Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peer Instruction
Uploaded by
Asnifa MamaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peer Instruction
Uploaded by
Asnifa MamaCopyright:
Available Formats
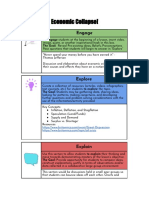
PEER INSTRUCTION
The teacher poses a question that challenges students to link or apply real-world examples of
previously learned concepts (ConcepTests) by deciding the solution and articulating their
rationale 10 another student in an attempt to persuade them of their accuracy. Students are
given a few minutes to think about the answer on their own before raising their hands or using
clickers to indicate their response. Students then collaborate in pairs or small groups to
persuade the other students of their point of view. After a few minutes, students are asked to
respond to the question once more.
Concept Mapping Graphical Organizers/Mind Mapping
Students can use graphic organizers to turn difficult knowledge into understandable visual
displays. Students may use graphic organizers to improve their abilities to make inferences,
synthesize. and integrate information and ideas. Students are given a primary theme to learn
about (s). The core graphic depicts this thought, with related themes/concepts spreading out as
"branches." Mind mapping theonzes that each of these map components might work as a hook,
linking new information with previous knowledge, making it simpler to learn and retain
Jigsaw Group Projects
Each group member is expected to finish a certain portion of a task or to become an expert on
one area of a subject. After each group member has accomplished his or her allotted duty, they
reassemble and teach the content to the remaining members of their group. They then put this
information to use in order to achieve a shared objective. For instance in a chemistry class each
student group may investigate a different type of energy generation (nuclear fossil fuel,
hydroelectric, etc). The groups are then restructured such that each has a specialist in one type
of electricity generating. They then address the issue of how much prominence each strategy
should get.
You might also like
- Lesson Plan Observation 6Document3 pagesLesson Plan Observation 6api-448690566No ratings yet
- Inquiry (5E) Lesson Plan Template: For TeachersDocument5 pagesInquiry (5E) Lesson Plan Template: For Teachersapi-487905844No ratings yet
- C.A.T. Concept MappingDocument11 pagesC.A.T. Concept Mappinglife.equippersNo ratings yet
- Angels Basic Productivity ToolsDocument2 pagesAngels Basic Productivity Toolsapi-688135233No ratings yet
- Activating Prior Knowledge and Reflective ToolsDocument4 pagesActivating Prior Knowledge and Reflective ToolsMaria Sabbah GhandourNo ratings yet
- Concept Maps: Why Use A Concept Map?Document4 pagesConcept Maps: Why Use A Concept Map?astien26No ratings yet
- Learning TheoryDocument1 pageLearning Theoryapi-397708830No ratings yet
- LP 542 Lesson 4Document3 pagesLP 542 Lesson 4api-233188563No ratings yet
- Malt 611 Teach Your Genre LessonDocument6 pagesMalt 611 Teach Your Genre Lessonapi-242610364No ratings yet
- Learning About Mathematical Ratios Lesson Plan - Nagiba Algharazi 1Document2 pagesLearning About Mathematical Ratios Lesson Plan - Nagiba Algharazi 1api-740590074No ratings yet
- Note MakingDocument3 pagesNote Makinghira bibiNo ratings yet
- Math UnitDocument15 pagesMath UnitLubna AlozNo ratings yet
- 04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea TemplateDocument2 pages04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea Templateapi-523153506No ratings yet
- Accelerated Learning Practice Mind MappingDocument3 pagesAccelerated Learning Practice Mind MappingsoloiosochisonoNo ratings yet
- Active Learning Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesActive Learning Lesson Planapi-535388004No ratings yet
- SRT LessonDocument3 pagesSRT Lessonapi-547934001No ratings yet
- Formative Assessment StrategiesDocument5 pagesFormative Assessment StrategiesJonielNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Strategies For Gathering Evidence of Student LearningDocument7 pagesFormative Assessment Strategies For Gathering Evidence of Student LearningJohn Paul Viñas PhNo ratings yet
- How Do You Effectively Engage Your Students in LearningDocument22 pagesHow Do You Effectively Engage Your Students in LearningKim B. AlcanceNo ratings yet
- Lesson Idea 4 TemplateDocument2 pagesLesson Idea 4 Templateapi-630696785No ratings yet
- Cep Lesson Plan Id Day1-2Document6 pagesCep Lesson Plan Id Day1-2api-733936233No ratings yet
- LP 542 1Document3 pagesLP 542 1api-233188563No ratings yet
