Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C++ Circular Queue Data Structure
Uploaded by
Ishaan kataraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C++ Circular Queue Data Structure
Uploaded by
Ishaan kataraCopyright:
Available Formats
Circular Queue Data Structure
In this tutorial, you will learn what a circular queue is. Also, you will find
implementation of circular queue in C, C++, Java and Python.
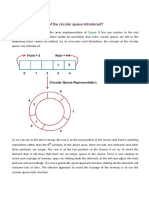
A circular queue is the extended version of a regular queue where the last
element is connected to the first element. Thus forming a circle-like
structure.
Circular queue representation
The circular queue solves the major limitation of the normal queue. In a
normal queue, after a bit of insertion and deletion, there will be non-usable
empty space.
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
Limitation of the
regular Queue
Here, indexes 0 and 1 can only be used after resetting the queue (deletion
of all elements). This reduces the actual size of the queue.
How Circular Queue Works
Circular Queue works by the process of circular increment i.e. when we try
to increment the pointer and we reach the end of the queue, we start from
the beginning of the queue.
Here, the circular increment is performed by modulo division with the queue
size. That is,
if REAR + 1 == 5 (overflow!), REAR = (REAR + 1)%5 = 0 (start of queue)
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
Circular Queue Operations
The circular queue work as follows:
• two pointers FRONT and REAR
• FRONT track the first element of the queue
• REAR track the last elements of the queue
• initially, set value of FRONT and REAR to -1
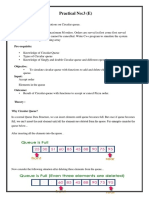
1. Enqueue Operation
• check if the queue is full
• for the first element, set value of FRONT to 0
• circularly increase the REAR index by 1 (i.e. if the rear reaches the end,
next it would be at the start of the queue)
• add the new element in the position pointed to by REAR
2. Dequeue Operation
• check if the queue is empty
• return the value pointed by FRONT
• circularly increase the FRONT index by 1
• for the last element, reset the values of FRONT and REAR to -1
However, the check for full queue has a new additional case:
• Case 1: FRONT = 0 && REAR == SIZE - 1
• Case 2: FRONT = REAR + 1
The second case happens when REAR starts from 0 due to circular increment
and when its value is just 1 less than FRONT , the queue is full.
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
Enque and Deque Operations
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
Circular Queue Implementations in C++
The most common queue implementation is using arrays, but it can also be
implemented using lists.
// Circular Queue implementation in C++
#include <iostream>
#define SIZE 5 /* Size of Circular Queue */
using namespace std;
class Queue {
private:
int items[SIZE], front, rear;
public:
Queue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Check if the queue is full
bool isFull() {
if (front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1) {
return true;
}
if (front == rear + 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Check if the queue is empty
bool isEmpty() {
if (front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Adding an element
void enQueue(int element) {
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue is full";
} else {
if (front == -1) front = 0;
rear = (rear + 1) % SIZE;
items[rear] = element;
cout << endl
<< "Inserted " << element << endl;
}
}
// Removing an element
int deQueue() {
int element;
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty" << endl;
return (-1);
} else {
element = items[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Q has only one element,
// so we reset the queue after deleting it.
else {
front = (front + 1) % SIZE;
}
return (element);
}
}
void display() {
// Function to display status of Circular Queue
int i;
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << endl
<< "Empty Queue" << endl;
} else {
cout << "Front -> " << front;
cout << endl
<< "Items -> ";
for (i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % SIZE)
cout << items[i];
cout << items[i];
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
cout << endl
<< "Rear -> " << rear;
}
}
};
int main() {
Queue q;
// Fails because front = -1
q.deQueue();
q.enQueue(1);
q.enQueue(2);
q.enQueue(3);
q.enQueue(4);
q.enQueue(5);
// Fails to enqueue because front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1
q.enQueue(6);
q.display();
int elem = q.deQueue();
if (elem != -1)
cout << endl
<< "Deleted Element is " << elem;
q.display();
q.enQueue(7);
q.display();
// Fails to enqueue because front == rear + 1
q.enQueue(8);
return 0;
}
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
Circular Queue Complexity Analysis
The complexity of the enqueue and dequeue operations of a circular queue
is O(1) for (array implementations).
