Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Warnings
Warnings
Uploaded by
abcdeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Warnings
Warnings
Uploaded by
abcdeCopyright:
Available Formats
Warnings
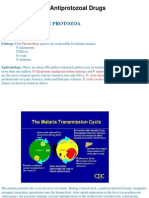
Chloroquine-Resistant Malaria
Chloroquine phosphate is not effective against Chloroquine-or hydroxyChloroquine-
resistant strains of Plasmodium species Chloroquine resistance is widespread in P.
falciparum and is reported in P. vivax. Before using Chloroquine for prophylaxis, it
should be ascertained whether Chloroquine is appropriate for use in the region to
be visited by the traveler. Information regarding the geographic areas where
resistance to Chloroquine occurs, is available at the Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention. Patients infected with a resistant strain of plasmodia as shown by the
fact that normally adequate doses have failed to prevent or cure clinical malaria or
parasitemia should be treated with another form of antimalarial therapy.
Treatment of Exo-Erythrocytic Forms of Malaria
Chloroquine does not treat the hypnozoite liver stage forms of Plasmodium and will
therefore not prevent relapses of malaria due to P. vivax or P. ovale. Additional
treatment with an anti-malarial agent active against these forms, such as an 8-
aminoquinoline, is required for the treatment of infections with P. vivax and P. ovale.
Cardiac Effects
Cases of cardiomyopathy resulting in cardiac failure, in some cases with fatal
outcome, have been reported in patients treated during long term therapy at high
doses with Chloroquine. Monitor for signs and symptoms of cardiomyopathy and
discontinue Chloroquine if cardiomyopathy develops. Chronic toxicity should be
considered when conduction disorders (bundle branch block / atrio-ventricular heart
block) are diagnosed. If cardiotoxicity is suspected, prompt discontinuation of
Chloroquine may prevent life-threatening complications. QT interval prolongation,
torsades de pointes, and ventricular arrhythmias have been reported. The risk is
greater if Chloroquine is administered at high doses. Fatal cases have been reported.
Chloroquine should be used with caution in patients with cardiac disease, a history
of ventricular arrhythmias, uncorrected hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia, or
bradycardia (˂50 bpm), and during concomitant administration with QT interval
prolonging agents due to potential for QT interval prolongation
You might also like
- Antiparasitic Drugs (Antiprotozoal: DR John EgbagbaDocument37 pagesAntiparasitic Drugs (Antiprotozoal: DR John EgbagbaPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Inactive Ingredients: Dibasic Calcium Phosphate USP, Hypromellose USP, Magnesium Stearate NFDocument11 pagesInactive Ingredients: Dibasic Calcium Phosphate USP, Hypromellose USP, Magnesium Stearate NFJuan CaponeNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal DrugsDocument37 pagesAntiprotozoal DrugsMoneto CasaganNo ratings yet
- Plaquenil Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Tablets, UspDocument11 pagesPlaquenil Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Tablets, UspAnmol KudalNo ratings yet
- Anti-Malarial DrugsDocument58 pagesAnti-Malarial Drugs88AKKNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument41 pagesMalariaMohiuddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument3 pagesAnticoagulantsKarthik SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial Drug CologyDocument15 pagesAntimalarial Drug CologyManthan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Eua Chloroquine Fs For HCP 4.3.2020Document7 pagesEua Chloroquine Fs For HCP 4.3.2020Henrique StuckerNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument33 pagesAntimalarial DrugsPinakin Dhirajlal Jadav100% (1)
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome Guidelines 2014Document13 pagesTumor Lysis Syndrome Guidelines 2014Dinesh KamalNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaDocument12 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaStefan HutsonNo ratings yet
- Step-2-Ck-Notes-Syrian-Student - HTML: Cardiology UWDocument15 pagesStep-2-Ck-Notes-Syrian-Student - HTML: Cardiology UWLoyla RoseNo ratings yet
- UK Malaria Treatment GuidelinesDocument11 pagesUK Malaria Treatment GuidelinesikaNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoals Part IDocument46 pagesAntiprotozoals Part IAYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- Endoxan: List of ExcipientsDocument4 pagesEndoxan: List of ExcipientsBashyam RamNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaDocument12 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaLuciano Rodrigues SimoesNo ratings yet
- Anti Malaria LsDocument39 pagesAnti Malaria LsSolaNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Chemical StructureDocument10 pagesProduct Information: Chemical Structureddandan_2No ratings yet
