Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Secularism UPSC
Uploaded by
Nilesh SinghOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Secularism UPSC
Uploaded by
Nilesh SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Secularism in India and the United States - A
Comparison
Secularism has a meaning whose range is very wide, however, the most commonly used definition of the
term is the separation of religion from the civic affairs or the state. The other terms it may connote are
atheism, naturalism and banishment of religious symbols from the public sphere. In this article, you can
learn about the differences between secularism practiced or understood in India and the United States of
America, for the UPSC exam.
Secularism Meaning
The meaning of secularism differs in India and the West. In India, it basically connotes tolerance towards all
religions while in the West, it emphasizes a strict separation of religion and the State.
• It may seem that secularism is a relatively modern concept but references to it can be found in
ancient texts of various civilizations including the Charvaka system of philosophy in India, which
held direct perception, empiricism, and conditional inference as proper sources of knowledge, and
sought to reject the prevailing religious practices of that time.
• In the West, secularism was mentioned in the works of various Greek scholars but it re-emerged and
gained momentum through the reformation and Renaissance movements.
Secularism in India
In India, secularism means that the State in a neutral manner supports and participates in the religious affairs
of all groups. It also means that religion is kept separate from the political, social, economic and cultural
spheres of life. In the Constitution of India, the word “secular” finds a place in the Preamble itself. In
addition, the concept of secularism is reflected in Articles 25-28 of the Fundamental Rights Chapter. Article
25 gives individuals the following rights:
• Right to practice any religion.
• Right to profess any religion.
• Right to propagate any religion.
• Freedom of Conscience.
These religious freedoms are available to citizens as well as non-citizens, however, these freedoms are not
absolute and reasonable restrictions can be imposed and as such the Central or the State governments can
interfere with religious affairs at the time of need.
The secular character of India is a basic feature of the Indian Constitution and the same was held by the
Supreme Court in the S.R.Bommai case. This in essence means that the secular feature of the Constitution
cannot be taken away even by the Parliament and if it does enact a law to this effect it will be
unconstitutional. The Indian Constitution reflects what is known as positive secularism i.e. it envisages
equal respect for all religions. Moreover, if a state government propagates anti-secular policies it will face
action according to Article 356.
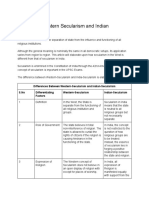
Also read: Differences between Western Secularism and Indian Secularism
Secularism in the United States
Secularism in the United States refers to the separation of church and state irrespective of one’s own religion
or lack thereof.
• The modern concept of secularism owes a lot to the movement of Separation of Church and State in
the United States.
• The United States is also credited with being the first explicitly secular nation, not only in the West
but in the entire world.
• In the United States, the Establishment Clause in the first amendment is the basis for many cases
involving the sponsorship of religion in the public sphere.
• In the United States, the stance of being secular is more of passive neutrality rather than an active
effort to rid religion for the public indefinitely.
However, despite it being neutral, there have been court cases that have clearly been pro-secular, blurred the
lines between the separation of church and state, and encouraged the resurgence of religious influence in the
government arena.
• The Establishment Clause is not a perfect defence, but it is one of the most prominent walls blocking
an established religion in the United States.
• However, contradictions have occurred between the Establishment Clause and the Free Exercise
Clause.
• The Founding Fathers of the United States did, indeed, create a secular state.
• The historical forces that led them to inscribe absolute liberty of conscience in matters of religion in
the Constitution, and to cast a wary eye on religion, also supported the process of disestablishing
state churches.
• The intent, as Madison (one of the founding fathers and the fourth President of the US) explained,
was "the idea of religious freedom as protected by the separation of church and state."
Conclusion
In conclusion, it may be said that even though both countries practice secularism as a policy but the cultural
and social realities make these approaches distinct from each other.
