Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounting for Time Value of Money
Uploaded by
Jessie John Credo Jr.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounting for Time Value of Money
Uploaded by
Jessie John Credo Jr.Copyright:
Available Formats
Accounting 21 Intermediate Accounting 1
Accounting and The Time Value of Money
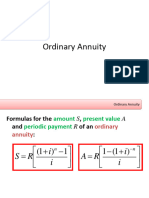
FORMULA
Present Value Future Value
One
Ordinary Annuity of One
Annuity due of One
In perpetuity
DIAGRAM
On the right are six diagrams representing six different present and future value concepts stated on the left. Identify the
diagrams with the concepts by writing the identifying letter of the diagram on the blank line at the left. Assume n = 4 and i =
8%.
Concept Diagram of Concept
_____ 1. Future value of 1. ? P1
a. | | | | |
_____ 2. Present value of 1.
?
_____ 3. Future value of an annuity P1 P1 P1 P1
due of 1. b. |- - - - | | | |
_____ 4. Future value of an ordinary
annuity of 1. ?
P1 P1 P1 P1
_____ 5. Present value of an ordinary c. | | | |- - - - |
annuity of 1.
_____ 6. Present value of an annuity ? P1 P1 P1 P1
due of 1. d. | | | | |
P1 ?
e. | | | | |
P1 P1 P1 P1 ?
f. | | | | |
PROBLEM
1. Jan Green established a savings account for her son's college education by making annual deposits of P6,000 at the
beginning of each of six years to a savings account paying 8%. At the end of the sixth year, the account balance was
transferred to a bank paying 10%, and annual deposits of P6,000 were made at the end of each year from the seventh
through the tenth years. What was the account balance at the end of the tenth year?
2. Part (a) Compute the amount that a P20,000 investments today would accumulate at 10% (compound interest) by the
end of 6 years.
Part (b) Tom wants to retire at the end of this year (2010). His life expectancy is 20 years from his retirement. Tom has
come to you, his CPA, to learn how much he should deposit on December 31, 2010 to be able to withdraw
P40,000 at the end of each year for the next 20 years, assuming the amount on deposit will earn 8% interest
annually.
Danes Derick C. Dolz | 1
Accounting 21 Intermediate Accounting 1
Accounting and The Time Value of Money
Part (c) Judy Thomas has a P1,200 overdue debt for medical books and supplies at Joe's Bookstore. She has only P400
in her checking account and doesn't want her parents to know about this debt. Joe's tells her that she may settle
the account in one of two ways since she can't pay it all now:
1. Pay P400 now and P1,000 when she completes her residency, two years from today.
2. Pay P1,600 one year after completion of residency, three years from today.
Assuming that the cost of money is the only factor in Judy's decision and that the cost of money to her is 8%,
which alternative should she choose? Your answer must be supported with calculations.
3. Jill Morris is presently leasing a small business computer from Eller Office Equipment Company. The lease requires 10
annual payments of P4,000 at the end of each year and provides the lessor (Eller) with an 8% return on its investment. You
may use the following 8% interest factors:
9 Periods 10 Periods 11 Periods
Future Value of 1 1.99900 2.15892 2.33164
Present Value of 1 .50025 .46319 .42888
Future Value of Ordinary Annuity of 1 12.48756 14.48656 16.64549
Present Value of Ordinary Annuity of 1 6.24689 6.71008 7.13896
Present Value of Annuity Due of 1 6.74664 7.24689 7.71008
Instructions
(a) Assuming the computer has a ten-year life and will have no salvage value at the expiration of the lease, what was the
original cost of the computer to Eller?
(b) What amount would each payment be if the ten annual payments are to be made at the beginning of each period?
4. Bates Company has entered into two lease agreements. In each case the cash equivalent purchase price of the asset
acquired is known and you wish to find the interest rate which is applicable to the lease payments.
Instructions
Calculate the implied interest rate for the lease payments.
Lease A — Lease A covers office equipment which could be purchased for P36,048. Bates Company has, however, chosen
to lease the equipment for P10,000 per year, payable at the end of each of the next 5 years.
