Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cyber Security and Cyber Law Syllabus
Uploaded by
Yash Xtra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Cyber security and cyber law syllabus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views4 pagesCyber Security and Cyber Law Syllabus
Uploaded by
Yash XtraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
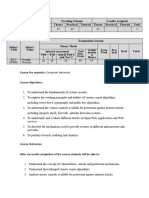
CS472: CYBER SECURITY AND CYBER LAW
Credit and Hours:
Teaching Scheme Theory Practical Total Credit
Hours/week 4 2 6
5
Marks 100 50 150
A. Objective of the Course:
The main objective to give the course is
• To be able to identify vulnerabilities in system, software or web application
• To be able to identify security risks and take preventive steps
• To be able investigate cybercrime and collect evidences by understanding cyber
laws.
• Able to use knowledge of forensic tools and software
B. Outline of the Course:
Sr Minimum number
Title of the unit
No. of Hours
1 Introduction to Cyber Security 06
2 Cyber Security Vulnerabilities and Cyber Security 13
Safeguards
3 Securing Web Application, Services and Servers 10
4 Intrusion Detection and Prevention 14
5 Cryptography and Network Security 07
6 Introduction to Cyberspace and the Law 04
7 Cyber Forensic 06
Total Hours (Theory): 60
Total Hours (Lab): 30
Total Hours: 90
C. Detailed Syllabus:
1 Introduction to Cyber Security 06 hours 10%
1.1 Overview of Cyber Security
1.2 Internet Governance – Challenges and Constraints
1.3 Cyber Threats:- Cyber Warfare-Cyber Crime-Cyber terrorism-Cyber Espionage
1.4 Need for a Comprehensive Cyber Security Policy, Need for a Nodal Authority,
Need for an International convention on Cyberspace.
2 Cyber Security Vulnerabilities and Cyber Security Safeguards 13 hours 22%
2.1 Cyber Security Vulnerabilities-Overview
2.2 Vulnerabilities in software, System administration,Complex Network
Architectures, Open Access to Organizational Data,Weak Authentication,
Unprotected Broadband communications, Poor Cyber Security Awareness.
2.3 Cyber Security Safeguards- Overview
2.4 Access control, Audit, Authentication, Biometrics,Cryptography,
Deception, Denial of Service Filters
2.5 Ethical Hacking, Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems, Response, Scanning,
Security policy, Threat Management.
3 Securing Web Application, Services and Servers 10 hours 15%
3.1 Introduction, Basic security for HTTP Applications and Services, Basic Security
for SOAP Services
3.2 Identity Management and Web Services, Authorization Patterns
3.3 OWASP Top 10 ,Security Considerations, Challenges
4 Intrusion Detection and Prevention 14 hours 25%
4.1 Introduction of Intrusion Detection and Prevention,Physical Theft, Abuse of
Privileges, Unauthorized Access by Outsider, Malware infection
4.2 Intrusion detection and Prevention Techniques, Anti-Malware
software
4.3 Network based Intrusion detection Systems, Network based
Intrusion Prevention Systems
4.4 Host based Intrusion prevention Systems, Security Information
Management
4.5 Network Session Analysis, System Integrity Validation
5 Cryptography and Network Security 07 hours 12%
5.1 Introduction to Cryptography
5.2 Symmetric key Cryptography, Asymmetric key Cryptography,
5.3 Message Authentication, Digital Signatures,Applications of
Cryptography.
5.4 Overview of Firewalls- Types of Firewalls, User Management
5.5 VPN Security Protocols: - security at the Application Layer- PGP and S/MIME
5.6 Security at Transport Layer- SSL and TLS, Security at Network Layer-IPSec
6 Introduction to Cyberspace and the Law 04 hours 06%
6.1 Introduction, Cyber Security Regulations
6.2 Roles of International Law, the state and Private Sector in
Cyberspace, Cyber Security Standards
6.3 The INDIAN Cyberspace, National Cyber Security Policy 2013.
7 Cyber Forensics 06 hours 10%
7.1 Introduction to Cyber Forensics, Handling Preliminary Investigations,
Controlling an Investigation
7.2 Conducting disk-based analysis, Investigating Information-hiding
7.3 Scrutinizing E-mail, Validating E-mail header information, Tracing
Internet access, Tracing memory in real-time.
D. Instructional Methods and Pedagogy:
● At the start, of course, the course delivery pattern, prerequisite of the subject will be
discussed.
