Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture - 3 - Part 1
Uploaded by
h01iOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture - 3 - Part 1
Uploaded by
h01iCopyright:
Available Formats
Foundations Engineering (0504421)
By:
Dr Mahmoud Alrsai
(m.alrsai@ahu.edu.jo)
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 1
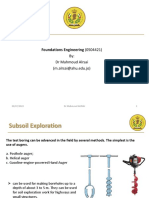
Subsoil Exploration
Introduction:
This chapter aims at understanding the types of soil deposits that will support the
foundation.
The soil at any site frequently is nonhomogeneous; that is, the soil profile may vary.
Therefore, evaluation of site conditions and soil parameters is a must. To do this
requires some knowledge of the geological process by which the soil deposit at the site
was formed, supplemented by subsurface exploration.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 2
Subsoil Exploration
Subsurface Exploration
Subsurface exploration can be defined as the process of determining the layers of
natural soil deposits that will underlie a proposed structure and their physical
properties.
Purpose of Subsurface Exploration:
• nature of soil.
• type and depth of foundation.
• load-bearing capacity of the foundation.
• probable settlement of a structure.
• potential foundation problems (e.g., expansive soil, collapsible soil, sanitary
landfill, etc.).
• location of water table.
• depth and nature of bedrock, if encountered.
• in situ field tests, such as permeability tests, van shear test, and standard
penetration test.
• lateral earth pressure for structures, such as retaining walls, sheet pile, and
braced cuts.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 3
Subsoil Exploration
Subsurface Exploration
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 4
Subsoil Exploration
Number of Borings
• If various soil strata are more or less uniform and predictable, fewer boreholes
are needed than in nonhomogeneous soil strata.
• One boring at each corner of the building and one boring at the center of the
building should be provided.
• The table below gives some general guidelines for the spacing between
boreholes for different types of structures:
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 5
Subsoil Exploration
Depth of borings
To determine the approximate minimum depth of boring, engineers may use the rules
established by the ASCE(1972):
1. Determine the net increase in the effective stress,∆𝜎𝜎′,under a foundation with
depth as shown in the figure below.
2. Estimate the variation of the vertical effective stress, 𝜎𝜎𝑜𝑜′, with depth.
3. Determine the depth, 𝐷𝐷=𝐷𝐷1, at which the effective stress increase ∆𝜎𝜎′is equal to
(1/10) 𝑞𝑞(q = estimated net stress on the foundation).
4. Determine the depth, 𝐷𝐷=𝐷𝐷2, at which ∆𝜎𝜎′/𝜎𝜎𝑜𝑜′=0.05.
5. Determine the depth, 𝐷𝐷=𝐷𝐷3, which is the distance from the lower face of the
foundation to the bedrock (if encountered).
6. Choose the smaller of the two depths, 𝐷𝐷1, 𝐷𝐷2and 𝐷𝐷2, just determined as the
approximate minimum depth of boring required.
7. Add up the depth of the foundation to the depth value determined in the previous
step to get the total boring depth, as given under:
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 6
Subsoil Exploration
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 7
Subsoil Exploration
Effective Stress ( )
The normal stress acting on a point within a saturated soil mass is shared by the soil
grains and the water. The component carried by the soil grains is the effective stress,
and the remainder carried by the pore water is called the pore water pressure.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 8
Subsoil Exploration
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 9
Subsoil Exploration
The increase in vertical effective stress(Δ )
Two alternatives are available:
(1) By determining the vertical stress value regarding the lower face of the foundation.
