Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lovely May A. M-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Rose ann OlaerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lovely May A. M-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Rose ann OlaerCopyright:
Available Formats
“The ECOSYSTEM”
Lovely may A. Magdaong
B.S in tourism and management
1st year
Science and technology
(Term paper)
-jasmine zyra Erandio
INTRODUCTION:
An ecosystem consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they
interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles
and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into
plant tissue.
Ecosystem diversity addresses the combined characteristics of biotic properties
(biodiversity) and abiotic properties (geodiversity). It is the variation in the ecosystems
found in a region or the variation in ecosystems over the whole planet.
Ecosystems have no particular size. An ecosystem can be as large as a desert or as small as a
tree. The major parts of an ecosystem are: water, water temperature, plants, animals, air,
light and soil.
The living organisms in an ecosystem can be divided into three categories: producers,
consumers and decomposers. They are all important parts of an ecosystem. Producers are
the green plants.
The ecosystem is the structural and functional unit of ecology where the living organisms.
interact with each other and the surrounding environment. In other words, an ecosystem is
a. chain of interaction between organisms and their environment.
There are three broad categories of ecosystems based on their general environment:
freshwater, marine, and terrestrial.The World Ocean is the largest existing ecosystem on our
planet.
Environment refers to the surroundings, whereas, ecosystem is the interaction between the
environment and the living organisms. Environment is the area where living organisms live.
Ecosystem is the community where the biotic and abiotic elements interact with each other
Ecosystem structure is a network of interactions between abiotic and biotic components of
the system. The biotic structure of the ecosystem is characterized by the composition of the
biological community including species numbers, biomass, life-form, life-history and spatial
distribution of species.
BODY AND CONCLUSION:
Ecosystem diversity deals with the study of different ecosystems in a certain location and
their overall effects on humans and the environment as a whole. It is one of the types of
biodiversity along with species diversity, genetic diversity, and functional diversity.
Ecosystem diversity focuses on both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Also, it includes the
variation of a biological community such as the number of levels of ecosystem diversity and
different niches or habitat diversity, and other ecological processes. Ecosystem diversity has
a great deal on both genetic and species diversity, thus it is coined as the “largest scale of
biodiversity”. Grasslands, tundras, deserts, rainforests, terrestrial and marine ecosystems,
are some examples of ecosystems that are diverse and contribute a lot to creating a well-
balanced environment.
The wide variety of species that takes place in a specific region is known as its species
richness. It is defined as the species richness in any habitat and is the common currency of
the examination of biodiversity. Species richness index is a degree of the wide variety of
species in a described sampling unit Species richness is a characteristic of sample size.
However, it ought to now no longer be stressed with species abundance. Each natural
habitat has quite a few species, which range in their relative abundance. No community
includes species of identical abundance; a few species are rare, others are common and
nevertheless, others can be abundant. Species variety measures are frequently more
comprehensive and informative than species counts alone. There’s the significance of taking
an organism’s eye view of community variations”. This remark applies to structural diversity
as it’s far from species composition.Resource diversity means the variety of resources that
an organism (species) utilizes. For example, a few fish species withinside the hill-streams
have an extensive trophic niche and depend upon zooplankton, bugs, and algae, and
diatoms for their meals. In many instances, food sources fed on by an organism differ during
specific levels of the life cycle, consisting of fry, fingerling, and adult degrees in the case of
fish. Thus, niche width is the measure of the variety of resources used by a species.