● Faculty would use coached problem-solving method as it is the class format in which
faculty provide a structured, guided context for students working collaboratively to solve
problems.
● Assignments based on topic content will be given to the students at the end of each
unit/topic.
● Surprise tests/Quizzes will be conducted.
● The course includes a laboratory, where students have an opportunity to build an
appreciation for the concepts being taught in lectures.
E. Student Learning Outcomes / Objectives:
Upon completion of this course, students will be able to do the following:
• After learning the course, students should able to learn about cyber-attack, type of
cybercrimes
• Learn cyber security vulnerabilities and security safeguard.
• Learn hand-on on how to prevent the web using different web application tools.
• Learn about how to protect the network using different network tools and Intrusion
detection and prevention techniques,
• Learn basic of Cryptography and network security
• Understand about cyber laws
• Learn about cyber Forensics and investigation of information hiding.
• Learn about how to protect them self and ultimately society from cyber-attacks.
F. Recommended Study Material:
❖ Text Books:
1. Cybersecurity: The Beginner’s Guide Dr.ErdalOzkaya
❖ Reference Books:
1. Digital Privacy and Security Using Windows: A Practical Guide ByNihad Hassan,
Rami Hijazi, Apress
2. Cyber Security Understanding Cyber Crimes, Computer Forensics and Legal
Perspectives by Nina Godbole and SunitBelpure, Publication Wiley
You might also like
- Toronto University Cyber PTDocument14 pagesToronto University Cyber PTSahil VarmaNo ratings yet
- MTA 98-367 Security Fundamentals Core ConceptsDocument6 pagesMTA 98-367 Security Fundamentals Core Conceptsنكت مضحكةNo ratings yet
- Sales Funnel FINAL PDFDocument128 pagesSales Funnel FINAL PDFCamelia100% (7)
- Introduction To Cyber SecurityDocument106 pagesIntroduction To Cyber Securitysaju100% (1)
- IT502 - Information SecurityDocument3 pagesIT502 - Information SecurityNader AzalNo ratings yet
- CSE4003 Cyber-Security ETH 1 AC41Document8 pagesCSE4003 Cyber-Security ETH 1 AC41govindNo ratings yet
- CT702-N Cyber SecurityDocument4 pagesCT702-N Cyber SecurityDevanshNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument3 pagesCyber Securitysweta.jethava24460No ratings yet
- Cit 110 PDFDocument150 pagesCit 110 PDFweng.pam2005No ratings yet
- IT 513 Course OutlineDocument4 pagesIT 513 Course OutlineWaleed HussainNo ratings yet
- System SecurityDocument4 pagesSystem SecurityTanishka MayekarNo ratings yet
- Ce348: Information Security: Teaching Scheme Theory Practical Tutorial Total CreditDocument5 pagesCe348: Information Security: Teaching Scheme Theory Practical Tutorial Total CreditAaliya SharmaNo ratings yet
- CybersecurityDocument3 pagesCybersecurityjnwahangidjolNo ratings yet
- W.E.F Academic Year 2012-13 G' SchemeDocument5 pagesW.E.F Academic Year 2012-13 G' SchemeSanket bhosaleNo ratings yet
- Network CsDocument5 pagesNetwork Csnotsubhash2000No ratings yet
- Information Security Analysis and Audit CourseDocument3 pagesInformation Security Analysis and Audit CourseSukriti Jaitly100% (1)
- IIT Jammu Times Offers Post Graduate Diploma in Cyber Security - BrochureDocument22 pagesIIT Jammu Times Offers Post Graduate Diploma in Cyber Security - BrochureKhushal OzaNo ratings yet
- Network and System Security Course OverviewDocument3 pagesNetwork and System Security Course OverviewVibhuNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument3 pagesCyber SecuritySAMAY N. JAINNo ratings yet
- 17CS61Document2 pages17CS61Ravikumar KhilariNo ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument224 pagesInformation SecurityflypixxNo ratings yet
- 2ceit6pe7 Ethical HackingDocument2 pages2ceit6pe7 Ethical Hackingfarhanmansuri0606No ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCourse OutlinemubareklibenNo ratings yet
- CNCS2004-Cybersecurity SyllabusDocument3 pagesCNCS2004-Cybersecurity SyllabusZoyaNo ratings yet
- Network Security Course OverviewDocument42 pagesNetwork Security Course OverviewFiras ZawaidehNo ratings yet