Lease B — Lease B applies to a machine which can be purchased for P57,489. Bates Company has chosen to lease the
machine for P12,000 per year on a 6-year lease. Payments are due at the start of each year.
5. Pine Leasing Company purchased specialized equipment from Wayne Company on December 31, 2009 for P400,000. On
the same date, it leased this equipment to Sears Company for 5 years, the useful life of the equipment. The lease payments
begin January 1, 2010 and are made every 6 months until July 1, 2014. Pine Leasing wants to earn 10% annually on its
investment.
Various Factors at 10%
Periods Future Present Future Value of an PV of an
or Rents Value of P1 Value of P1 Ordinary Annuity Ordinary Annuity
9 2.35795 .42410 13.57948 5.75902
10 2.59374 .38554 15.93743 6.14457
11 2.85312 .35049 18.53117 6.49506
Various Factors at 5%
Periods Future Present Future Value of an PV of an
or Rents Value of P1 Value of P1 Ordinary Annuity Ordinary Annuity
9 1.55133 .64461 11.02656 7.10782
10 1.62889 .61391 12.57789 7.72173
11 1.71034 .58468 14.20679 8.30641
Instructions
(a) Calculate the amount of each rent.
(b) How much interest revenue will Pine earn in 2010?
Danes Derick C. Dolz | 2
Accounting 21 Intermediate Accounting 1
Accounting and The Time Value of Money
6. Carey Company owns a plot of land on which buried toxic wastes have been discovered. Since it will require several years
and a considerable sum of money before the property is fully detoxified and capable of generating revenues, Carey wishes
to sell the land now. It has located two potential buyers: Buyer A, who is willing to pay P320,000 for the land now, and Buyer
B, who is willing to make 20 annual payments of P50,000 each, with the first payment to be made 5 years from today.
Assuming that the appropriate rate of interest is 9%, to whom should Carey sell the land? Show calculations.
7. Lupo's Washers Dryers offers a 2-year warranty on all appliances sold. The company is trying to estimate the warranty
expense for 2011 and the related warranty liability at December 31, 2011. Because there is no ready market for such
warranty contracts, the company must estimate the fair value of the contracts using the expected cash flow approach
shown below are the estimated cash flows and probability assessments for 2011 and 2012.
Cost flow Probability
Estimate Assessment
2011 *3,900 30%
6,400 50%
7,600 20%
2012 *5,500 20%
7,400 50%
8,000 30%
Instructions:
Assuming a risk-free rate of 6% and that the cash flows occurs at year-end, calculate the warranty obligation:
AMORTIZATION
TERM TERM TERM SERIAL SERIAL SERIAL
Non-Interest Interest Interest Non-interest Interest Interest
Bearing Bearing Bearing bearing Bearing Bearing
Premium Discount Ordinary Annuity Due
Annuity
Effective 12% 10% 14% 12% 12% 12%
Nominal none 12% 12% None 10% 10%
Note Date Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013
Issue Date Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013 Jan 1, 2013
Maturity Date Dec 31, 2017 Dec 31, 2017 Dec 31, 2017 Dec 31, 2017 Dec 31, 2017 Dec 31, 2017
Period 5 5 5 5 5 5
Interest none 120,000 120,000 none multiple multiple
Annuity none none none 1,000,000 1,000,000 1,000,000
Future Value 5,000,000 1,000,000 1,000,000 5,000,000 5,000,000 5,000,000
Present Value ? ? ? ? ? ?
