Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Bio Assignment 2
Uploaded by
Toga Brandon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThe fluid mosaic cell membrane structure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe fluid mosaic cell membrane structure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesCell Bio Assignment 2
Uploaded by
Toga BrandonThe fluid mosaic cell membrane structure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CHINHOYI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY
NAME : TOGA BRANDON
REG NUMBER : C22151745G
PROGRAM : BIOTECHNOLOGY ( BSBIO )
MODULE : MICROBIOLOGY(CUBIO103)
LECTURER : MS. M CHIMHOWA
ASSIGNMENT : 2
Assignment 2
1. The cell membrane consists of membrane proteins which enables it to undergo its functions.
The cell membrane is composed of a lipid bilayer with transmembrane proteins such as globular
proteins that run through both layers of the lipid bilayer. The trans/integral proteins help in the
transportation of substances such as glucose in facilitated diffusion. The peripheral membrane
proteins usually found on either surface of the lipid bilayer help in cell signal transduction that is
function as receptors for peptide hormones. Membrane proteins act as junctions by linking
intercellular components of the cell to extracellular ones. Glycoproteins with carbohydrate
groups attached to them function as cell surface receptor sites. Glycoproteins keep cells moist
and allow adhesion of molecules to take place. Some interior proteins such as spectrins and
clathrins are situated structurally to support the plasma membrane. Some proteins are for
production of enzymes to perform metabolic reactions in the cell membrane. Peripheral
membrane proteins enable cell to cell recognition and also attachment of cytoskeleton and the
extracellular matrix. Integral proteins allow both active and passive transport to occur enabling
exchange of certain substances such as sodium ions across the plasma membrane.
2. The cell surface membrane has a unique structure which enables it to carry out its functions of
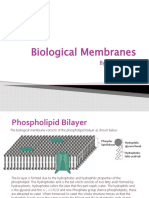
the cell. The membrane is called the Fluid Mosaic Model because it is always in constant motion
and fluid. The cell membrane has major components which include the phospholipid bilayer, the
transmembrane proteins, peripheral membrane proteins and the cell surface receptors also known
as surface markers. The peripheral membrane proteins are those attached to either surface of the
bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer covers a larger surface area because it contains 2 layers of non-
polar tails which point inward and the polar head which face the outside environment on the
membrane surface. The lipid bilayer has hydrophilic heads which are water loving due to their
polarity and hydrophobic tails (saturated or unsaturated) which are fat loving due to their long
hydrocarbon chains. Bilayer is fluid since the interaction of the lipids and the outer aqueous
surrounding keeps the lipids floating in the bilayer. The unsaturated hydrocarbon tails keep the
more fluid. Cell membrane has cholesterol mostly found on areas with lots of unsaturated fats
which helps in maintaining membrane fluidity by stabilizing the bilayer when it becomes less
fluid and permeable. The cell membrane is selectively permeable due to hydrophobic interior
hence regulates the entry and exit of molecules such as water, oxygen, and amino acids. The
lipid bilayer consists of globular proteins which help in selective transportation of substances
such as glucose through facilitated diffusion. The cell membrane contains channel proteins
which can change shape and spin which aid special movement of substances. Some proteins
function as enzymes in speeding up biochemical reactions. The cell surface membrane also
consists of carbohydrates chains sometimes found attached to proteins or lipids on the outside of
the membrane. These carbohydrates form the glycocalyx which function as protection and in cell
recognition as markers for a variety of cell-cell interactions.