(2) Using the so-called 2:1 Method as shown in the figure given under.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 10
Subsoil Exploration
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 11
Subsoil Exploration
Sampling Procedure
Two types of soil samples can be obtained during subsurface exploration:
(1) Disturbed–Split-spoon samplers:
Split-spoon samplers can be used in the field to obtain soil samples that are generally
disturbed to be used for:
a. Grain-size analysis
b. Determination of liquid and plastic limits
c. Specific gravity of soil solids
d. Determination of organic content
(2) Undisturbed–Thin-walled tubes:
Thin-walled tubes that are sometimes referred to as Shelby tubes are made of seamless
steel and are frequently used to obtain undisturbed clayey soils to be used for:
a. Consolidation test
b. Hydraulic Conductivity test
c. Shear Strength tests
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 12
Subsoil Exploration
The degree of disturbance for a soil sample
For a standard split-spoon sampler. When the area ratio is 10% or less, the sample
generally is considered to be undisturbed.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 13
Subsoil Exploration
Problem (1):
Determine the degree of disturbance to a sample taken by the standard split-spoon
sampler. (inside diameter = 34.93 mm and an outside diameter = 50.8 mm.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 14
Subsoil Exploration
Problem (2):
Site investigation is to be made for a structure of 100m length and 70m width. The soil
profile is shown below, if the structure is subjected to 200 KN/m^2, what is the
approximate depth of borehole, assuming 𝛾𝛾𝑤𝑤=10KN/m^3.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 15
Subsoil Exploration
Problem (3):
Site investigation is to be made for
2500 KN load carried on (3.0 m x
2.0 m) footing. The foundation will
be built on layered soil as shown in
the figure below, estimate the
depth of borehole, assuming
𝛾𝛾𝑤𝑤=10KN/m^3.
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 16
• Remember to do something good today!!!
20/07/2022 Dr Mahmoud ALRSAI 17
You might also like
- Chapter (2) Subsoil ExplorationDocument22 pagesChapter (2) Subsoil Explorationيقين يقين100% (1)
- Lecture - 3 - Part 2Document37 pagesLecture - 3 - Part 2h01iNo ratings yet
- Basics of Foundation Engineering With Solved ProblemsDocument274 pagesBasics of Foundation Engineering With Solved Problemsmogesi100% (21)
- Notes Foundation and MasonryDocument45 pagesNotes Foundation and MasonryGurupadaswamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fondation IDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Fondation IKubaNo ratings yet
- Soil InvestigationsDocument44 pagesSoil InvestigationsMr Professor0% (1)
- Foundation Engineering I PPT ALLDocument143 pagesFoundation Engineering I PPT ALLTekle Germariam100% (1)
- Subsurface Exploration (Site Investigation) PDFDocument92 pagesSubsurface Exploration (Site Investigation) PDFrenrenzNo ratings yet
- Ce 483 Subsoil Exploration 38-39 IDocument108 pagesCe 483 Subsoil Exploration 38-39 IAman Raj MajhiNo ratings yet
- Subsurface Exploration NotesDocument178 pagesSubsurface Exploration NotesiannjodyeNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration: GENERAL: Soil Is Used AsDocument16 pagesSoil Exploration: GENERAL: Soil Is Used AsPaulo Parenas100% (1)
- Basics of Foundation Engineering With Solved ProblemsDocument274 pagesBasics of Foundation Engineering With Solved ProblemsSuir Isahu100% (2)
- Site Investigation: Fayoum UniversityDocument56 pagesSite Investigation: Fayoum Universitymuhaned mayserhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Site Investigation PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 1 Site Investigation PDFafnan hamimiNo ratings yet
- Site Investigation or Soil ExplorationsDocument13 pagesSite Investigation or Soil ExplorationspengniumNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 Geotechnical InvestigationDocument76 pagesLecture8 Geotechnical Investigationadia kajunaNo ratings yet
- Alviar, Darryil Guian Lo V. June 26, 2013 CE - 3/2010105520 Engr. Flordeliza Villasenor HomeworkDocument10 pagesAlviar, Darryil Guian Lo V. June 26, 2013 CE - 3/2010105520 Engr. Flordeliza Villasenor HomeworkDarryil AlviarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document40 pagesChapter 11Casao JonroeNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Subsoil Exploration (15-71) New3Document61 pagesCh2 Subsoil Exploration (15-71) New3Rafi SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Geotech FinalDocument13 pagesGroup 1 Geotech FinalTakudzwa Calvin ChibudaNo ratings yet
