Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SciPyGUIA PYTHON-02
SciPyGUIA PYTHON-02
Uploaded by
Danilo ZanichelliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SciPyGUIA PYTHON-02
SciPyGUIA PYTHON-02
Uploaded by
Danilo ZanichelliCopyright:
Available Formats
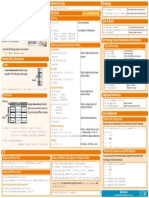
> Linear Algebra Also see NumPy
Python For Data Science You’ll use the linalg and sparse modules. Matrix Functions
Note that scipy.linalg contains and expands on numpy.linalg.
Addition
>>> from scipy import linalg, sparse
SciPy Cheat Sheet >>> np.add(A,D) #Addition
Subtraction
Creating Matrices
Learn SciPy online at www.DataCamp.com >>> np.subtract(A,D) #Subtraction
>>> A = np.matrix(np.random.random((2,2))) vs
Di i ion
>>> B = np.asmatrix(b) >>> np.divide(A,D) #Division
>>> C = np.mat(np.random.random((10,5)))
>>> D = np.mat([[3,4], [5,6]]) Multiplication
>>> np.multiply(D,A) #Multiplication
>>> np.dot(A,D) #Dot product
SciPy Basic Matrix Routines >>> np.vdot(A,D) #Vector dot product
>>> np.inner(A,D) #Inner product
Inverse >>> np.outer(A,D) #Outer product
The SciPy library is one of the core packages fo >>> np.tensordot(A,D) #Tensor dot product
>>> A.I #Inverse >>> np.kron(A,D) #Kronecker product
scientiic computing that provides mathematica >>> linalg.inv(A) #Inverse
algorithms and convenience functions built on th >>> A.T #Tranpose matrix Exponential Functions
>>> A.H #Conjugate transposition >>> linalg.expm(A) #Matrix exponential
NumPy extension of Python. >>> np.trace(A) #Trace >>> linalg.expm2(A) #Matrix exponential (Taylor Series)
Norm >>> linalg.expm3(D) #Matrix exponential (eigenvalue decomposition)
>>> linalg.norm(A) #Frobenius norm Logarithm Function
Also see NumPy >>> linalg.norm(A,1) #L1 norm (max column sum) >>> linalg.logm(A) #Matrix logarithm
> Interacting With NumPy >>> linalg.norm(A,np.inf) #L inf norm (max row sum)
Trigonometric Functions
Rank
>>> import numpy as np >>> linalg.sinm(D) Matrix sine
>>> a = np.array([1,2,3]) >>> np.linalg.matrix_rank(C) #Matrix rank >>> linalg.cosm(D) Matrix cosine
>>> b = np.array([(1+5j,2j,3j), (4j,5j,6j)]) >>> linalg.tanm(A) Matrix tangent
Deter minant
>>> c = np.array([[(1.5,2,3), (4,5,6)], [(3,2,1), (4,5,6)]]) Hyperbolic Trigonometric Functions
>>> linalg.det(A) #Determinant
>>> linalg.sinhm(D) #Hypberbolic matrix sine
So lving linear problems
Index Tricks >>> linalg.coshm(D) #Hyperbolic matrix cosine
>>> linalg.solve(A,b) #Solver for dense matrices >>> linalg.tanhm(A) #Hyperbolic matrix tangent
>>> E = np.mat(a).T #Solver for dense matrices
>>> np.mgrid[0:5,0:5] #Create a dense meshgrid >>> linalg.lstsq(D,E) #Least-squares solution to linear matrix equation Matrix Sign Function
>>> np.ogrid[0:2,0:2] #Create an open meshgrid >>> np.sigm(A) #Matrix sign function
>>> np.r_[[3,[0]*5,-1:1:10j] #Stack arrays vertically (row-wise) Generalized inverse
>>> np.c_[b,c] #Create stacked column-wise arrays >>> linalg.pinv(C) #Compute the pseudo-inverse of a matrix (least-squares solver) Matrix Square Root
>>> linalg.pinv2(C) #Compute the pseudo-inverse of a matrix (SVD) >>> linalg.sqrtm(A) #Matrix square root
Arbitrary Functions
Shape Manipulation
Creating Sparse Matrices >>> linalg.funm(A, lambda x: x*x) #Evaluate matrix function
>>> np.transpose(b) #Permute array dimensions
>>> b.flatten() #Flatten the array >>> F = np.eye(3, k=1) #Create a 2X2 identity matrix
Decompositions
>>> np.hstack((b,c)) #Stack arrays horizontally (column-wise) >>> G = np.mat(np.identity(2)) #Create a 2x2 identity matrix
>>> np.vstack((a,b)) #Stack arrays vertically (row-wise) >>> C[C > 0.5] = 0
>>> np.hsplit(c,2) #Split the array horizontally at the 2nd index >>> H = sparse.csr_matrix(C) #Compressed Sparse Row matrix Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
>>> np.vpslit(d,2) #Split the array vertically at the 2nd index >>> I = sparse.csc_matrix(D) #Compressed Sparse Column matrix >>> la, v = linalg.eig(A) #Solve ordinary or generalized eigenvalue problem for square matrix
>>> J = sparse.dok_matrix(A) #Dictionary Of Keys matrix >>> l1, l2 = la #Unpack eigenvalues
>>> E.todense() #Sparse matrix to full matrix >>> v[:,0] #First eigenvector
Polynomials >>> sparse.isspmatrix_csc(A) #Identify sparse matrix >>> v[:,1] #Second eigenvector
>>> linalg.eigvals(A) #Unpack eigenvalues
>>> from numpy import poly1d gular Value Decomposition