You might also like
- Lecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of LifeDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of Lifeochienganthony001No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document8 pagesUnit 2cyberdevil403No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane in Transport MechanismsDocument29 pagesCell Membrane in Transport MechanismsAnnie LouNo ratings yet
- 2 - kh201295 kh201295Document11 pages2 - kh201295 kh201295murtada gubaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument15 pagesCell MembraneAyesha SaleemNo ratings yet
- SF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaDocument10 pagesSF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaAlly OmaryNo ratings yet
- The Fluid Mosaic Model and DiffusionDocument11 pagesThe Fluid Mosaic Model and DiffusionElizabeth JardineNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesCell MembraneKhadija ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Genbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerEleah MelchorNo ratings yet
- Struct-Function Cell OrgaDocument30 pagesStruct-Function Cell OrgaSiaw Sing OngNo ratings yet
- Cell & Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesCell & Its Functionsamber tariqNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell WallDocument4 pagesCell Membrane and Cell WallViral DaftaryNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes and Transport As BiologyDocument41 pagesCell Membranes and Transport As BiologyADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Membrane BiochemistryDocument106 pagesCell Biology and Membrane BiochemistryVijay Bhasker TekulapallyNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyAttaullah36No ratings yet
- CMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadDocument24 pagesCMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Document6 pagesCell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane DeutschDocument5 pagesPlasma Membrane DeutschSafeer SefiNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Cellular Physiology Organization Structure and Functions of The CellDocument77 pages2.1. Cellular Physiology Organization Structure and Functions of The CellalfonsoNo ratings yet
- Biological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiDocument10 pagesBiological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiMariam El KhatibNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 5Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 5karyo eseymNo ratings yet
- Functional and Structural Properties of Natural BiomembranesDocument7 pagesFunctional and Structural Properties of Natural BiomembranesAhsan RazaNo ratings yet
- 16.plasma membr-WPS OfficeDocument4 pages16.plasma membr-WPS OfficeMohamed RizwanNo ratings yet
- BIO 315. NotesDocument42 pagesBIO 315. NotesKevin KipropNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Functions and CompositionsDocument45 pagesCell Membrane Functions and CompositionslhiannicoleeNo ratings yet
- CSIR Life Science Sample Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCSIR Life Science Sample Cell Biologygamer zoneNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesTransport MechanismStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniNo ratings yet
- 2a-Membranes and Transport 2Document67 pages2a-Membranes and Transport 2kfy8vr7wtwNo ratings yet
- Structural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Document12 pagesStructural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Jeongyeonnie OppaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 1Document17 pagesCell Organelles 1James IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Navigation SearchDocument10 pagesCell Membrane: Navigation SearchMuhassanah Abd AzizNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument17 pagesCell MembraneEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesCell Membrane: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediabanana_flavorNo ratings yet
- Plasma MembraneDocument35 pagesPlasma MembraneMini RůžičkaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?Document6 pagesUnit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?juan mondaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document42 pagesCell Organelles 2James IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lipid AssignmentDocument4 pagesLipid AssignmentZainab AliNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument31 pagesCell Membrane Structure and FunctionXembergNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ReportDocument30 pagesCell Membrane ReportRetchel Cadayong NavalesNo ratings yet
- 3 Cytology Membran JunctionDocument48 pages3 Cytology Membran JunctionSamNo ratings yet
- Biyoloji IngilizceDocument21 pagesBiyoloji Ingilizced46smsfpwcNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document39 pagesLec 1Hussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec1Document24 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory Lec1ao868598No ratings yet
- 3 B Cytology-Membrane StructuresDocument19 pages3 B Cytology-Membrane Structuresm.mansoor3377No ratings yet
- Course 2Document28 pagesCourse 2managerw1sbusinessNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument7 pagesCell MembraneRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- The Cell MembraneDocument36 pagesThe Cell Membraneanulorance98No ratings yet
- Cell Structure & MembraneDocument24 pagesCell Structure & MembraneAbhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- 2structure and Functions of Cell MembraneDocument19 pages2structure and Functions of Cell MembraneedriansamaNo ratings yet
- Tissue (2021 - 01 - 21 00 - 20 - 54 UTC)Document33 pagesTissue (2021 - 01 - 21 00 - 20 - 54 UTC)Shalik WalkerNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument3 pagesCell BiologyjamjamjamNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol Is A Type of Steroid Which Is Helpful in Regulating Molecules Entering and ExitingDocument2 pagesCholesterol Is A Type of Steroid Which Is Helpful in Regulating Molecules Entering and ExitingAce RafaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesUnit 2 Revieweraaleah moscaNo ratings yet