It is the quantity of habitat classification in a defined geographical location. This is an index,
which quantifies the structural complexity of the habitat. This structural complexity of the
environment, in turn, is responsible for the presence of an extensive type of spatial and
trophic niches. This means that if any habitat helps extra microhabitats, its biological
diversity may be greater compared to a habitat that has a much less wide variety of
microhabitats. More research on habitat diversity had been made for terrestrial
environments.The diversity of the ecosystems in a particular geographical location may be
identified and studied so as to understand their overall impact on human existence and the
environment. It can be dealt with at a micro-level (small scale) or at a macro-level (large
scale). Macro-scale ecosystem diversity would therefore be concerned with the variations
in the ecosystems at a large scope, such as oceans, forests, and wetlands. Conversely, small-
scale ecosystem diversity would be interested in the variations in the ecosystems over a
relatively small geographical space or area
You might also like
- The Web of Life: Understanding Ecology and Our Place in ItFrom EverandThe Web of Life: Understanding Ecology and Our Place in ItNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument27 pagesBiodiversityLawrence LeyesaNo ratings yet
- ScopeDocument7 pagesScopemkray0No ratings yet
- Kaawaan Niyo Kami!!!Document36 pagesKaawaan Niyo Kami!!!Karen PrimeroNo ratings yet
- Ecology AND Economic DevelopmentDocument24 pagesEcology AND Economic Developmentjohanna sequeiraNo ratings yet
- Tejas Patil EvsDocument13 pagesTejas Patil EvsAtharva LakhanNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology - EcologyDocument74 pagesCSEC Biology - EcologyRic Flamboyant FraserNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - Biodiversity - Science, Technology and SocietyDocument7 pagesSection 2 - Biodiversity - Science, Technology and SocietyclpagtalunanNo ratings yet
- Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument3 pagesLiving Things and Their EnvironmentVergzMonch EspielNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument25 pagesBiodiversityOrane CassanovaNo ratings yet
- EM Module3 Q1 2 6 7 PDFDocument10 pagesEM Module3 Q1 2 6 7 PDFSnehal KoliNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Their ServicesDocument22 pagesEcosystem and Their ServicesMauro Valdivia CarterNo ratings yet
- Levels of BiodiversityDocument4 pagesLevels of BiodiversitySachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Week 3 ModuleDocument34 pagesWeek 3 ModuleLaxamana, MarcNo ratings yet
- Convention On Biological DiversityDocument10 pagesConvention On Biological DiversityAmol ToraskarNo ratings yet
- As 110 & Ae 23 Group 8Document25 pagesAs 110 & Ae 23 Group 8Richan RulogNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Derive Energy Earth Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Hydrogen Sulfide Water Lithosphere HydrosphereDocument21 pagesAtmosphere Derive Energy Earth Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Hydrogen Sulfide Water Lithosphere HydrosphereSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Ecology Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesConcepts of Ecology Lecture NotesOguh AugustineNo ratings yet
- Ecology of Life: Group 1 Bayrante, Angelo Cañeso, Francia F. Foliente, Erish Paul Ponciano, Jovelt Sahurda, Christine BDocument12 pagesEcology of Life: Group 1 Bayrante, Angelo Cañeso, Francia F. Foliente, Erish Paul Ponciano, Jovelt Sahurda, Christine BPaul VallegaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life 1Document61 pagesEarth and Life 1Glyneth Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Variety and Ecology of The Living WorldDocument7 pagesVariety and Ecology of The Living WorldIqra SadiqNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Explore the Diversity of Life on Earth with Environmental Science Activities for KidsFrom EverandBiodiversity: Explore the Diversity of Life on Earth with Environmental Science Activities for KidsNo ratings yet
- Biosphere and Diversity of Life ExplainedDocument21 pagesBiosphere and Diversity of Life ExplainedSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and EcosystemsDocument4 pagesBiodiversity and EcosystemsNandini SharmaNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument79 pagesEcologylastyngugiNo ratings yet
- Ecological Forces & Sustainability: Department of Architecture Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, GwaliorDocument46 pagesEcological Forces & Sustainability: Department of Architecture Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, GwaliorAjitAgrawalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry, Le# 3 (Dr. Adeela Naureen)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry, Le# 3 (Dr. Adeela Naureen)Sadaf BatoolNo ratings yet