Applications of Circular Queue
• CPU scheduling
• Memory management
• Traffic Management
Website: www.vcaretechnicalinstitute.com For Batches Call Now: +91-8319004365
You might also like
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Akshat Kumar - Data Structures & AlgorithmDocument18 pagesAkshat Kumar - Data Structures & AlgorithmJYOTIRMOY CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- 8 QueueDocument26 pages8 QueueANANT SHARMANo ratings yet
- CH8 - QueuesDocument30 pagesCH8 - QueuesAbdi NegassaNo ratings yet
- LEC - 3 QueueDocument23 pagesLEC - 3 Queuedemro channelNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - QueueDocument17 pagesModule 6 - QueuearturogallardoedNo ratings yet
- DS Circular Queue - JavatpointDocument13 pagesDS Circular Queue - JavatpointGovinda DasNo ratings yet
- DS Unit 2-NotesDocument68 pagesDS Unit 2-NotesAmisha ShettyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 5 - DS - QueuesDocument29 pagesLecture 4 5 - DS - QueuesMp Inayat UllahNo ratings yet
- Circular Queue OperationsDocument4 pagesCircular Queue OperationsakurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- CS 319 - 8 QueuesDocument65 pagesCS 319 - 8 QueuesAyesha FarooqNo ratings yet
- Ds Unit2Document28 pagesDs Unit2Azeem AnsariNo ratings yet
- LAB TASK 6-Circular Queue and Implementation of Deque Using Circular ArrayDocument14 pagesLAB TASK 6-Circular Queue and Implementation of Deque Using Circular ArrayMohsin MajeedNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument61 pagesQueue20F128LAVEENKUMAR L ITANo ratings yet
- QueuesDocument25 pagesQueuesvanishkagNo ratings yet
- QueuesDocument18 pagesQueuescalvinakiweley54No ratings yet
- Queues in Data Structure Using CDocument52 pagesQueues in Data Structure Using CKaran RoyNo ratings yet
- 7Document40 pages7minutesacademyofficialNo ratings yet
- Data Structures & AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesData Structures & AlgorithmsHuzaifa UbaidNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: The QueuesDocument37 pagesData Structures: The Queuesshawal aliNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument33 pagesQueueBhupesh DhapolaNo ratings yet
- BCS304 - DataDocument17 pagesBCS304 - Datablank accountNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument21 pagesQueueMerry SinghNo ratings yet
- FIFO Queues ExplainedDocument50 pagesFIFO Queues ExplainedBimbo De LeonNo ratings yet
- Queue ADT Implementation and Applications in 40 CharactersDocument26 pagesQueue ADT Implementation and Applications in 40 CharactersSri Pritika BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- DSA QueueDocument32 pagesDSA QueueRiyaz ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 - Dsa Lab FileDocument18 pagesExp 4 - Dsa Lab Fileparamita.chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument55 pagesQueueshahida18No ratings yet
- The Queues: FrontDocument22 pagesThe Queues: FrontSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- DSA Lec 9-10 (Queues)Document54 pagesDSA Lec 9-10 (Queues)M.No ratings yet
- Data Structures & Algorithms: Dated: 06-12-2010Document45 pagesData Structures & Algorithms: Dated: 06-12-2010Vicky ButtNo ratings yet
- Unit II Linear Data StructuresDocument25 pagesUnit II Linear Data StructuresLavanya JNo ratings yet
- Assignment No:14Document4 pagesAssignment No:14Ayush SinhaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Theory 2Document4 pagesExperiment Theory 2soham kulkarniNo ratings yet
- DS-Lecture 13 & 14 QueuesDocument40 pagesDS-Lecture 13 & 14 QueuesFaizan HameedNo ratings yet