You might also like
- Secularism: (As Promoted by Secular Advocates)Document4 pagesSecularism: (As Promoted by Secular Advocates)Ibn Sadiq100% (1)
- Study Material Sociology-Ii Unit-I Secularism: DR M.Kalimullah Assistant Professor Department of LawDocument13 pagesStudy Material Sociology-Ii Unit-I Secularism: DR M.Kalimullah Assistant Professor Department of LawSaquib khanNo ratings yet
- Secularism in IndiaDocument37 pagesSecularism in Indiaapi-3832446100% (1)
- Secularism: by Arijit, Manya, Nikitaa and PeehuDocument28 pagesSecularism: by Arijit, Manya, Nikitaa and PeehupeehuNo ratings yet
- Secularism India Uk UasDocument13 pagesSecularism India Uk UasVishwajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Secularism and Practice in IndiaDocument17 pagesSecularism and Practice in IndiaArun MozhiNo ratings yet
- SecularismDocument18 pagesSecularismvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Understanding SecularismDocument21 pagesUnderstanding SecularismShagufta KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit II (D) SecularismDocument4 pagesUnit II (D) SecularismMahira SarafNo ratings yet
- Understanding SecularismDocument17 pagesUnderstanding SecularismyashishNo ratings yet
- Secularism: AnkushDocument20 pagesSecularism: AnkushElsa CherianNo ratings yet
- SECULARISM DEBATE IN DIVERSE INDIADocument6 pagesSECULARISM DEBATE IN DIVERSE INDIAKayara “Vk” VaradaNo ratings yet
- Religious Conversion and Freedom of Religion in India: Debates and DilemmasDocument11 pagesReligious Conversion and Freedom of Religion in India: Debates and DilemmasNasir AlamNo ratings yet
- Religious Conversion and Freedom of Religion in IndiaDocument11 pagesReligious Conversion and Freedom of Religion in IndiaSaurabh YadavNo ratings yet
- Hinduism, Secularism and the Indian JudiciaryDocument24 pagesHinduism, Secularism and the Indian JudiciaryHarshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Secularism Project A Study of Compatibility of Anti Conversion Laws With Right To Freedom NewDocument43 pagesSecularism Project A Study of Compatibility of Anti Conversion Laws With Right To Freedom Newletter2lalNo ratings yet
- Secularism principles separating religion civic affairsDocument3 pagesSecularism principles separating religion civic affairsVishal Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Secularism - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesSecularism - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- India's Constitutional Protections of Religious FreedomDocument16 pagesIndia's Constitutional Protections of Religious FreedomDain PhilipNo ratings yet
- 3 - Civics - CHAPTER  " 2nd  œUNDERSTANDING SECULARISMâ (12 Aug. 21)Document3 pages3 - Civics - CHAPTER  " 2nd  œUNDERSTANDING SECULARISMâ (12 Aug. 21)AadiNo ratings yet
- Separation of Politics and ReligionDocument16 pagesSeparation of Politics and ReligiongeonardNo ratings yet
- Winnifred Fallers Sullivan We Are All Religious Now AgainDocument18 pagesWinnifred Fallers Sullivan We Are All Religious Now AgainAfthab EllathNo ratings yet
- No religion mandates killing for sustenanceDocument64 pagesNo religion mandates killing for sustenancevicky .mNo ratings yet
- POLITICAL LAW: Freedom of Religion and Free SpeechDocument3 pagesPOLITICAL LAW: Freedom of Religion and Free SpeechMichelle Montenegro - AraujoNo ratings yet
- Interpreting the Free Exercise of Religion: The Constitution and American PluralismFrom EverandInterpreting the Free Exercise of Religion: The Constitution and American PluralismNo ratings yet
- ExplainedDocument9 pagesExplainedMulualem AberaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 5Document5 pagesAssessment 5Qainat AmanNo ratings yet
- What Secularism Means and Where It Needs to Be HeadedDocument25 pagesWhat Secularism Means and Where It Needs to Be HeadedPawan SwamiNo ratings yet
- JurosDocument3 pagesJurosJehanzaib AminNo ratings yet
- Secularism 1 PDFDocument5 pagesSecularism 1 PDFManish KumarNo ratings yet
- HhbbkkojDocument5 pagesHhbbkkojanimesh singhNo ratings yet
- Secularism - Ashwathi Nair XI - DDocument14 pagesSecularism - Ashwathi Nair XI - DAshwathi NairNo ratings yet