- Environment 28 FebDocument2 pagesEnvironment 28 Feb170130636.tapiaNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITY StsDocument6 pagesBIODIVERSITY StsDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Conservation IntroductionDocument22 pagesBiodiversity Conservation IntroductionSOHEL BANGINo ratings yet
- 0 EcosystemDocument3 pages0 EcosystemAnghellycha ParadaNo ratings yet
- Ecology DefinitionsDocument5 pagesEcology DefinitionsSeth VandenbergNo ratings yet
- Ecology A Branch of Biology (From Greek: "House" and "Study Of") Is TheDocument4 pagesEcology A Branch of Biology (From Greek: "House" and "Study Of") Is TheImmanuel HostNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity CHAPTER 3Document204 pagesBiodiversity CHAPTER 3Chaitanya LingamNo ratings yet
- Concept of EcosystemDocument2 pagesConcept of EcosystemPalashNo ratings yet
- Mod 7 INTERACTION AND INTERDEPENDENCEDocument4 pagesMod 7 INTERACTION AND INTERDEPENDENCErvsfbwhf82No ratings yet
- Ecosystems and Population ChangeDocument36 pagesEcosystems and Population ChangeNicole DennillNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and EcosystemsDocument4 pagesBiodiversity and EcosystemsRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Meve 14Document9 pagesMeve 14Prime VideoNo ratings yet
- Understanding BiodiversityDocument4 pagesUnderstanding BiodiversityEyna Syafina Nik ManNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity AssignmentDocument8 pagesBiodiversity AssignmentAngelica Irish Tolentino100% (1)
- Ensci NotesDocument7 pagesEnsci NotesJen PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Module1-Environment and Sustainability (Introduction)Document13 pagesModule1-Environment and Sustainability (Introduction)Vishwanth Sagar SNo ratings yet
- What Is BiodiversityDocument13 pagesWhat Is BiodiversitySachin NarangNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDocument22 pagesUnit Ii Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDevraj KhudotiyaNo ratings yet
- 1.pengantar Ekosistem, Lingkungan Hidup Dan GeografiDocument8 pages1.pengantar Ekosistem, Lingkungan Hidup Dan Geografimobster44No ratings yet
- Biology and EcologyDocument5 pagesBiology and EcologykarennNo ratings yet
- Types of Biodiversity: Genetic, Species, EcosystemDocument2 pagesTypes of Biodiversity: Genetic, Species, EcosystemCristianNo ratings yet
- Ecology: Arris Cristever Evarola BSCOE-IV Irish Veronica Cruz Bscoe-Iv Lilet Licuanan Bscoe-IvDocument8 pagesEcology: Arris Cristever Evarola BSCOE-IV Irish Veronica Cruz Bscoe-Iv Lilet Licuanan Bscoe-IvArrah CristelleNo ratings yet
- Community EcologyDocument4 pagesCommunity EcologyBiju ThomasNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument13 pagesBiodiversitySanjay JadhavNo ratings yet
- What Is BiodiversityDocument4 pagesWhat Is BiodiversityJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Bba312 PDFDocument107 pagesBba312 PDFSahil KalraNo ratings yet
- FY Lecture Notes BiodiversityDocument2 pagesFY Lecture Notes Biodiversityvijend100% (2)
- Ecological Concepts Introduction To Environmental Engineering and Ecology of LifeDocument16 pagesEcological Concepts Introduction To Environmental Engineering and Ecology of LifeJhasper FLores0% (1)
- Types of EcologyDocument8 pagesTypes of EcologypriyaNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document1 pageNotes 2mohdaltafbro92No ratings yet
- Scope of EcologyDocument11 pagesScope of Ecologybrowneyes_luke6052100% (3)
- Rose Ann MiceDocument21 pagesRose Ann MiceRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Safe & Quality " Travel Agency: Conquer The Word With The Best Travel Agency "Document1 pageSafe & Quality " Travel Agency: Conquer The Word With The Best Travel Agency "Rose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Volleyball (P.e)Document20 pagesVolleyball (P.e)Rose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Rooms Division OperationsDocument20 pagesRooms Division OperationsRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Lit Up WPS - OfficeDocument5 pagesLit Up WPS - OfficeRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy Promises and RisksDocument3 pagesGene Therapy Promises and RisksRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Top Aurora tourist attractions under 40 charactersDocument2 pagesTop Aurora tourist attractions under 40 charactersRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Tourist RoseannDocument14 pagesTourist RoseannRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and EcosystemsDocument4 pagesBiodiversity and EcosystemsRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Rose Ann MiceDocument20 pagesRose Ann MiceRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Synopsis 0.1Document1 pageSynopsis 0.1Rose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity's Role in Human Health and SocietyDocument3 pagesBiodiversity's Role in Human Health and SocietyRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
