Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lifecycle of A Medicaldevice
Uploaded by
Jezreel ZaragosaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lifecycle of A Medicaldevice
Uploaded by
Jezreel ZaragosaCopyright:
Available Formats
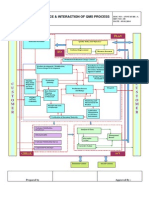
The different stakeholders in the process
The tasks of Swissmedic – Lifecycle of a medical device DB / designated body Swissmedic Manufacturer
Phase 1: Pre-market development to market conformity Phase 2: Market launch Phase 3: Post-market surveillance
(before market launch) (after market launch)
Medical devices by risk class
Risk class III
e.g. artificial hip joint, artificial heart, Involvement of a DB
cardiac pacemaker Special additional procedures for:
• certain products in Class III and IIb
The Agency receives suspicion reports, implements the necessary corrective actions in a risk-based manner and monitors implementation.
• tissues or cells of human or animal origin
Issuing of registration number (CHRN**)
Risk class IIb or their derivatives
• IVD, class I products, systems and procedure packs, MEP-DEVIT (until product registration is possible according to oMedDO***)
e.g. intraocular lenses, insulin pumps • substances or combinations of substances that
are absorbed by the human body or distributed
Evaluate clinical data/performance evaluation, complete clinical evaluation report/performance report
locally in the body CE nnnn
Risk class IIa
e.g. surgical gloves,
ultrasound equipment
and instructions for use, assess compliance with fundamental requirements
PMS plan, PMSR (for Class A, B and I), PSUR (for Class IIa, llb, III, C and D),
Quality management system: responsibilities, procedures, processes and
management resources to ensure compliance with ordinance(s
Risk class Is / Im / Ir
If necessary, the application for exemptions is approved
The manufacturer issues the Declaration of Conformity
serious events, FSCA, PSR, trend report by manufcturer
e.g. sterile plasters, patient scales,
reusable surgical instruments
The DB audits the quality management system
• Approval and monitoring of clinical trials with non-CE-labelled or off-label-use medical devices
Intended use and classification / Borderline issues
• Approval and monitoring of combined trials with medicinal products and non-CE-labelled or
Issue export certificates (FSC)
Risk class I
e.g. wheelchair The manufacturer is responsible for CE
verifying safety and performance
• MEP and IVD (in-house products) made and used in health establishments
Risk class A
e.g. sample containers, laboratory analysers
off-label-use medical devices (e.g. companion diagnostics)
Products with no medical
• Publication of field safety notices (FSN) (e.g. recalls)
• DEVIT products (until a special ordinance is enacted)
intended use*
CE nnnn
e.g. contact lenses without vision correction,
with or without a medicinal product component
Involvement of a DB
equipment for removing tattoos or hair
Registration of stakeholders
• Collect and evaluate vigilance reports
• Relabelled/repackaged MEP and IVD
Process notifications concerning:
Risk class B
e.g. pregnancy tests
Administrative proceedings
• Inspections of clinical trials
• Custom-made devices
Risk class C
e.g. devices for self-use for blood glucose
testing, breast cancer test
Special additional procedures for:
Risk class D • certain class D products
e.g. Sars-CoV-2 test, Ebola test
Designation/renewal of designation of the DB Surveillance of the DB
Inspections of hospitals (reporting system, reprocessing and maintenance) and companies (for cause and provision of support to foreign authorities)
*Unless Swissmedic has designated common specifications in accordance with Article 8 paragraph 1, these products are subject to the old legislation. **CHRN = Swiss Single Registration Number ***Medical Devices Ordinance of 17 October 2001 (version of 1 August 2020)
You might also like