- Preview of Political Theory An Introduction 5Document10 pagesPreview of Political Theory An Introduction 5Muhammad LuqmanNo ratings yet
- 4 SecularismDocument9 pages4 SecularismJaidi Singnar PatorNo ratings yet
- Right To Freedom of Religion: Start Download View PDFDocument12 pagesRight To Freedom of Religion: Start Download View PDFVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - UNDERSTANDING SECULARISM NCERT SolutionsDocument3 pagesCH 2 - UNDERSTANDING SECULARISM NCERT SolutionsAkshita SethiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5 Religion and Politics:: Debates On SecularismDocument12 pagesUNIT-5 Religion and Politics:: Debates On SecularismNimrat kaurNo ratings yet
- Separation of Chruch and StateDocument3 pagesSeparation of Chruch and StateProud AthariNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Understanding Secularism: Page No: 26Document3 pagesCH 2 Understanding Secularism: Page No: 26SUSHRUT PATILNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Understanding Secularism WatermarkDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Understanding Secularism WatermarkKrypton HalideNo ratings yet
- What Is Secularism?Document4 pagesWhat Is Secularism?SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution and Understanding Secularism - NotesDocument6 pagesIndian Constitution and Understanding Secularism - NotesSaksham SinghNo ratings yet
- Secularism in IndiaDocument10 pagesSecularism in IndiaSubhajit BeraNo ratings yet
- SecularismDocument12 pagesSecularismIreno SNo ratings yet
- The Wheel of Law: India's Secularism in Comparative Constitutional ContextFrom EverandThe Wheel of Law: India's Secularism in Comparative Constitutional ContextRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Final Exam EthicsDocument4 pagesFinal Exam EthicsKenneth BactulNo ratings yet
- AGENDA 1 and 2 - AIPPM MilMUN CBE'23Document33 pagesAGENDA 1 and 2 - AIPPM MilMUN CBE'23akhi18012006No ratings yet
- Modernization and SecularizationDocument14 pagesModernization and SecularizationrickyNo ratings yet
- India As A Secular State - (23-1-2021)Document10 pagesIndia As A Secular State - (23-1-2021)Jaqen h'gharNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Dimension of Secularism in IndiaDocument80 pagesConstitutional Dimension of Secularism in Indiagodwin antony100% (1)
- Benefits of Freedom of Worship Rule To The CommunityDocument5 pagesBenefits of Freedom of Worship Rule To The CommunityHOSEA CHELUGONo ratings yet
- Khalidi Hinduising IndiaDocument18 pagesKhalidi Hinduising Indiaayubkhan2020No ratings yet
- Muskan Research On PoliticalDocument5 pagesMuskan Research On Politicalmohd.mudassir9615No ratings yet
- Right To Freedom ReligionDocument3 pagesRight To Freedom ReligionHarsh DixitNo ratings yet
- Romila Thapar SecularismDocument26 pagesRomila Thapar Secularismsrushti100% (1)
- Document 5Document6 pagesDocument 5khalidaNo ratings yet
- SecularismDocument8 pagesSecularismPat ONo ratings yet
- The Superiority of an Evangelical Model of Religious Liberty: A Critique of Secular and Roman Catholic ConceptionsFrom EverandThe Superiority of an Evangelical Model of Religious Liberty: A Critique of Secular and Roman Catholic ConceptionsNo ratings yet
- SecularismDocument10 pagesSecularismRoha EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Religion, Freedom of Religion and PoliticsDocument4 pagesReligion, Freedom of Religion and PoliticsJayra Mijares DoroteoNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Communalism Regionalism and SecularismDocument3 pagesDifference Between Communalism Regionalism and SecularismNilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Difference Western Secularism and Indian SecularismDocument2 pagesDifference Western Secularism and Indian SecularismNilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- World History: The Russian Revolu4onDocument33 pagesWorld History: The Russian Revolu4onNilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Inflation Sample NotesDocument7 pagesInflation Sample NotesNilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- World Political Geography PYQs (1995 - 2020)Document31 pagesWorld Political Geography PYQs (1995 - 2020)Nilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Agriculture (Geography) PYQ (1995 - 2020)Document24 pagesAgriculture (Geography) PYQ (1995 - 2020)Nilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Application Guide: Installation Guidelines For Landfill LiningDocument6 pagesApplication Guide: Installation Guidelines For Landfill LiningLuis Rolando AguilarNo ratings yet