- Rachel Global Food Security in Todays WorldDocument10 pagesRachel Global Food Security in Todays WorldRose ann OlaerNo ratings yet
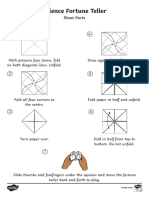
- Plant Parts Science Fortune TellerDocument2 pagesPlant Parts Science Fortune TellerNguyen DuongNo ratings yet
- Efektifitas Trico Dan Fungisida Propineb Dalam Pengendalian Penyakit Karat Pada Bawang DaunDocument14 pagesEfektifitas Trico Dan Fungisida Propineb Dalam Pengendalian Penyakit Karat Pada Bawang DaunMuhammad AzisNo ratings yet
- Varbal Analytic and Quantitaive ReasoningDocument44 pagesVarbal Analytic and Quantitaive ReasoningTauqeer Hassan100% (1)
- Statistical techniques in plant breedingDocument2 pagesStatistical techniques in plant breedingrifad najibNo ratings yet
- GK Worksheets for Places, Transport, Animals & IndiaDocument4 pagesGK Worksheets for Places, Transport, Animals & IndiaShourya RajputNo ratings yet
- STS-Finals - Andes, Juvic A. BSA1G2Document11 pagesSTS-Finals - Andes, Juvic A. BSA1G2Juvic AndesNo ratings yet
- Projektovanje I Izgradnja Zelenih Krovova U Funkciji Zaštite Životne Sredine 77500Document8 pagesProjektovanje I Izgradnja Zelenih Krovova U Funkciji Zaštite Životne Sredine 77500kacavukovic87No ratings yet
- ECO WorkbookDocument17 pagesECO Workbookdaniwilson245No ratings yet
- Topic: Learning To Be A Better Student: Course Code and Title: GE 101 - Understanding The SelfDocument9 pagesTopic: Learning To Be A Better Student: Course Code and Title: GE 101 - Understanding The SelfAliana Mariz BolañosNo ratings yet
- Examenes Del 1 Al 4Document10 pagesExamenes Del 1 Al 4DAVID ALEJANDRO MUÑOZ BETANCURNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 7.Document3 pagesActivity No. 7.ALEXA JOIE CONCEPCION ARMONIANo ratings yet
- Boundless Biology Study Guides - 1702859293714Document9 pagesBoundless Biology Study Guides - 1702859293714Kayizzi SilverNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement PostersDocument7 pagesThesis Statement Postersafcnzfamt100% (2)
- GenomicsDocument3 pagesGenomicsSUMEDHA PALLANo ratings yet
- Sigma Xi, The Scientific Research SocietyDocument10 pagesSigma Xi, The Scientific Research SocietyDeive AlvesNo ratings yet
- Reading Exam 2 Pialp 2019-2020Document3 pagesReading Exam 2 Pialp 2019-2020Judithea CMNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 6: Evidence of EvolutionDocument32 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 6: Evidence of EvolutionJennifer LomboyNo ratings yet
- Ebook Discover Biology 6Th Edition Singh Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesEbook Discover Biology 6Th Edition Singh Test Bank Full Chapter PDFjamesreedycemzqadtp100% (10)
- UNIT 2 Notes PDFDocument88 pagesUNIT 2 Notes PDFAjNo ratings yet
- 9781003287056_12-1201Document256 pages9781003287056_12-1201Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Stop codon mutation caused Lucy's immunodeficiencyDocument2 pagesStop codon mutation caused Lucy's immunodeficiencySnowmobilepicsfromcanada 12No ratings yet
- General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument1 pageGeneral Biology 2 ReviewerAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- Stedman's AnatomyDocument31 pagesStedman's AnatomyHein Aung ZawNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Human Skeleton and Muscles: Energy Flows Question Loop Speaking ActivityDocument3 pagesWorksheet Human Skeleton and Muscles: Energy Flows Question Loop Speaking ActivityMaksym BuchekNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Earth Science: Bachelor of Applied Science (Natural Resource Science) With HonoursDocument17 pagesFaculty of Earth Science: Bachelor of Applied Science (Natural Resource Science) With HonoursNALINI MANIMARANNo ratings yet
- Stem - Bio11 /12-La-C-5: Wake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsDocument2 pagesStem - Bio11 /12-La-C-5: Wake Up, Eat Breakfast and Get Ready For The Scheduled LessonsMarianne GonzalesNo ratings yet
- (Environmental and Microbial Biotechnology) Ram Prasad, Shi-Hong Zhang - Beneficial Microorganisms in Agriculture-Springer (2022)Document356 pages(Environmental and Microbial Biotechnology) Ram Prasad, Shi-Hong Zhang - Beneficial Microorganisms in Agriculture-Springer (2022)paulocesarNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone and The Alveolar ProcessDocument15 pagesAlveolar Bone and The Alveolar ProcessSebastián BernalNo ratings yet
- A Career in Chromosomes: Matters! Matters!Document1 pageA Career in Chromosomes: Matters! Matters!Hartford CourantNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Science Chapter OverviewDocument2 pagesIntroduction to Science Chapter Overviewemanu frnandezNo ratings yet