its Working MechanismBais JumaniNo ratings yet
- Components of HardwareDocument9 pagesComponents of HardwareNUTS GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Processing: CPU and Memory. Without These A Computer Could Not FunctionDocument9 pagesProcessing: CPU and Memory. Without These A Computer Could Not FunctionThirdy CatalanNo ratings yet
- EXPOSICION What Is Inside A PC SystemDocument7 pagesEXPOSICION What Is Inside A PC SystemxavierNo ratings yet
- What Components Can We Find in A Computer System?Document2 pagesWhat Components Can We Find in A Computer System?Rocio A RubecindoNo ratings yet
- 9Document1 page9Sahoo DipaliNo ratings yet
- 2 LectureDocument10 pages2 LecturealexpiusNo ratings yet
- Types of Processors and RAM'sDocument26 pagesTypes of Processors and RAM'sSneha NairNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument5 pagesCentral Processing Unitchintu yadavNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document11 pagesAssignment 7ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- Adrian Tyler - Senior Thesis Rough DraftDocument17 pagesAdrian Tyler - Senior Thesis Rough Draftapi-748077790No ratings yet
- Hardware Specifications in Computer SystemsDocument5 pagesHardware Specifications in Computer SystemsKeron CatonNo ratings yet
- Instruction Set ArchitectureDocument7 pagesInstruction Set ArchitectureKuzo TribeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Revision CSDocument4 pages1.1 Revision CSsophiederryNo ratings yet
- What Is Inside A PC SystemDocument1 pageWhat Is Inside A PC SystemáNo ratings yet
- IT Unit 3Document33 pagesIT Unit 3shahisaman23No ratings yet
- What Is A Central Processing UnitDocument1 pageWhat Is A Central Processing UnitSuzana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Make A PaperDocument2 pagesMake A PaperIT Rsud BatangNo ratings yet
- It AuditDocument1 pageIt AuditIT Rsud BatangNo ratings yet
- TensorFlow Is An OpenDocument1 pageTensorFlow Is An OpenIT Rsud BatangNo ratings yet
- Deep LearningDocument1 pageDeep LearningIT Rsud BatangNo ratings yet