Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Is 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 14
Is 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 14
Uploaded by
Svapnesh ParikhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Is 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 14
Is 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 14
Uploaded by
Svapnesh ParikhCopyright:
Available Formats
IS 1828 (Part 1) :2005
1s07500-1:1999
Annex C
(informative)
Alternative method of testing machine classification
This alternative method of classifying testing machines is based on the global error concept which requires all
values (not only the average) to be within certain limits.
The accuracy error of the testing machine is determined as a percentage of the force applied or indicated by the
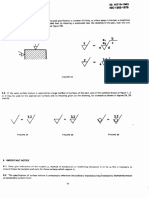
testing machine. Using the symbols given in Table 1, the relative error is calculated as follows
6–F
q.— Xloo (Cl)
F
The repeatability error is determined based on the definition for repeatability in OIML vocabulary [~, where only one
variable has to be changed and this variable is another application of approximately the same force. In this case,
the repeatability calculation which determines the accuracy of the testing machine is from one application of force to
another of same approximate value. It is recommended that two applications of approximately the same force value
are needed to calculate the repeatability and that the repeatability is calculated from the algebraic difference
between accuracy errors:
b=/ql-q2/ (C.2)
where q, and q2 are the relative errors for each force application.
Since the second application of the force does not have to be identical to the first, the variables associated with
operator skills or parameters of the machine control do not influence the repeatability of the accuracy of the force
measurement.
The classification of the testing machine given in Table 2 does not change, only the method of calculating the
accuracy and repeatability changes. The use of this method makes it easier to automate the calibration process.
NOTE If this alternative method is used, reference to its use should be noted on the report.
12
You might also like
- ASTM E1049-1985 Standard Practices For Cycle Counting in Fatigue AnalysisDocument10 pagesASTM E1049-1985 Standard Practices For Cycle Counting in Fatigue AnalysisSVV_companyNo ratings yet
- Power Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesFrom EverandPower Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- EURAMET EA-10-04 U in Force MeasurementsDocument16 pagesEURAMET EA-10-04 U in Force MeasurementsdanicanaNo ratings yet
- t22 PDFDocument18 pagest22 PDFRaunak TimilsinaNo ratings yet
- Astm E467Document6 pagesAstm E467shreedharkolekarNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Testing of Medium Induction Motors-A Comment On IEEE STD 112-1991Document5 pagesEfficiency Testing of Medium Induction Motors-A Comment On IEEE STD 112-1991Aviv AlRasyidNo ratings yet
- The Determination of Uncertainties in Charpy Impact TestingDocument19 pagesThe Determination of Uncertainties in Charpy Impact TestingAfriandiBayuNo ratings yet
- Contingency IndexDocument7 pagesContingency IndexRico YudhiantoNo ratings yet
- ASTM E4 16 Standard Practices For Force Verification of Testing MachinesDocument14 pagesASTM E4 16 Standard Practices For Force Verification of Testing Machinesoki handinataNo ratings yet
- Astm E4Document10 pagesAstm E4Kanikannan.SNo ratings yet
- Astm - E4-07Document10 pagesAstm - E4-07tdzeienNo ratings yet
- E4 Standard Practices For Force Verification of Testing MachineDocument10 pagesE4 Standard Practices For Force Verification of Testing MachineJuan Castañeda100% (1)
- Is 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 5Document1 pageIs 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 5SvapneshNo ratings yet
- BS 7882 - 2008 PaperDocument25 pagesBS 7882 - 2008 PaperMohamed Naser0% (1)
- Is 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 7Document1 pageIs 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 7Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Astm E4-16Document11 pagesAstm E4-16Adam Chin100% (3)
- Force Verification of Testing Machines: Standard Practices ForDocument9 pagesForce Verification of Testing Machines: Standard Practices ForAngel Alvarez CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Ethods For Contingency Screening and Ranking For Voltage Stability Analysis of Power - SystemsDocument7 pagesEthods For Contingency Screening and Ranking For Voltage Stability Analysis of Power - SystemsRameshPatelNo ratings yet