- SiteinvestigationDocument56 pagesSiteinvestigationAbdul KabasyNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Mr. C SASIDHAR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, SRET, TirupatiDocument4 pagesUnit-I: Mr. C SASIDHAR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, SRET, TirupatiSasi HoneyNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration: ATME College of EngineeringDocument95 pagesSoil Exploration: ATME College of EngineeringMohit BhagatNo ratings yet
- Site InvestgationDocument11 pagesSite Investgationone engNo ratings yet
- Ceng 3204 Lecture Note - SDDocument64 pagesCeng 3204 Lecture Note - SDhabtamuterefe01No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Internship ReportDocument46 pagesAcknowledgement: Internship Reportadeel abbasNo ratings yet
- Methods of Subsoil InvestigationDocument16 pagesMethods of Subsoil InvestigationUduebor Micheal71% (14)
- Chapter 4: Subsurface InvestigationDocument21 pagesChapter 4: Subsurface InvestigationHisham MohamadNo ratings yet
- Site InvestigationDocument71 pagesSite Investigationpeiyin88100% (4)
- Soil Investigation & Foundation DesignDocument12 pagesSoil Investigation & Foundation DesignMunna Bhai100% (1)
- 12.0 GROUND INVESTIGATION ZZZ (Repaired)Document19 pages12.0 GROUND INVESTIGATION ZZZ (Repaired)DanielsNo ratings yet
- University of Duhok College of Engineering Engineering Consulting BureauDocument11 pagesUniversity of Duhok College of Engineering Engineering Consulting BureauRafi Mahmoud SulaimanNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe Faculty of EngineeringDocument9 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe Faculty of EngineeringTakudzwa Calvin ChibudaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document161 pagesChapter 1nurhusein mollaNo ratings yet
- Diapositivas de FundacionesDocument168 pagesDiapositivas de Fundacioneskaren yojhana garcia ramosNo ratings yet
- Sec-A, Iqbal Boulevard, Phase-Ii, Dha, Islamabad: Geotechnical Site InvestigationDocument21 pagesSec-A, Iqbal Boulevard, Phase-Ii, Dha, Islamabad: Geotechnical Site InvestigationShakir UllahNo ratings yet
- Site InvestigationDocument87 pagesSite InvestigationAhmad Mensa100% (1)
- Foundation Engineering: 1.0 Site InvestigationDocument47 pagesFoundation Engineering: 1.0 Site InvestigationKHAI HONG GANNo ratings yet
- Ground Mast 3Document21 pagesGround Mast 3Ajiboye MubarakNo ratings yet
- 2022-07-23 STR Pit-1 ITI College Fatehgarh Jaisalmer RajasthanDocument27 pages2022-07-23 STR Pit-1 ITI College Fatehgarh Jaisalmer Rajasthanprakash mokhaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Fuziah Ismail: Earthwork: Site InvestigationDocument9 pagesPrepared By: Fuziah Ismail: Earthwork: Site Investigationroslanarahman100% (1)
- 2 Site Exploration and Characterization 1458731717Document63 pages2 Site Exploration and Characterization 1458731717Abed SolimanNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document27 pagesModule 1Venu Gopal0% (1)
- Term Paper On SDocument12 pagesTerm Paper On SAzeez TundeNo ratings yet
- 2022-07-23 STR Pit-1 ITI College Bhaniyana Pokhran Jaisalmer RajasthanDocument26 pages2022-07-23 STR Pit-1 ITI College Bhaniyana Pokhran Jaisalmer Rajasthanprakash mokhaNo ratings yet
- 1 SiteinvestigationDocument51 pages1 SiteinvestigationSelah AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration SeeDocument37 pagesSoil Exploration SeeRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration SeeDocument39 pagesSoil Exploration SeeRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- 5351 TXTDocument10 pages5351 TXTYousif Mohammed YousifNo ratings yet
- Foundation HandoutDocument78 pagesFoundation HandoutMc KaLiNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Boring Spacing & DepthDocument24 pagesExploratory Boring Spacing & Depth18106 Mahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Site InvestgationDocument82 pagesSite Investgationtesera addisNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Definition and Purpose: Chapter One Site ExplorationDocument62 pages2.1 Definition and Purpose: Chapter One Site Explorationabel shimelesNo ratings yet
- Soil InvestigationDocument6 pagesSoil InvestigationWong Pei Yin100% (1)
- Chap 2Document49 pagesChap 2medo eidNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and Foundation DesignFrom EverandSoil Investigation and Foundation DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Lecture 8Document44 pagesLecture 8h01iNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document34 pagesLecture 4h01iNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document11 pagesChapter 03h01iNo ratings yet
- SlidesDocument51 pagesSlidesh01iNo ratings yet