- 039 Reyes Vicente Dela Cruz, Et - Al. v. Hon. Edgardo Paras, Et - Al.Document2 pages039 Reyes Vicente Dela Cruz, Et - Al. v. Hon. Edgardo Paras, Et - Al.Carissa CruzNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals Second Circuit.: No. 129. Docket 27710Document9 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals Second Circuit.: No. 129. Docket 27710Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Opposition of Motion To DismissDocument5 pagesOpposition of Motion To DismissBonnie BoldenNo ratings yet
- The Community Semi D House (Dengkil-Under New Way)Document4 pagesThe Community Semi D House (Dengkil-Under New Way)Dania IrdinaNo ratings yet
- Amended by LawsDocument28 pagesAmended by LawsWard M LiliNo ratings yet
- Barut v. Cabacungan, G.R. No. 6285, (February 15, 1912), 21 PHIL 461-473)Document9 pagesBarut v. Cabacungan, G.R. No. 6285, (February 15, 1912), 21 PHIL 461-473)yasuren2No ratings yet
- Jaca V PeopleDocument3 pagesJaca V PeoplelarrybirdyNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Definitions of LawDocument220 pagesConcepts and Definitions of Lawmunira sheraliNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement SlipDocument1 pageAcknowledgement Slipparas niosNo ratings yet
- Change Your Identity PDFDocument394 pagesChange Your Identity PDFdsfargeg100% (2)
- GOLLUM2 Academic Licence AgreementDocument1 pageGOLLUM2 Academic Licence AgreementAP SCNo ratings yet
- Cui Vs Madayag (Case)Document8 pagesCui Vs Madayag (Case)Danz MadayagNo ratings yet
- Amgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 399Document18 pagesAmgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 399Justia.comNo ratings yet
- (DLB) (PC) Janoiko v. Cox - Document No. 3Document2 pages(DLB) (PC) Janoiko v. Cox - Document No. 3Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Prop-1-Damian Ignacio v. Elias Hilaro, Et - Al., 76 Phil 605, GR No. L-175, Apr 30, 1946Document4 pagesProp-1-Damian Ignacio v. Elias Hilaro, Et - Al., 76 Phil 605, GR No. L-175, Apr 30, 1946Galilee RomasantaNo ratings yet
- Close Corporation Properties Belong to Cease FamilyDocument2 pagesClose Corporation Properties Belong to Cease FamilyTrxc MagsinoNo ratings yet
- TP101 - Festo DidacticDocument5 pagesTP101 - Festo DidacticAlberto CastroNo ratings yet
- Armed Conflict and DisplacementDocument34 pagesArmed Conflict and DisplacementcardeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Approval Document ASSET DOC 6090380 PDFDocument26 pagesApproval Document ASSET DOC 6090380 PDFSaturnino Ferreira GomesNo ratings yet
- 2005 Iaasb HandbookDocument976 pages2005 Iaasb Handbookvienkhach89No ratings yet
- Introduction To Marine Safety Environmental Protection: Revision Date: 14 Sept 2010Document105 pagesIntroduction To Marine Safety Environmental Protection: Revision Date: 14 Sept 2010Christopher MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Judges Book PDFDocument68 pagesJudges Book PDFleo_san_rjNo ratings yet
- Martin v. GuerreroDocument3 pagesMartin v. Guerrerolouis jansenNo ratings yet
- CSC ReviewerDocument5 pagesCSC ReviewerJethron EbreoNo ratings yet
- CA upholds conviction of petitioner for illegal possession of firearm and violation of election gun banDocument14 pagesCA upholds conviction of petitioner for illegal possession of firearm and violation of election gun banLansingNo ratings yet
- Domestic Building Contract 2018 SpecimenDocument34 pagesDomestic Building Contract 2018 SpecimenChad GallowayNo ratings yet
- Feminism EssayDocument5 pagesFeminism EssayDarienNo ratings yet
- AASHTO Truck Size and Weight Survey - Draft - 12!18!07Document28 pagesAASHTO Truck Size and Weight Survey - Draft - 12!18!07Akua AlderNo ratings yet
- 22 Festejo Vs Fernando 50 OG 1556Document4 pages22 Festejo Vs Fernando 50 OG 1556kalantiaoNo ratings yet