- IAQG SCMH-3.4.3-FOD-Risk-Assessment-FOD-Prevention-Program-Assessment-Dated-17APR2018Document4 pagesIAQG SCMH-3.4.3-FOD-Risk-Assessment-FOD-Prevention-Program-Assessment-Dated-17APR2018LiherNo ratings yet
- 04 - Graphs of Trig Functions PDFDocument4 pages04 - Graphs of Trig Functions PDFMark Abion ValladolidNo ratings yet
- DS1000D E User's GuideDocument166 pagesDS1000D E User's GuideRicardo de AzambujaNo ratings yet
- Nclex RN Test - Free Nclex RN Test HelpDocument7 pagesNclex RN Test - Free Nclex RN Test Helppasstest1234No ratings yet
- Startup Financial ModelDocument7 pagesStartup Financial ModelSandeep JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Wabco Products CatalogDocument114 pagesWabco Products CatalogCvita Cvitić100% (1)
- Blood Specimen Collection: Elaine M. KeohaneDocument15 pagesBlood Specimen Collection: Elaine M. KeohanePrince Guevara100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis DKA Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis DKA Care Planعبدالله خليل العسل100% (1)
- Screening, Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Autism Spectrum DisordersDocument5 pagesScreening, Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Autism Spectrum DisordersDaniele PendezaNo ratings yet
- Process MappingDocument1 pageProcess MappingG Sathesh KumarNo ratings yet
- YOGADocument43 pagesYOGASugaam Physio clinicNo ratings yet
- NDT Post Mid Term AnswersDocument36 pagesNDT Post Mid Term AnswersAnonymousTargetNo ratings yet
- WW ISO10993 Biocompatibility White Paper EMERGODocument20 pagesWW ISO10993 Biocompatibility White Paper EMERGOJezreel ZaragosaNo ratings yet
- Post Mature Neonate, Infant of Diabetic and Substance Abuse MotherDocument14 pagesPost Mature Neonate, Infant of Diabetic and Substance Abuse MotherShilpa JoshiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Worldwide FPSO UnitsDocument1 page2022 Worldwide FPSO UnitscourarodrigoNo ratings yet
- Transportation of Critically Ill PatientDocument18 pagesTransportation of Critically Ill Patientfirdaus che daud100% (3)
- Maternal and Child Nursing - Intrapartum PeriodDocument91 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing - Intrapartum Periodchuppepay20% (5)
- 2011 WABCO Product CatalogDocument143 pages2011 WABCO Product Catalogrrosa_9962720% (1)
- Minimental QuirogaDocument12 pagesMinimental QuirogaLeonardo Rodrigo Vivanco PazNo ratings yet
- Example Biological Evaluation Submission Form Iso 10993 Part 1 Rev2Document7 pagesExample Biological Evaluation Submission Form Iso 10993 Part 1 Rev2Jezreel ZaragosaNo ratings yet
- Fm-Ims-Gr-009 Risk Register Rev. 0Document2 pagesFm-Ims-Gr-009 Risk Register Rev. 0Rofelin SamarNo ratings yet
- Advertisement Skills - III Semester (Study Materials)Document82 pagesAdvertisement Skills - III Semester (Study Materials)Gladwin Joseph E Nitte School of Fashion Technology and Interior DesignNo ratings yet
- GIIRS Company Report YARETANOL ProgramDocument6 pagesGIIRS Company Report YARETANOL ProgramIvaneth Silva PernaletteNo ratings yet
- Diky Jancuk - 105550 2Document1 pageDiky Jancuk - 105550 2ffdy4fvn6sNo ratings yet
- DahmannDocument20 pagesDahmanncoopter zhangNo ratings yet
- Mouser EIU July 2022Document46 pagesMouser EIU July 2022Ludo BagmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PerceptionDocument1 pageChapter 3 PerceptionTIN NGUYEN BUI MINHNo ratings yet
- How To Open Without Using Preview For MacDocument2 pagesHow To Open Without Using Preview For Macmurillo.guilherme.2006No ratings yet
- BCM (Body Control Module) - W - Intelligent Key System (Body Control Systems) - ALLDATA RepairDocument1 pageBCM (Body Control Module) - W - Intelligent Key System (Body Control Systems) - ALLDATA RepairStas PikalovNo ratings yet
- نشرة الأرقام القياسية للمنتجين عن شهرى ديسمبر2020 - يناير2021Document58 pagesنشرة الأرقام القياسية للمنتجين عن شهرى ديسمبر2020 - يناير2021Hussain ElarabiNo ratings yet
- نشرة الأرقام القياسية لأسعار المنتجين ابريل - مايو 2021Document58 pagesنشرة الأرقام القياسية لأسعار المنتجين ابريل - مايو 2021Hussain ElarabiNo ratings yet