- Integrative ModelDocument1 pageIntegrative Modelapi-313409388No ratings yet
- Revised Lesson Idea 2 TemplateDocument2 pagesRevised Lesson Idea 2 Templateapi-630714035No ratings yet
- Modals With Activities For LearnersDocument24 pagesModals With Activities For LearnersJohn Jabez LuceroNo ratings yet
- Classroom Modeling - PhippsDocument8 pagesClassroom Modeling - Phippsapi-399906068No ratings yet
- m07 Communcation and Collaborationtools Lesson Idea 2022Document4 pagesm07 Communcation and Collaborationtools Lesson Idea 2022api-618166851No ratings yet
- Edma3200 Lesson5practicumDocument3 pagesEdma3200 Lesson5practicumapi-252533855No ratings yet
- Itec Lesson Plan Instruction TechDocument3 pagesItec Lesson Plan Instruction Techapi-618145762No ratings yet
- Section Activities 1Document5 pagesSection Activities 1aboalfotohNo ratings yet
- 101 Teaching StrategiesDocument22 pages101 Teaching StrategiesRj Nerf Monteverde CalasangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Idea 6 TemplateDocument2 pagesLesson Idea 6 Templateapi-630714035No ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument11 pagesBrainstormingSuzette MiagaNo ratings yet
- Social Science Concept of Integrative ApproachDocument27 pagesSocial Science Concept of Integrative ApproachSync KichiiNo ratings yet
- How To Define EnergyDocument4 pagesHow To Define Energypatrick clarkeNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies ReflectionsDocument3 pagesTeaching Strategies Reflectionsapi-295350191No ratings yet
- 32 Teaching Strategies in MathDocument35 pages32 Teaching Strategies in Matheinsteinspy100% (1)
- Original Math LessonDocument8 pagesOriginal Math Lessonapi-385014399No ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning With Graphic OrganizersDocument8 pagesTeaching and Learning With Graphic OrganizersPeter BobilesNo ratings yet
- Active LearningDocument2 pagesActive LearningLoveniath MieerahNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document9 pagesModule 7Risshel Arcillas Manalo PilarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document11 pagesTopic 1Mercy MissionNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pages5e Lesson Plan Templatesheri hines100% (1)
- 6 Steps in Lesson PlanningDocument18 pages6 Steps in Lesson PlanningAljepric GalangNo ratings yet
- DoylebbptlessonplanDocument2 pagesDoylebbptlessonplanapi-629546127No ratings yet
- Student Engagement Techniques PDFDocument5 pagesStudent Engagement Techniques PDFGrace FebbyaniNo ratings yet
- Authentic Classroom Teaching StrategyDocument102 pagesAuthentic Classroom Teaching StrategyALESSANDRA REMONTALNo ratings yet
- Web 2Document3 pagesWeb 2api-618424404No ratings yet
- Classroom Application of Concept Map: Prepared By: Paloma I. Castillon Bsed-3 MathematicsDocument13 pagesClassroom Application of Concept Map: Prepared By: Paloma I. Castillon Bsed-3 MathematicsErnie CeradoNo ratings yet
- Classroom Application of Concept Map: Prepared By: Paloma I. Castillon Bsed-3 MathematicsDocument13 pagesClassroom Application of Concept Map: Prepared By: Paloma I. Castillon Bsed-3 MathematicsErnie CeradoNo ratings yet
- Low Risk TechniquesDocument14 pagesLow Risk TechniquesRajesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Mini Lesson Ubd Doc 2Document4 pagesMini Lesson Ubd Doc 2api-356637264No ratings yet
- BBPT LessonDocument3 pagesBBPT Lessonapi-554082469No ratings yet
- APU Standard Lesson Plan Template: Academic Content Standard (SDocument9 pagesAPU Standard Lesson Plan Template: Academic Content Standard (Sapi-666483113No ratings yet
- Srat LessonDocument3 pagesSrat Lessonapi-688132005No ratings yet
- Instructional Software Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesInstructional Software Lesson Planapi-630048293No ratings yet
- Tel 311 HyperdocDocument2 pagesTel 311 Hyperdocapi-534241653No ratings yet
- Explicit Instruction: Learning, Followed by A Clear Explanation of What ToDocument5 pagesExplicit Instruction: Learning, Followed by A Clear Explanation of What ToMay Queen LuegaNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pages5e Lesson Plan TemplateEric John Carlos DimasakatNo ratings yet
- Informational Text Toolkit: Research-based Strategies for the Common Core StandardsFrom EverandInformational Text Toolkit: Research-based Strategies for the Common Core StandardsNo ratings yet
- Traditional ASSESSMENTDocument1 pageTraditional ASSESSMENTAsnifa MamaNo ratings yet
- Report SampleDocument8 pagesReport SampleAsnifa MamaNo ratings yet
- Figurative DLPDocument5 pagesFigurative DLPAsnifa Mama100% (1)
- Conversation AnalysisDocument2 pagesConversation AnalysisAsnifa MamaNo ratings yet