- Current - Syllabus - 0112301 - Cyber Security Law and PolicyDocument5 pagesCurrent - Syllabus - 0112301 - Cyber Security Law and PolicyMaryamNo ratings yet
- Course Outline SCS4110 (1)Document3 pagesCourse Outline SCS4110 (1)n02019697mNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUSDocument3 pagesSYLLABUSLaugh For FunNo ratings yet
- CEHv11 Outline CondensedDocument4 pagesCEHv11 Outline Condenseduzochukwue953No ratings yet
- Information and Network SecurityDocument4 pagesInformation and Network SecurityMananNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For cs6324.001 05f Taught by Hsingmean Sha (Edsha)Document3 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For cs6324.001 05f Taught by Hsingmean Sha (Edsha)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Certificate Programme On: Cybersecurity and Data PrivacyDocument4 pagesCertificate Programme On: Cybersecurity and Data PrivacyKritika KakkarNo ratings yet
- Sem720 17 18Document2 pagesSem720 17 18Reshma BasuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Overview & Course ProjectsDocument74 pagesLecture 1-Overview & Course ProjectsHasham AkramNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Basic Literacy - 0Document1 pageCyber Security Basic Literacy - 0Imshan TalibNo ratings yet
- Certificate in Cyber SecurityDocument3 pagesCertificate in Cyber SecurityIratech JohnNo ratings yet
- To Provide Knowledge of Web Security Model. To Provide Knowledge of Client and Server Side SecurityDocument2 pagesTo Provide Knowledge of Web Security Model. To Provide Knowledge of Client and Server Side SecurityKesehoNo ratings yet
- IT602-N Information SecurityDocument3 pagesIT602-N Information Securityjainam acharyaNo ratings yet
- Bcse Whitehat - Bkav Certified Security Essential Whitehat, A Course For CyberDocument3 pagesBcse Whitehat - Bkav Certified Security Essential Whitehat, A Course For CyberpmedinacuNo ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument2 pagesInformation Securityvowafe1088No ratings yet
- Cyber Security: Master's ProgramDocument25 pagesCyber Security: Master's ProgramKishore.v Kishore.VNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCourse OutlineFasiledesNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime Investigation Syllabus - Dr. Jayakumar .VDocument1 pageCyber Crime Investigation Syllabus - Dr. Jayakumar .VPrasoonNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity PlanDocument7 pagesCybersecurity Planyoussefyahoo2No ratings yet
- SYLLABUSDocument3 pagesSYLLABUSOpanyin GabbiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Diploma in Cyber SecurityDocument4 pagesSyllabus For Diploma in Cyber SecurityppghoshinNo ratings yet
- DIS10.1 Ethical Hacking and CountermeasuresDocument14 pagesDIS10.1 Ethical Hacking and CountermeasuresJaspal Singh RanaNo ratings yet
- 17CS61 - Chethana CDocument309 pages17CS61 - Chethana CMARVEL AJNo ratings yet
- Lahore College For Women University: Department of Computer ScienceDocument2 pagesLahore College For Women University: Department of Computer SciencesabaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument2 pagesCryptography and Network SecurityVishwa Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- 03 CSE III Semester Cyber SecurityDocument2 pages03 CSE III Semester Cyber Securitymuninder ITNo ratings yet
- CSCD 418 Computer Systems Security Course Outline - 2021Document3 pagesCSCD 418 Computer Systems Security Course Outline - 2021TrialNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCybersecurity Course OutlineOlalekan IyanuoluwaNo ratings yet
- TECH3701 Security June 2005Document2 pagesTECH3701 Security June 2005conor1990No ratings yet
- Penetration Testing and Ethical Hacking Syllabus 2023 2.2024 UpdateDocument9 pagesPenetration Testing and Ethical Hacking Syllabus 2023 2.2024 UpdateSanjay DilipNo ratings yet
- CEN-COE-444-S24-SyllabiDocument4 pagesCEN-COE-444-S24-SyllabiOmar AboelfadlNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security - Course Outline CES LUMSDocument3 pagesCyber Security - Course Outline CES LUMSxovor75189No ratings yet
- LCEH Course DescriptionDocument17 pagesLCEH Course DescriptionRedCodeLinuxNo ratings yet