- KASTO 206 (인장 및 압축 시험기) PDFDocument28 pagesKASTO 206 (인장 및 압축 시험기) PDFTJNo ratings yet
- ASTM E74-and-Uncertainty-Calculation-ExampleDocument48 pagesASTM E74-and-Uncertainty-Calculation-ExampleLuân Nguyễn QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- 20160224-Full Paper-E515 MTaufiq - GunawanDocument4 pages20160224-Full Paper-E515 MTaufiq - GunawanMuhammad TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Sequence Components-Based Fault Location Technique For Distribution Systems Considering Time Varying LoadsDocument6 pagesSequence Components-Based Fault Location Technique For Distribution Systems Considering Time Varying LoadsSherif M. DabourNo ratings yet
- Force Verification of Testing Machines: Standard Practices ForDocument10 pagesForce Verification of Testing Machines: Standard Practices Forruben carcamoNo ratings yet
- M.K.MittalDocument8 pagesM.K.MittalK Vijay Bhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Iso 67892003Document5 pagesIso 67892003Sebar48No ratings yet
- Is 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 8Document1 pageIs 1828-1 (Iso 7500-1) - 8Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Comparacion IEC IEEEDocument7 pagesComparacion IEC IEEEGiampaolo CiardielloNo ratings yet
- Experimental Evaluation of The Tolerance For Control-Flow Test CriteriaDocument21 pagesExperimental Evaluation of The Tolerance For Control-Flow Test CriteriaBama Raja SegaranNo ratings yet
- Force Verification of Testing Machines: Standard Practices ForDocument10 pagesForce Verification of Testing Machines: Standard Practices ForRajan SteeveNo ratings yet
- EURAMET CG 18 02 Non Automatic Weighing InstrumentsDocument83 pagesEURAMET CG 18 02 Non Automatic Weighing InstrumentsPurwanto NugrohoNo ratings yet
- EDQM Qualification of BalancesDocument19 pagesEDQM Qualification of BalancesVania CanaparNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Pooled SampleDocument4 pagesDissolution Pooled SampleKeyuri ParikhNo ratings yet
- Surface Vehicle Standard: Fuel Economy Measurement Road Test ProcedureDocument22 pagesSurface Vehicle Standard: Fuel Economy Measurement Road Test ProcedureLuis MunozNo ratings yet
- CookBook 15 Assessment Trueness Measurement Procedure by Use of RM - 10-2018 PDFDocument3 pagesCookBook 15 Assessment Trueness Measurement Procedure by Use of RM - 10-2018 PDFJacek SobczykNo ratings yet
- EURAMET CG 17.01 Electromechanical ManometersDocument36 pagesEURAMET CG 17.01 Electromechanical Manometersyohagg100% (1)
- A21. Precision and Bias (Mandatory)Document3 pagesA21. Precision and Bias (Mandatory)Rithesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- Overview of Methods For Voltage Sag Performance EstimationDocument5 pagesOverview of Methods For Voltage Sag Performance EstimationJay F. KuizonNo ratings yet
- USP-NF 41 BalancesDocument3 pagesUSP-NF 41 BalancesMahmoud Abdelhakem mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Unceruianly Pressure GaugeDocument5 pagesUnceruianly Pressure GaugeMd HossainNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Induction Motor Field Efficiency Evaluation MethodDocument10 pagesComparison of Induction Motor Field Efficiency Evaluation MethodDr.P.Venkatesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Identification of Variable Frequency Induction Motor Models From Operating DataDocument8 pagesIdentification of Variable Frequency Induction Motor Models From Operating Datani60No ratings yet
- Sensitive Load Voltage Compensation Performed by A Suitable Control MethodDocument6 pagesSensitive Load Voltage Compensation Performed by A Suitable Control MethodSanjivee SachinNo ratings yet
- WCE2008 pp1542-1547.pdsdffDocument6 pagesWCE2008 pp1542-1547.pdsdffPeter LoNo ratings yet
- EUROLAB Cook Book - Doc No 8 Determination of Conformance - Rev. 2017Document3 pagesEUROLAB Cook Book - Doc No 8 Determination of Conformance - Rev. 2017Pataki SandorNo ratings yet
- Journal of Electrical EngineeringDocument16 pagesJournal of Electrical EngineeringkodandaramNo ratings yet
- Re Produc IbilityDocument4 pagesRe Produc IbilityEulises De Lazaro ToribioNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Improved Gage RR Measurement StudiesDocument3 pagesPart 1 Improved Gage RR Measurement Studiesnelson.rodriguezm6142No ratings yet