- Sp3d Installation ProcedureDocument70 pagesSp3d Installation ProcedureAvadhoot DabholkarNo ratings yet
- TFtree Gazebo SimulationDocument1 pageTFtree Gazebo SimulationMexNo ratings yet
- Dr. Jorge P. Royeca Hospital: Palarpalar, Eillen GayDocument2 pagesDr. Jorge P. Royeca Hospital: Palarpalar, Eillen GayClarisse Marion DenilaNo ratings yet
- ETM ViewerDocument1 pageETM Viewerdmitry esaulkovNo ratings yet
- Mate ComprobanteDocument375 pagesMate ComprobanteNatalia ArroyaveNo ratings yet
- HL7 ER ModelDocument2 pagesHL7 ER ModelHEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEMS/SOFTWARENo ratings yet
- 2020 Worldwide Survey of Floating Production, Storage and Offloading (Fpso) UnitsDocument1 page2020 Worldwide Survey of Floating Production, Storage and Offloading (Fpso) UnitsAndreManhaesNo ratings yet
- Inspection Data Sheet (I.D.S.) : Company Job. Country RevisionDocument2 pagesInspection Data Sheet (I.D.S.) : Company Job. Country Revisionbrome2014No ratings yet
- Stren Exer Ngth/weigh Rcise HTS: Sets # Weight R Reps Wei Ight Reps Weight Reps Wei Ight RepsDocument1 pageStren Exer Ngth/weigh Rcise HTS: Sets # Weight R Reps Wei Ight Reps Weight Reps Wei Ight RepsPhong LeNo ratings yet
- Schemes of AP NewDocument22 pagesSchemes of AP NewdarimaduguNo ratings yet
- Final Ad Case Studies Commercial Complex1Document30 pagesFinal Ad Case Studies Commercial Complex1Deepali Pisolkar HejibNo ratings yet
- 1691873504-Brochure Pavani Royale - Availaible - 07!08!2023Document5 pages1691873504-Brochure Pavani Royale - Availaible - 07!08!2023miraj ahmedNo ratings yet
- Navigation Aids Panel Data Sheet: Company Job. Country RevisionDocument3 pagesNavigation Aids Panel Data Sheet: Company Job. Country Revisionbrome2014No ratings yet
- IFRS FrameworkDocument2 pagesIFRS Framework21ubha116 21ubha116No ratings yet
- COVID Vaccine Policy - Medical Exemption FormDocument4 pagesCOVID Vaccine Policy - Medical Exemption FormjurkachhNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - Smarwatch AssigmentDocument11 pagesMarketing Management - Smarwatch AssigmentNguyen WoabeNo ratings yet
- 5G System (5Gs) Architecture: 5G Core - Service Based Representation 5G Core - Reference Point RepresentationDocument1 page5G System (5Gs) Architecture: 5G Core - Service Based Representation 5G Core - Reference Point RepresentationAsit SwainNo ratings yet
- Karanam ApprovedDocument1 pageKaranam ApprovedswapnilNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual (EN)Document24 pagesParts Manual (EN)Dean AversNo ratings yet
- ATS LAY K5 02 EEQSM 001 WorkDocument1 pageATS LAY K5 02 EEQSM 001 WorkLee WenjianNo ratings yet
- Thinkmoney/: Is The Vix Still Relevant?Document44 pagesThinkmoney/: Is The Vix Still Relevant?cruzsanta2012No ratings yet
- Edexcel iGCSE ICT Software MindmapDocument1 pageEdexcel iGCSE ICT Software MindmapPaul ZambonNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW Pcmcindia Gov InpdfpdfvillageMoshi PDFDocument1 pageHTTPSWWW Pcmcindia Gov InpdfpdfvillageMoshi PDFPankaj SawantNo ratings yet
- AAAA - Job Safety & Environmental Analysis Worksheet BLANKDocument1 pageAAAA - Job Safety & Environmental Analysis Worksheet BLANKJade Louise PatolilicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Markets Allocating ResourcesDocument2 pagesChapter 6 - Markets Allocating ResourcesShayna ButtNo ratings yet
- IIT2021040 POE C1 Assignment1Document8 pagesIIT2021040 POE C1 Assignment1Aditya ExtraNo ratings yet
- Pretest User Manual V 1.0Document3 pagesPretest User Manual V 1.0Kleberson HenriqueNo ratings yet
- 04 - 4 - Graphs of Trig FunctionsDocument4 pages04 - 4 - Graphs of Trig FunctionsSUNGMIN CHOINo ratings yet
- Facilities/Machinery/ Equipment Mode of Acquisition Year Acquired Brand/ Model Condition/ RemarksDocument3 pagesFacilities/Machinery/ Equipment Mode of Acquisition Year Acquired Brand/ Model Condition/ RemarksmichaelNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Pre Stressed Concrete Ground AnchorsDocument1 pageDesign and Construction of Pre Stressed Concrete Ground Anchorsakshay kothiyalNo ratings yet