8. Provide the present value.
9. Prepare the amortization table.
Term – Non-interest Bearing
Year Interest
Payment Expense Principal Amortization Balance
2013
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Danes Derick C. Dolz | 3
Accounting 21 Intermediate Accounting 1
Accounting and The Time Value of Money
Term – Interest Bearing - Premium
Year Interest
Payment Expense Principal Amortization Balance
2013
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Term – Interest Bearing - Discount
Year Interest
Payment Expense Principal Amortization Balance
2013
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Serial – Non-Interest Bearing
Year Interest
Payment Expense Principal Amortization Balance
2013
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Serial – Interest Bearing Ordinary Annuity
Year Interest
Payment Expense Principal Amortization Balance
2013
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Serial – Interest Bearing Annuity Due
Year Interest
Payment Expense Principal Amortization Balance
01-01-13
01-01-13
01-01-14
01-01-15
01-01-16
01-01-17
Danes Derick C. Dolz | 4
You might also like
- CFA Level 1 Calculation Workbook: 300 Calculations to Prepare for the CFA Level 1 Exam (2023 Edition)From EverandCFA Level 1 Calculation Workbook: 300 Calculations to Prepare for the CFA Level 1 Exam (2023 Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- CFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- JSMSC - TDv3 6 20Document251 pagesJSMSC - TDv3 6 20Jason20170% (1)
- USA Gas TurbineDocument4 pagesUSA Gas TurbineJustin MercadoNo ratings yet
- Accounting 21 Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 1Document5 pagesAccounting 21 Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 1Faith BariasNo ratings yet
- Shs General Mathematics q2 m4Document16 pagesShs General Mathematics q2 m4Christian Leimer Gahisan100% (1)
- TVM Quiz ReviewerDocument3 pagesTVM Quiz ReviewerAra FloresNo ratings yet
- ANNUITY Econ Review Problems Sep 25, 2019 QDocument4 pagesANNUITY Econ Review Problems Sep 25, 2019 QzybelleNo ratings yet
- Problems Chapters 4 and 5 RevisedDocument3 pagesProblems Chapters 4 and 5 RevisedKyla Alyssa SamiaNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Q2 Week 4 1Document11 pagesGeneral Mathematics Q2 Week 4 1Santos, Mart Czendric Y.No ratings yet
- MS 3411 Risks Returns and Capital StructureDocument4 pagesMS 3411 Risks Returns and Capital StructureMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Economics Simple InterestDocument8 pagesEconomics Simple InterestbabadapbadapNo ratings yet
- MMI1060 Fall 2022 - Class 1 - TVM - STUDENTDocument23 pagesMMI1060 Fall 2022 - Class 1 - TVM - STUDENTxtremewhizNo ratings yet
- Local Media7317823616470129558Document2 pagesLocal Media7317823616470129558Jeffrey RegondolaNo ratings yet
- Final Examination in General MathematicsDocument1 pageFinal Examination in General MathematicsBeberly LocsinNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Lesson-Exemplar - Module 4Document15 pagesBusiness Finance Lesson-Exemplar - Module 4Divina Grace Rodriguez - Librea100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Valuation of Stocks and Bonds: 2.1 Time Value of MoneyDocument61 pagesChapter 2: Valuation of Stocks and Bonds: 2.1 Time Value of MoneyDhara dhakadNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets: Example, Requires Compounded Semiannualiy. Equivalent CompoundedDocument5 pagesProblem Sets: Example, Requires Compounded Semiannualiy. Equivalent CompoundedvineethNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument35 pagesTime Value of MoneysandhurstalabNo ratings yet
- Fmac315 Quiz-Bee Qbeehan 11.14.2023 Am32Document28 pagesFmac315 Quiz-Bee Qbeehan 11.14.2023 Am32renelyn.cas06No ratings yet
- GCT CIVIL ENGINEERING REVIEW CLASS NOTESDocument2 pagesGCT CIVIL ENGINEERING REVIEW CLASS NOTESUnknown Engr.No ratings yet
- ENGINEERING ECONOMY CALCULATIONSDocument2 pagesENGINEERING ECONOMY CALCULATIONSrenzon272No ratings yet
- Measuring Investment ReturnsDocument8 pagesMeasuring Investment ReturnsErrah Jenn CajesNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Simple and CompoundDocument42 pages2.1 Simple and CompoundEmmanuel SulitNo ratings yet