- QueusDocument25 pagesQueusNisha JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Circular Queue Datastructure ExplainedDocument10 pagesCircular Queue Datastructure ExplainedPUB-G DREAMINGNo ratings yet
- CJCDDHJXHCJDocument15 pagesCJCDDHJXHCJAditya BajpaiNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument8 pagesQueueZainab NadeemNo ratings yet
- CSC 221 DSA Queue Arrays - Linked List Implementation 10032023 055715pmDocument59 pagesCSC 221 DSA Queue Arrays - Linked List Implementation 10032023 055715pmKumail RazaNo ratings yet
- Notes To The StudentsDocument21 pagesNotes To The Studentssai suryaNo ratings yet
- Theory PDFDocument26 pagesTheory PDFNibedan PalNo ratings yet
- Module 2 QueueDocument11 pagesModule 2 QueueHarshitha DeviNo ratings yet
- Algorithm For Insertion in A Circular QueueDocument3 pagesAlgorithm For Insertion in A Circular QueuesatNo ratings yet
- Queue ADT Chapter ExplainedDocument33 pagesQueue ADT Chapter ExplainedbharathkumarNo ratings yet
- DataStructure - Circular, Double Ended, Priority QueuesDocument29 pagesDataStructure - Circular, Double Ended, Priority Queuesaliyaraza150% (2)
- Queue: SE Computer Engineering Unit VIDocument25 pagesQueue: SE Computer Engineering Unit VIA-56- Priyanaka PawarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Data Structure QueueDocument32 pagesLecture 4 Data Structure QueueSello HlabeliNo ratings yet
- DSA Lab 3 - Queue Implementation and Palindrome CheckDocument18 pagesDSA Lab 3 - Queue Implementation and Palindrome CheckHASSAN MALIKNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument16 pagesQueueLol TelrNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Array Implementation of Circular Queue - GeeksforGeeks-5Document17 pagesIntroduction and Array Implementation of Circular Queue - GeeksforGeeks-5ENG19CS0357 Vedha Murthy N LNo ratings yet
- Java PracticalsDocument8 pagesJava Practicalss1062230079No ratings yet
- 08 Queue and Circular QueueDocument37 pages08 Queue and Circular QueueHaseeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Implementing Queues in Arrays and Linked ListsDocument20 pagesImplementing Queues in Arrays and Linked ListsSantosh Kumar DevalNo ratings yet
- Queue 1Document15 pagesQueue 1focaba4283No ratings yet
- Lech 8Document5 pagesLech 8MUSTAFA BshNo ratings yet
- DS Lab 7Document13 pagesDS Lab 7Harsh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- lec 7Queue final.pptxDocument16 pageslec 7Queue final.pptxPrince ZaidNo ratings yet
- Queues: Front RearDocument17 pagesQueues: Front RearNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- CSN 102: Data Structures: Queue: Queue Fundamentals, Application of QueueDocument23 pagesCSN 102: Data Structures: Queue: Queue Fundamentals, Application of QueueAgrim DewanNo ratings yet
- C++ Linked List OperationsDocument10 pagesC++ Linked List OperationsIshaan kataraNo ratings yet
- C++ Linked List Data StructureDocument5 pagesC++ Linked List Data StructureIshaan kataraNo ratings yet
- 15.1 C++ Circular Linked ListDocument13 pages15.1 C++ Circular Linked ListIshaan kataraNo ratings yet
- 15.2 C++ Doubly Linked ListDocument19 pages15.2 C++ Doubly Linked ListIshaan kataraNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document112 pagesModule 2Amrutha VarshaNo ratings yet
- 2021 01 26 DUET CSE UGP Course Curriculum A4 1Document419 pages2021 01 26 DUET CSE UGP Course Curriculum A4 1Sornali PaulNo ratings yet
- ORA System With VerifyEye Plus Operators ManualDocument193 pagesORA System With VerifyEye Plus Operators Manualmiranda vzlaNo ratings yet