- Cell MebraneDocument10 pagesCell MebraneChandra SihombingNo ratings yet
- General Physiology Cell Membrane: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradDocument21 pagesGeneral Physiology Cell Membrane: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradibrahimNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane The Big PictureDocument4 pagesPlasma Membrane The Big PictureNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Local Media2437312247486514219Document29 pagesLocal Media2437312247486514219Olive Vergara MuscaNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument16 pagesCritical ThinkingAnotida MagwenziNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Allergy Skin Prick TestingDocument6 pagesPaediatric Allergy Skin Prick TestingTor JaNo ratings yet
- Catalase LabDocument7 pagesCatalase LabToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- LIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFDocument8 pagesLIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES NotesDocument9 pagesCARBOHYDRATES NotesToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- EnzomologyDocument26 pagesEnzomologyToga Brandon100% (1)
- Titration Use of PH Meter BiochemDocument4 pagesTitration Use of PH Meter BiochemToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Prac ReportDocument3 pagesPrac ReportToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Excel PH Titration CurvesDocument1 pageExcel PH Titration CurvesToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Tkue 1Document1 pageTkue 1Toga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Cell-Mediated Immunity (CMI) Lecture 6Document29 pagesCell-Mediated Immunity (CMI) Lecture 6Toga BrandonNo ratings yet
- TOGA Immlgy Assignmnt 3Document3 pagesTOGA Immlgy Assignmnt 3Toga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Nematode PracDocument5 pagesNematode PracToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Gram Stain Prac ReportDocument4 pagesGram Stain Prac ReportToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Toga BrandonNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Manual 6vem eDocument67 pagesMotherboard Manual 6vem eAri Ercilio Farias FereirraNo ratings yet
- Halftrack Track Chains InstructionsDocument4 pagesHalftrack Track Chains Instructionsddlevy0% (1)
- Name - ESM 2104 Sample Final ExamDocument7 pagesName - ESM 2104 Sample Final ExamCOCO12432345No ratings yet
- Grade 6 - HEALTH - Q4 Module 1 - W1Document12 pagesGrade 6 - HEALTH - Q4 Module 1 - W1Love Lei67% (3)
- EtamolDocument5 pagesEtamolthonyyanmuNo ratings yet
- Gta 07-10-002 Advanced Infantry MarksmanshipDocument2 pagesGta 07-10-002 Advanced Infantry MarksmanshipMark CheneyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: DR Hiten KalraDocument81 pagesNutrition: DR Hiten KalraAmit SagarNo ratings yet
- Level 5 Part 1: Listening Comprehension (V.9) : Nro. de Control: ......Document16 pagesLevel 5 Part 1: Listening Comprehension (V.9) : Nro. de Control: ......Maco cacoseNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Practice Test 2 Answer ExplanationsDocument14 pagesAP Physics 1 Practice Test 2 Answer Explanations장준오No ratings yet
- BRT SylabussDocument29 pagesBRT SylabussAadityaNo ratings yet
- Romanian Association of Drilling Contractors ACFRDocument83 pagesRomanian Association of Drilling Contractors ACFRFuBasho33% (3)
- Angkasa Pura II - AR 2020 - 210813Document598 pagesAngkasa Pura II - AR 2020 - 210813Shreelalitha KarthikNo ratings yet
- 04.1 Foreign Graduates1Document30 pages04.1 Foreign Graduates1Frederico CavalcanteNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Masters in Psychology Entrance Examination Book (Power Within Psychology, Amit Panwar) (Z-Library)Document414 pagesPsychology - Masters in Psychology Entrance Examination Book (Power Within Psychology, Amit Panwar) (Z-Library)Suraj100% (12)
- WINTER 2023 Course Outline: ENME 479 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies IIDocument8 pagesWINTER 2023 Course Outline: ENME 479 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies IIKai McDermottNo ratings yet
- Europe MapDocument13 pagesEurope MapNguyên ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Reduction StationDocument2 pagesGas Pressure Reduction StationMathias OnosemuodeNo ratings yet
- Procurement Policy For Bank Group Funded OperationsDocument28 pagesProcurement Policy For Bank Group Funded OperationsNiyi FunminiyiNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: The Kimpton ExperienceDocument1 pageCase Analysis: The Kimpton ExperienceMaricel Ann BaccayNo ratings yet
- Procreate GuideDocument283 pagesProcreate GuideDiego D'Andrea100% (2)
- UNA010F-0-V2: Electrical SpecificationsDocument2 pagesUNA010F-0-V2: Electrical SpecificationsNiko ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Chison EBit 60 DatasheetDocument16 pagesChison EBit 60 DatasheetManuales TecnicosNo ratings yet
- Probability Practice QuesDocument9 pagesProbability Practice QuesYamu HiadeenNo ratings yet
- ToRs ESIA Maputo Sewerage System FinalDocument36 pagesToRs ESIA Maputo Sewerage System FinalVirgilio MuandoNo ratings yet
- M.S Engineering (Aerospace) Application Form: For Office UseDocument4 pagesM.S Engineering (Aerospace) Application Form: For Office Useshashasha123No ratings yet
- Microtronics Technologies: GSM Based Vehicle Theft Detection SystemDocument3 pagesMicrotronics Technologies: GSM Based Vehicle Theft Detection Systemابراهيم الثوبريNo ratings yet
- Afternoon Quiz Set 4Document66 pagesAfternoon Quiz Set 4pchakkrapani100% (1)
- Gr4 Reading InterventionDocument2 pagesGr4 Reading InterventionEvelyn Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document9 pagesLecture 7ngyx-ab22No ratings yet
- Competency Based Learning Materials: Housekeeping NciiDocument54 pagesCompetency Based Learning Materials: Housekeeping NciiNickolodian AsuncionNo ratings yet