- Probset EeconDocument3 pagesProbset Eecongail0% (1)
- Practice-Problems-9_EconDocument2 pagesPractice-Problems-9_EconJayve BasconNo ratings yet
- Simple and Compound InterestDocument2 pagesSimple and Compound InterestJeffrey Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Acelec 331 Summative1 Set ADocument5 pagesAcelec 331 Summative1 Set ALost AlienNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Problem Solving For Engineering EconomyDocument2 pagesLecture 8 - Problem Solving For Engineering Economyangelo diazNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument3 pagesFinal ExamJaninelaraNo ratings yet
- BusinessFinance M7-EDITED Removed-1Document21 pagesBusinessFinance M7-EDITED Removed-1Darren PulidoNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING ECONOMY REVIEWERDocument51 pagesENGINEERING ECONOMY REVIEWERRoss Sonny Cruz100% (2)
- Bmath A Revisit 1Document5 pagesBmath A Revisit 1Dettie BanawolNo ratings yet
- Populi - John - Nouel - B. - AT2B.docx - Filename UTF-8''Populi, John Nouel B. AT2BDocument8 pagesPopuli - John - Nouel - B. - AT2B.docx - Filename UTF-8''Populi, John Nouel B. AT2BKindred WolfeNo ratings yet
- General Math Second Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesGeneral Math Second Quarter ExamShiena Rhose Lucero100% (1)
- Engineering EconomyDocument53 pagesEngineering EconomyPaulo Emmanuele BetitaNo ratings yet
- NUt 6 SA9 SSN 65Document38 pagesNUt 6 SA9 SSN 65Don RomantikoNo ratings yet
- FAR-4214 (Bonds - Other Long-Term Liabilities)Document4 pagesFAR-4214 (Bonds - Other Long-Term Liabilities)saligumba mikeNo ratings yet
- Practice-Problems-Econ (1)Document2 pagesPractice-Problems-Econ (1)Jayve BasconNo ratings yet
- CHPT 4Document41 pagesCHPT 4ferahNo ratings yet
- 4 - AnnuityDocument13 pages4 - AnnuityAngel GraceNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomyDocument4 pagesEngineering EconomyRochelle Louise SampagaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of InvestmentDocument60 pagesMathematics of InvestmentJoshua FajardoNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING ECONOMY PRACTICE PROBLEMSDocument2 pagesENGINEERING ECONOMY PRACTICE PROBLEMSRyan CalicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1b - Time Value of Money-1Document33 pagesChapter 1b - Time Value of Money-1VENKATA SAI KRISHNA YAGANTINo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics: Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesEngineering Economics: Multiple ChoiceAlfredo CondeNo ratings yet
- PACKET 1-Lesson1Document8 pagesPACKET 1-Lesson1Irene VillasNo ratings yet
- General Math Second Quarter Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesGeneral Math Second Quarter Exam ReviewAgnes Ramo100% (1)
- Module in General Mathematics Grade 11 Second Quarter, Week 3 To Week 4Document39 pagesModule in General Mathematics Grade 11 Second Quarter, Week 3 To Week 4Hanseuuu100% (1)
- GENERAL MATHEMATICS 11 2nd Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesGENERAL MATHEMATICS 11 2nd Quarter ExamPOTENCIANO JR TUNAY100% (1)
- Time Value of Money Time Value of MoneyDocument29 pagesTime Value of Money Time Value of MoneyEunice Dimple CaliwagNo ratings yet
- Engg EconDocument6 pagesEngg EconSean Earl NapeNo ratings yet
- Homework4 With Ans JDocument18 pagesHomework4 With Ans JBarakaNo ratings yet
- Mid - Term - Performance Assessment 1 - Time Value of Money: Multiple Choice Questions Problem Solving (100 Points)Document4 pagesMid - Term - Performance Assessment 1 - Time Value of Money: Multiple Choice Questions Problem Solving (100 Points)Nathaniel IricaNo ratings yet
- OrdinaryAnnuity Part2Document12 pagesOrdinaryAnnuity Part2Kim TNo ratings yet
- Capitalized CostDocument2 pagesCapitalized CostEstera ShawnNo ratings yet
- PRELEC1 Final ExamDocument4 pagesPRELEC1 Final ExamAramina Cabigting BocNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesPractice ProblemsThalia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Activity - Capital Investment AnalysisDocument5 pagesActivity - Capital Investment AnalysisKATHRYN CLAUDETTE RESENTENo ratings yet
- Test Question For Math 12Document5 pagesTest Question For Math 12Ernie Lahaylahay100% (1)