- Technical Evaluation Report of Medicines, CEO DHA DGKHAN 1ST MEDICINE FY2020-21Document36 pagesTechnical Evaluation Report of Medicines, CEO DHA DGKHAN 1ST MEDICINE FY2020-21M Irfan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Collar Pivot 38 MMDocument1 pageCollar Pivot 38 MMPreetam KumarNo ratings yet
- Portable Radio Logbook - LandscapeDocument1 pagePortable Radio Logbook - LandscapeJayantha PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Studies and Calculations PDFDocument1 pageElectrical Studies and Calculations PDFsaga2000cnNo ratings yet
- Attendance Register of BENGAL INDUSTRIES PRIVATE LIMITED Day or Night For The Month of AUGUST-2020Document8 pagesAttendance Register of BENGAL INDUSTRIES PRIVATE LIMITED Day or Night For The Month of AUGUST-2020Sharad RastogiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Fiche 1Document7 pagesMarketing Fiche 1CarlinNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual W465H, W475H/M, W485M, W4105H/M, W4130H/M, W4180H/M, W4240H, W4250M, W4300H, W4330M, W4280X, W4350X Clarus ControlDocument76 pagesOperating Manual W465H, W475H/M, W485M, W4105H/M, W4130H/M, W4180H/M, W4240H, W4250M, W4300H, W4330M, W4280X, W4350X Clarus ControlAgustin FernandezNo ratings yet
- Demetra Guideline1Document44 pagesDemetra Guideline1erererefgdfgdfgdfNo ratings yet
- Dental Barotrauma in French Military Divers: Results of The POP StudyDocument5 pagesDental Barotrauma in French Military Divers: Results of The POP StudyLiga Odontopediatria RondonienseNo ratings yet
- Pb5522en MKDocument152 pagesPb5522en MKJezreel ZaragosaNo ratings yet
- MD Assessment of BiocompatibilityDocument6 pagesMD Assessment of BiocompatibilityJezreel ZaragosaNo ratings yet
- Logo NegaraDocument448 pagesLogo NegaraIndah PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 RH TypingDocument22 pagesChapter 7 RH TypingYo Issei Hyodono100% (1)
- Aminoglycosides and SulfonamidesDocument35 pagesAminoglycosides and SulfonamidesPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Anemia Overview: The Third Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen UniversityDocument77 pagesAnemia Overview: The Third Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen UniversityMazlina MaidinNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Exam 1Document8 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Exam 1Marjorie TuazonNo ratings yet
- Hilton Et Al, 1997 (Ab To BSA) PDFDocument10 pagesHilton Et Al, 1997 (Ab To BSA) PDFFarkhanda SadafNo ratings yet
- Ashwagandha Leaves Medicinal UsesDocument3 pagesAshwagandha Leaves Medicinal UsesSanjay PatilNo ratings yet
- Neisseria Spp.Document22 pagesNeisseria Spp.sajad abasNo ratings yet
- Pharma Notes 3Document10 pagesPharma Notes 3Mayya FirdousNo ratings yet
- Pathology Quality ManualDocument40 pagesPathology Quality ManualInn MironNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesDrug Study LosartanQueenie Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Price ListDocument119 pagesPrice ListDanielNo ratings yet
- Letter - Physical ExamDocument6 pagesLetter - Physical ExamLaurence LesmorasNo ratings yet
- Neurology Physical Therapy Residency: The Johns Hopkins Hospital and University of DelawareDocument1 pageNeurology Physical Therapy Residency: The Johns Hopkins Hospital and University of Delawareapi-241031382No ratings yet
- Coass V-Ear TumorsDocument32 pagesCoass V-Ear TumorsErshine Villany100% (1)
- ImmunogeneticsDocument26 pagesImmunogeneticsOanaDorofteNo ratings yet
- NSQHS Standards Fact Sheet Standard 7Document2 pagesNSQHS Standards Fact Sheet Standard 7Annette LowryNo ratings yet
- Neo DentDocument46 pagesNeo DentPaul BurgosNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors AreDocument10 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factors ArenurNo ratings yet
- Glycerol BlankingDocument4 pagesGlycerol BlankingDiah Puspita RiniNo ratings yet