- Malaria Treatment Bis 07Document11 pagesMalaria Treatment Bis 07braggsNo ratings yet
- VernakalantDocument15 pagesVernakalantAkif AhamadNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument5 pagesMalariaMo MonuNo ratings yet
- Malaria PocketcardDocument2 pagesMalaria PocketcardYudha fedrian AKNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoa 14Document60 pagesAntiprotozoa 14adilaNo ratings yet
- Vincristine: Dosis Larutan Suntik 1Mg / ML Leukemia Akut 1,4 MG / M Iv Qweek Terapi Kombinasi KankerDocument22 pagesVincristine: Dosis Larutan Suntik 1Mg / ML Leukemia Akut 1,4 MG / M Iv Qweek Terapi Kombinasi KankerKevin Christofer FadillahNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi 4 (Antimalaria)Document7 pagesFarmakologi 4 (Antimalaria)Gifanichan MvpshawolandromedaNo ratings yet
- Anti Malarial Drugs by Salaria AnamikaDocument10 pagesAnti Malarial Drugs by Salaria AnamikaSalaria Anamika100% (1)
- Inferior Vena CavalDocument6 pagesInferior Vena Cavalv_vijayakanth7656No ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal Drugs NotesDocument22 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs NotesMae Lislie Canonigo - FloresNo ratings yet
- Antiparasitic TherapyDocument23 pagesAntiparasitic TherapyLeticia Ascarrunz CamachoNo ratings yet
- Immune Thrombositopenic Purpura (Itp)Document10 pagesImmune Thrombositopenic Purpura (Itp)Affy SyifaraniNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Reading Management SVTDocument44 pagesJurnal Reading Management SVTsuho exoNo ratings yet
- 18 Nov 2018 PDFDocument10 pages18 Nov 2018 PDFAffy SyifaraniNo ratings yet
- Dr.T.Venkatachalam Professor of Anaesthesiology Madras Medical College, ChennaiDocument35 pagesDr.T.Venkatachalam Professor of Anaesthesiology Madras Medical College, ChennaiNailahRahmahNo ratings yet
- LMWH QML 06Document7 pagesLMWH QML 06pd7qmlNo ratings yet
- 'Mbbs Lecture Note Malaria - pptx2021-1Document56 pages'Mbbs Lecture Note Malaria - pptx2021-1Noah OlumideNo ratings yet
- Trombembolismul PulmonarDocument9 pagesTrombembolismul PulmonarCătălina Raluca CojoceaNo ratings yet
- Afb5 - 1. Antimalarials MedicalDocument63 pagesAfb5 - 1. Antimalarials MedicalAx D98No ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Atrial Fibrillation Part-IIDocument66 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Atrial Fibrillation Part-IIJamil Muqtadir BhattiNo ratings yet
- UFH LMWH Fonda - 06september2020Document7 pagesUFH LMWH Fonda - 06september2020gabrimarteNo ratings yet
- CyclophosphamideDocument2 pagesCyclophosphamideksumanpharma8801No ratings yet
- Malaria 1Document28 pagesMalaria 1Ivy KapendaNo ratings yet
- #MD-01 Chloroquine - Chlo 2014Document4 pages#MD-01 Chloroquine - Chlo 2014Aris SetiyoNo ratings yet
- Heparin Sodium Injection, USP: RX Only DescriptionDocument29 pagesHeparin Sodium Injection, USP: RX Only DescriptionArchie TobiasNo ratings yet
- Efectoas Adversos AtbDocument13 pagesEfectoas Adversos AtbAgueda MaribelNo ratings yet
- LEUKERAN-chlorambucil Tablet, Film Coated Waylis Therapeutics LLCDocument12 pagesLEUKERAN-chlorambucil Tablet, Film Coated Waylis Therapeutics LLCAkoro SeraishiNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial Drugs Review - TaggedDocument29 pagesAntimalarial Drugs Review - Taggeddagehi6880No ratings yet
- Arte Sun AteDocument9 pagesArte Sun Atebaitur_rohmah8372No ratings yet
- Oncology: Volume 5 Issue 3: July/August 2010 - WWW - Oncologynews.bizDocument40 pagesOncology: Volume 5 Issue 3: July/August 2010 - WWW - Oncologynews.bizds.neetaNo ratings yet
- Chloroquine - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument9 pagesChloroquine - Drug Information - UpToDatedfdfffffNo ratings yet
- Clinicalguidance Malaria Treatment, CDCDocument8 pagesClinicalguidance Malaria Treatment, CDCSultanaNo ratings yet
- Updated DSC-Hydroxychloroquine ChloroquineDocument3 pagesUpdated DSC-Hydroxychloroquine ChloroquineSAMIRAH QATRUNNADA PNo ratings yet
- 19-Antiprotozoal Drugs IIDocument37 pages19-Antiprotozoal Drugs IIShashidharan MenonNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Mechanism of ActionDocument7 pagesWarfarin Mechanism of ActionIna GrigorasNo ratings yet
- 7 Adverse Reactions ToDocument11 pages7 Adverse Reactions TodrkamalakarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Management of Atrial Fibrilillation: Dr. Dilip Kumar Jain Dr. RajmaniDocument34 pagesManagement of Atrial Fibrilillation: Dr. Dilip Kumar Jain Dr. RajmaniAshish SoniNo ratings yet
- MOXIFLOXACIN MonographDocument3 pagesMOXIFLOXACIN Monographfayrouz fathiNo ratings yet
- 2009 Pearl SheetDocument19 pages2009 Pearl Sheetmikez100% (1)
- VitaminsDocument1 pageVitaminsabcdeNo ratings yet
- Water and Minerals PDFDocument1 pageWater and Minerals PDFabcdeNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument2 pagesSulfonamidesabcdeNo ratings yet
- PhenyltriazineDocument2 pagesPhenyltriazineabcdeNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus and ChlorideDocument2 pagesPhosphorus and ChlorideabcdeNo ratings yet