- Midterm exam questions on capital budgeting, break-even analysis, loans, NPVDocument1 pageMidterm exam questions on capital budgeting, break-even analysis, loans, NPVJoebel CristalesNo ratings yet
- EE4Document40 pagesEE4Jeiel Valencia0% (1)
- Millenials & Gen-ZDocument6 pagesMillenials & Gen-ZJessie John Credo Jr.No ratings yet
- Doctrines Under Political LawDocument3 pagesDoctrines Under Political LawJessie John Credo Jr.No ratings yet
- GEC 19 ClassDocument82 pagesGEC 19 ClassJessie John Credo Jr.No ratings yet
- IA1-Handouts-01-Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesIA1-Handouts-01-Cash and Cash EquivalentsJessie John Credo Jr.No ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument13 pagesEnzyme KineticsMohib100% (1)
- FLG 212 Study GuideDocument19 pagesFLG 212 Study GuidecynthiaNo ratings yet
- Python operators and data types quizDocument34 pagesPython operators and data types quizATUL SHARMANo ratings yet
- Assignement 4Document6 pagesAssignement 4sam khanNo ratings yet
- ANNEXURE IV Dec 2022 enDocument17 pagesANNEXURE IV Dec 2022 enadvocacyindyaNo ratings yet
- BRTU-2000 Remote Terminal Unit for High Voltage NetworksDocument2 pagesBRTU-2000 Remote Terminal Unit for High Voltage NetworksLaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Machining (LBM)Document10 pagesLaser Beam Machining (LBM)RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Invoice Request for Digitize Global InovasiDocument1 pageInvoice Request for Digitize Global InovasiAsa Arya SudarmanNo ratings yet
- Dental Pulp TissueDocument77 pagesDental Pulp TissueJyoti RahejaNo ratings yet
- D-2 UTEP Currey Final ReportDocument23 pagesD-2 UTEP Currey Final ReporthmcNo ratings yet
- Dbms PracticalDocument31 pagesDbms Practicalgautamchauhan566No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy Business Management 2: Learning PacketDocument33 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy Business Management 2: Learning PacketArjae Dantes50% (2)
- Kaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010Document34 pagesKaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010markdavidboydNo ratings yet
- Tepache Kulit Nanas Sebagai Bahan Campuran Minuman 28 37Document10 pagesTepache Kulit Nanas Sebagai Bahan Campuran Minuman 28 37nabila sukmaNo ratings yet
- Consumer PerceptionDocument61 pagesConsumer PerceptionPrakhar DwivediNo ratings yet
- English 9Document26 pagesEnglish 9Joann Gaan YanocNo ratings yet
- Proposal Setting Gi Punagaya - R1Document31 pagesProposal Setting Gi Punagaya - R1wandy RJNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Document788 pagesProduct Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Eric GarciaNo ratings yet
- NAFTA CertificateDocument2 pagesNAFTA Certificateapi-522706100% (4)
- Asian Paint FMVRDocument20 pagesAsian Paint FMVRdeepaksg787No ratings yet
- Body Mechanics and Movement Learning Objectives:: by The End of This Lecture, The Student Will Be Able ToDocument19 pagesBody Mechanics and Movement Learning Objectives:: by The End of This Lecture, The Student Will Be Able TomahdiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Methods in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesTeaching Methods in The PhilippinesTonee Marie Gabriel60% (5)
- OSK Ekonomi 2016 - SoalDocument19 pagesOSK Ekonomi 2016 - SoalputeNo ratings yet
- MDF 504 Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management 61017926Document3 pagesMDF 504 Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management 61017926komalkataria2003No ratings yet
- Transportation Chapter 3Document17 pagesTransportation Chapter 3Tuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Sample Id: Sample Id: 6284347 Icmr Specimen Referral Form Icmr Specimen Referral Form For For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2)Document2 pagesSample Id: Sample Id: 6284347 Icmr Specimen Referral Form Icmr Specimen Referral Form For For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2)Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Barcode BasicsDocument3 pagesBarcode Basicsnikhilbajpai_88No ratings yet
- Boost productivity and networking with a co-working café in Iligan CityDocument4 pagesBoost productivity and networking with a co-working café in Iligan CityJewel Cabigon0% (1)