- Security OutlineDocument6 pagesSecurity Outlineshifara TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking and Counter Measures Course OutlineDocument7 pagesEthical Hacking and Counter Measures Course Outlineresearch.aiNo ratings yet
- CE00398-4 Security TechnologiesDocument4 pagesCE00398-4 Security Technologiesyoges_0695No ratings yet
- CISSP Exam Study Guide For Security Professionals: NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Risk Management, Digital Forensics & GovernanceFrom EverandCISSP Exam Study Guide For Security Professionals: NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Risk Management, Digital Forensics & GovernanceNo ratings yet
- Bite of The Crackers: Computing. Manila, Philippines: Mindshapers Co., Inc. (Chapter 5 - Computer HackersDocument9 pagesBite of The Crackers: Computing. Manila, Philippines: Mindshapers Co., Inc. (Chapter 5 - Computer HackersJay BermudezNo ratings yet
- What Is AES Encryption (With Examples) and How Does It WorkDocument1 pageWhat Is AES Encryption (With Examples) and How Does It WorkBAYUH MANDEFRONo ratings yet
- SEO For WebsitesDocument12 pagesSEO For WebsitesEmaús MoraNo ratings yet
- Security in Computing Brute Force Attack Demonstration ReportDocument27 pagesSecurity in Computing Brute Force Attack Demonstration ReportThe CarterNo ratings yet
- 25 Remote Hiring CompaniesDocument25 pages25 Remote Hiring CompaniessujithNo ratings yet
- Xfinity Connect InboxDocument1 pageXfinity Connect InboxHouston WhiteNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Class: Lesson 4 Using EmailDocument20 pagesBasic Computer Class: Lesson 4 Using EmailSelvaraju ParthibhanNo ratings yet
- Week 7: Learning Activty 1Document5 pagesWeek 7: Learning Activty 1Zaniyah AereeseNo ratings yet
- Revox B750 Service Manual (Page 54 of 62)Document1 pageRevox B750 Service Manual (Page 54 of 62)Сергей ТаировNo ratings yet
- BRKSEC-2028 Deploying Next Generation Firewall With ASA and Firepower Services PDFDocument73 pagesBRKSEC-2028 Deploying Next Generation Firewall With ASA and Firepower Services PDFluisNo ratings yet
- RecommendedDocument1 pageRecommendedBoris KPEGLONo ratings yet
- 3Document3 pages3playah hateNo ratings yet
- Lit - Where Do You People Find Your Ebooks - There Don'tDocument6 pagesLit - Where Do You People Find Your Ebooks - There Don'tMatthäus de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Quick Installation Guide Dvg-7111S: Voip Telephone AdapterDocument24 pagesQuick Installation Guide Dvg-7111S: Voip Telephone Adapterusr2suNo ratings yet
- Brand Awareness: Digital Marketing For Business: Jagga Rangavinay Teja Royal 20171CSE0258Document14 pagesBrand Awareness: Digital Marketing For Business: Jagga Rangavinay Teja Royal 20171CSE0258neha SinghNo ratings yet
- Zizek Multiculturalism or The Cultural Logic of Multinational CapitalismDocument22 pagesZizek Multiculturalism or The Cultural Logic of Multinational CapitalismsofiaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security ManualDocument195 pagesCyber Security ManualKrenarNo ratings yet
- Apiworld ProspectusDocument5 pagesApiworld Prospectusapi-279410189No ratings yet
- Microsoft 365 Business Secure Deployment GuideDocument24 pagesMicrosoft 365 Business Secure Deployment Guidesamehada cveNo ratings yet
- Data SecurityDocument12 pagesData SecurityjoshuabagacoNo ratings yet
- Matematika 2 Score and Accuracy ReportDocument14 pagesMatematika 2 Score and Accuracy ReportmalindaNo ratings yet
- 009 Assignment Download Install and Configure MetaMask-AS2-originalDocument11 pages009 Assignment Download Install and Configure MetaMask-AS2-originalZahid MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2Document5 pagesAssessment 2mwende faiyuuNo ratings yet
- Brute Forcing User IDs via CSRFDocument8 pagesBrute Forcing User IDs via CSRFAkNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint DeobfuscationDocument8 pagesFingerprint DeobfuscationSamuelNo ratings yet
- Data - Storage and BakcupDocument2 pagesData - Storage and BakcupJuan Carlos Antón SotoNo ratings yet
- SalesDocument6 pagesSalesjulian canoNo ratings yet