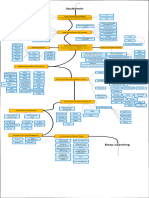
> Linear Algebra Also see NumPy
Python For Data Science
You’ll use the linalg and sparse modules.
Matrix Functions
Note that [Link] contains and expands on [Link].
Addition
>>> from scipy import linalg, sparse
SciPy Cheat Sheet >>> [Link](A,D) #Addition
Subtraction
Creating Matrices
Learn SciPy online at [Link] >>> [Link](A,D) #Subtraction
>>> A = [Link]([Link]((2,2)))
vs
Di i ion
>>> B = [Link](b)
>>> [Link](A,D) #Division
>>> C = [Link]([Link]((10,5)))
>>> D = [Link]([[3,4], [5,6]]) Multiplication
>>> [Link](D,A) #Multiplication
>>> [Link](A,D) #Dot product
SciPy Basic Matrix Routines >>> [Link](A,D) #Vector dot product
>>> [Link](A,D) #Inner product
Inverse >>> [Link](A,D) #Outer product
The SciPy library is one of the core packages for
>>> [Link](A,D) #Tensor dot product
>>> A.I #Inverse
>>> [Link](A,D) #Kronecker product
scientific computing that provides mathematical
>>> [Link](A) #Inverse
algorithms and convenience functions built on the
>>> A.T #Tranpose matrix
Exponential Functions
>>> A.H #Conjugate transposition
>>> [Link](A) #Matrix exponential
NumPy extension of Python. >>> [Link](A) #Trace >>> linalg.expm2(A) #Matrix exponential (Taylor Series)
Norm >>> linalg.expm3(D) #Matrix exponential (eigenvalue decomposition)
>>> [Link](A) #Frobenius norm
Logarithm Function
Also see NumPy >>> [Link](A,1) #L1 norm (max column sum)
>>> [Link](A) #Matrix logarithm
> Interacting With NumPy >>> [Link](A,[Link]) #L inf norm (max row sum)
Trigonometric Functions
Rank >>> [Link](D) Matrix sine
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = [Link]([1,2,3])
>>> [Link].matrix_rank(C) #Matrix rank >>> [Link](D) Matrix cosine
>>> b = [Link]([(1+5j,2j,3j), (4j,5j,6j)])
>>> [Link](A) Matrix tangent
Deter minant
>>> c = [Link]([[(1.5,2,3), (4,5,6)], [(3,2,1), (4,5,6)]])
Hyperbolic Trigonometric Functions
>>> [Link](A) #Determinant
>>> [Link](D) #Hypberbolic matrix sine
So lving linear problems
Index Tricks >>> [Link](D) #Hyperbolic matrix cosine
>>> [Link](A,b) #Solver for dense matrices
>>> [Link](A) #Hyperbolic matrix tangent
>>> E = [Link](a).T #Solver for dense matrices
>>> [Link][0:5,0:5] #Create a dense meshgrid
>>> [Link](D,E) #Least-squares solution to linear matrix equation Matrix Sign Function
>>> [Link][0:2,0:2] #Create an open meshgrid
>>> [Link](A) #Matrix sign function
>>> np.r_[[3,[0]*5,-[Link]j] #Stack arrays vertically (row-wise)
Generalized inverse
>>> np.c_[b,c] #Create stacked column-wise arrays >>> [Link](C) #Compute the pseudo-inverse of a matrix
(least-squares solver)
Matrix Square Root
>>> linalg.pinv2(C) #Compute the pseudo-inverse of a matrix
(SVD) >>> [Link](A) #Matrix square root
Arbitrary Functions
Shape Manipulation
Creating Sparse Matrices >>> [Link](A, lambda x: x*x) #Evaluate matrix function
>>> [Link](b) #Permute array dimensions
>>> [Link]() #Flatten the array
>>> F = [Link](3, k=1) #Create a 2X2 identity matrix
Decompositions
>>> [Link]((b,c)) #Stack arrays horizontally (column-wise)
>>> G = [Link]([Link](2)) #Create a 2x2 identity matrix
>>> [Link]((a,b)) #Stack arrays vertically (row-wise)
>>> C[C > 0.5] = 0
>>> [Link](c,2) #Split the array horizontally at the 2nd index
>>> H = sparse.csr_matrix(C) #Compressed Sparse Row matrix
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
>>> [Link](d,2) #Split the array vertically at the 2nd index >>> I = sparse.csc_matrix(D) #Compressed Sparse Column matrix
>>> la, v = [Link](A) #Solve ordinary or generalized
eigenvalue problem for square matrix
>>> J = sparse.dok_matrix(A) #Dictionary Of Keys matrix
>>> l1, l2 = la #Unpack eigenvalues
>>> [Link]() #Sparse matrix to full matrix
>>> v[:,0] #First eigenvector
Polynomials >>> sparse.isspmatrix_csc(A) #Identify sparse matrix >>> v[:,1] #Second eigenvector
>>> [Link](A) #Unpack eigenvalues
>>> from numpy import poly1d
gular Value Decomposition
>>> p = poly1d([3,4,5]) #Create a polynomial object Sparse Matrix Routines Sin
>>> U,s,Vh = [Link](B) #Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
Inverse >>> M,N = [Link]
Vectorizing Functions >>> [Link](I) #Inverse >>> Sig = [Link](s,M,N) #Construct sigma matrix in SVD
Norm LU Decomposition
>>> def myfunc(a): if a < 0:
>>> P,L,U = [Link](C) #LU Decomposition
return a*2
>>> [Link](I) #Norm
else:
Solving linear problems
return a/2
>>> [Link](H,I) #Solver for sparse matrices
>>> [Link](myfunc) #Vectorize functions
Sparse Matrix Functions
Type Handling
>>> [Link](I) #Sparse matrix exponential
>>> [Link](c) #Return the real part of the array elements
>>> [Link](c) #Return the imaginary part of the array elements
>>> np.real_if_close(c,tol=1000) #Return a real array if complex parts close to 0
Sparse Matrix Decompositions
>>> [Link]['f']([Link]) #Cast object to a data type
>>> la, v = [Link](F,1) #Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Other Useful Functions >>> [Link](H, 2) #SVD
>>> [Link](b,deg=True) #Return the angle of the complex argument
>>>
>>>
>>>
g = [Link](0,[Link],num=5) #Create an array of evenly spaced values(number of samples)
g [3:] += [Link]
[Link](g) #Unwrap
> A sking For Help Learn Data S ill k s Online at
[Link]
>>> [Link](0,10,3) #Create an array of evenly spaced values (log scale)
>>> [Link]([c<4],[c*2]) #Return values from a list of arrays depending on
conditions
>>> help([Link])
>>> [Link](a) #Factorial
>>> [Link]([Link])
>>> [Link](10,3,exact=True) #Combine N things taken at k time
>>> misc.central_diff_weights(3) #Weights for Np-point central derivative
>>> [Link](myfunc,1.0) #Find the n-th derivative of a function at a point