- Self-Adaptive Control SystemsDocument130 pagesSelf-Adaptive Control SystemsSd NvNo ratings yet
- ISO6892Document5 pagesISO6892jeridNo ratings yet
- Single Sampling Plans For Variables Indexed by Aql and Aoql Under Ewma ModelDocument10 pagesSingle Sampling Plans For Variables Indexed by Aql and Aoql Under Ewma ModelPratya PalaphanNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Different Methods of Correcting Combined Cycle Thermal PerformanceDocument18 pagesA Comparative Study of Different Methods of Correcting Combined Cycle Thermal PerformanceJung Kyung WooNo ratings yet
- Barras PilotoDocument5 pagesBarras Pilotofernando tipanNo ratings yet
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Experimentation, Validation, and Uncertainty Analysis for EngineersFrom EverandExperimentation, Validation, and Uncertainty Analysis for EngineersNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsFrom EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Statistical Inference: A Computational ApproachFrom EverandFundamental Statistical Inference: A Computational ApproachNo ratings yet
- Classical Approach to Constrained and Unconstrained Molecular DynamicsFrom EverandClassical Approach to Constrained and Unconstrained Molecular DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-5 - 1991 - 1Document1 pageIs 12308-5 - 1991 - 1Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-5 - 1991 - 3Document1 pageIs 12308-5 - 1991 - 3Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-8 - 1997 - 5Document1 pageIs 12308-8 - 1997 - 5Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-9 - 1993 - 1Document1 pageIs 12308-9 - 1993 - 1Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-8 - 1997 - 3Document1 pageIs 12308-8 - 1997 - 3Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-7 - 1991 - 3Document1 pageIs 12308-7 - 1991 - 3Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-7 - 1991 - 5Document1 pageIs 12308-7 - 1991 - 5Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-6 - 1991 - 4Document1 pageIs 12308-6 - 1991 - 4Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-3 - 1987 - 1Document1 pageIs 12308-3 - 1987 - 1Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-5 - 1991 - 5Document1 pageIs 12308-5 - 1991 - 5Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-6 - 1991 - 5Document1 pageIs 12308-6 - 1991 - 5Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 8Document1 pageIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 8Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 14Document1 pageIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 14Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 11166 - 1993 - 10Document1 pageIs 11166 - 1993 - 10Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 1Document1 pageIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 1Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 11Document1 pageIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 11Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 12308-4 - 1988 - 4Document1 pageIs 12308-4 - 1988 - 4Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 12Document1 pageIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 12Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-3 - 1977 - 1Document1 pageIs 8422-3 - 1977 - 1Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 4Document1 pageIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 4Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-2 - 1977 - 6Document1 pageIs 8422-2 - 1977 - 6Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 5Document1 pageIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 5Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-8 - 1977 - 5Document1 pageIs 8422-8 - 1977 - 5Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-8 - 1977 - 2Document1 pageIs 8422-8 - 1977 - 2Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-3 - 1977 - 3Document1 pageIs 8422-3 - 1977 - 3Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-6 - 1977 - 4Document1 pageIs 8422-6 - 1977 - 4Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-3 - 1977 - 2Document1 pageIs 8422-3 - 1977 - 2Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-1 - 1977 - 5Document1 pageIs 8422-1 - 1977 - 5Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-2 - 1977 - 3Document1 pageIs 8422-2 - 1977 - 3Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet
- Is 8422-1 - 1977 - 2Document1 pageIs 8422-1 - 1977 - 2Svapnesh ParikhNo ratings yet