- Logistica GrileDocument17 pagesLogistica GrileAlexandra IulianaNo ratings yet
- What Is Phishing, and How Not To Get CaughtDocument11 pagesWhat Is Phishing, and How Not To Get Caughtdanieljones0094No ratings yet
- Keywords, Ideas, And/or Concepts You Encounter in The Selection. Then Follow The Given Steps To Complete The ActivityDocument2 pagesKeywords, Ideas, And/or Concepts You Encounter in The Selection. Then Follow The Given Steps To Complete The ActivityJulie Basbas-CruzNo ratings yet
- BricsCAD V18 For AutoCAD UsersDocument348 pagesBricsCAD V18 For AutoCAD UsersAnonymous c3ikDa7GLzNo ratings yet
- Applied Art & Design, Sierra College: Program OverviewDocument127 pagesApplied Art & Design, Sierra College: Program OverviewNatalie RisheNo ratings yet
- Graphical Solution Method for Linear Programming ProblemsDocument12 pagesGraphical Solution Method for Linear Programming ProblemsAnne Maerick Jersey OteroNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper FileOpenSecureVirtualDataRoom1Document3 pagesWhitepaper FileOpenSecureVirtualDataRoom1Fxxukup SRNo ratings yet
- ES 4000 Controller Instruction GuideDocument20 pagesES 4000 Controller Instruction GuideВладислав Середа92% (25)
- Easergy P3 Protection Relays - REL52018Document5 pagesEasergy P3 Protection Relays - REL52018gigiopicheli731No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Jean-Baptiste SayDocument5 pagesEntrepreneurship: Jean-Baptiste SayPramod KumarNo ratings yet
- Schlage Le Series Data Sheet 111389Document4 pagesSchlage Le Series Data Sheet 111389vikrNo ratings yet
- 04 Automatic ControlDocument710 pages04 Automatic ControlAngel CelestialNo ratings yet
- Foreign Affairs - 01 2022Document216 pagesForeign Affairs - 01 2022Mary Ostrovska100% (6)
- Exams INWK 6113Document102 pagesExams INWK 6113shiva_201185No ratings yet
- Yeastar S20 Basic SetupDocument4 pagesYeastar S20 Basic SetupRonnie Van DykNo ratings yet
- Grocery Store ProjectDocument88 pagesGrocery Store ProjectSuffyan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Resume 2018-08-03 Jason Lindsay CrockettDocument4 pagesResume 2018-08-03 Jason Lindsay CrockettJason Lindsay CrockettNo ratings yet
- Amazon EC2 AutoscalingDocument212 pagesAmazon EC2 Autoscalingkarthikt27No ratings yet
- SE Lab ManualDocument37 pagesSE Lab ManualKrunal ShahNo ratings yet
- Tenorshare 4ukey 3.5.3 Crack + Registration Code Latest 2024Document8 pagesTenorshare 4ukey 3.5.3 Crack + Registration Code Latest 2024idmserialnumber.netofficialNo ratings yet
- Irregular Adjectives Compared in Communications DevicesDocument6 pagesIrregular Adjectives Compared in Communications DevicescamilaNo ratings yet
- Developed Intelligent Fire Alarm System: Journal of American Science October 2012Document11 pagesDeveloped Intelligent Fire Alarm System: Journal of American Science October 2012Al Amin Hossain SrabonNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: Mental Strain As Field of Action in The 4Th Industrial RevolutionDocument6 pagesSciencedirect: Mental Strain As Field of Action in The 4Th Industrial RevolutionAhmad JaenalNo ratings yet
- Animal Intrusion DetectionDocument18 pagesAnimal Intrusion DetectionABY MOTTY RMCAA20-23No ratings yet
- 20a Solar Power Controller ManualDocument8 pages20a Solar Power Controller ManualVeilleur De ConscienceNo ratings yet
- 100 zTidBits FICON HFP - A ReferenceDocument1 page100 zTidBits FICON HFP - A ReferenceNagaraj PudukotaiNo ratings yet
- ExamsDocument74 pagesExamsLong NguyễnNo ratings yet