>>> p = poly1d([3,4,5]) #Create a polynomial object Sparse Matrix Routines Sin
>>> U,s,Vh = linalg.svd(B) #Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
Inverse >>> M,N = B.shape
Vectorizing Functions >>> sparse.linalg.inv(I) #Inverse >>> Sig = linalg.diagsvd(s,M,N) #Construct sigma matrix in SVD
LU Decomposition
Norm
>>> def myfunc(a): if a < 0: >>> P,L,U = linalg.lu(C) #LU Decomposition
return a*2 >>> sparse.linalg.norm(I) #Norm
else: Solving linear problems
return a/2
>>> sparse.linalg.spsolve(H,I) #Solver for sparse matrices
>>> np.vectorize(myfunc) #Vectorize functions
Sparse Matrix Functions
Type Handling
>>> sparse.linalg.expm(I) #Sparse matrix exponential
>>> np.real(c) #Return the real part of the array elements
>>> np.imag(c) #Return the imaginary part of the array elements
>>> np.real_if_close(c,tol=1000) #Return a real array if complex parts close to 0
Sparse Matrix Decompositions
>>> np.cast['f'](np.pi) #Cast object to a data type
>>> la, v = sparse.linalg.eigs(F,1) #Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Other Useful Functions >>> sparse.linalg.svds(H, 2) #SVD
>>> np.angle(b,deg=True) #Return the angle of the complex argument
>>>
>>>
>>>
g = np.linspace(0,np.pi,num=5) #Create an array of evenly spaced values(number of samples)
g [3:] += np.pi
np.unwrap(g) #Unwrap
> A sking For Help Learn Data S ill k s Online at
www.DataCamp.com
>>> np.logspace(0,10,3) #Create an array of evenly spaced values (log scale)
>>> np.select([c<4],[c*2]) #Return values from a list of arrays depending on conditions >>> help(scipy.linalg.diagsvd)
>>> misc.factorial(a) #Factorial >>> np.info(np.matrix)
>>> misc.comb(10,3,exact=True) #Combine N things taken at k time
>>> misc.central_diff_weights(3) #Weights for Np-point central derivative
>>> misc.derivative(myfunc,1.0) #Find the n-th derivative of a function at a point
You might also like
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocument7 pagesNumpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDeepak Gupta100% (14)
- Python Cheat Sheets CompilationDocument14 pagesPython Cheat Sheets Compilationraghavandra ethish manickam100% (1)
- Python Matplotlib Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePython Matplotlib Cheat SheetsreedharNo ratings yet
- Pandas Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pagePandas Python For Data Sciencechowdamhemalatha100% (1)
- ML CheatsheetsDocument17 pagesML CheatsheetsGhikjh100% (2)
- Pandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelyDocument1 pagePandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelySofia HerreraNo ratings yet
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat SheetJosh Iz100% (1)
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat Sheetyellow_birdNo ratings yet
- Pandas Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pagePandas Python For Data ScienceaaaaNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8No ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Using Matlab With Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageUsing Matlab With Python Cheat Sheetpravin22757670% (1)
- Business Report: Advanced Statistics ProjectDocument24 pagesBusiness Report: Advanced Statistics ProjectVarun Bhayana100% (5)
- Numpy Python Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat Sheet PDFAbhijith S AnchanNo ratings yet
- Numerical-Methods Question and AnswerDocument32 pagesNumerical-Methods Question and AnswerNeha Anis100% (5)
- Numpy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Inspecting Your Array Sorting ArraysDocument1 pageNumpy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Inspecting Your Array Sorting ArraysSuhas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocument6 pagesNumpy Basics: Arithmetic Operationsmanish chavhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document12 pagesLesson 11ebi1234No ratings yet
- Numpy Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Cheat SheetKevin ChalcoNo ratings yet
- Matplotlib: Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMatplotlib: Cheat SheetJaimy HessNo ratings yet
- Python Matplotlib SheetDocument1 pagePython Matplotlib SheetHIDINo ratings yet
- Scipy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Linear AlgebraDocument1 pageScipy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Linear AlgebraLourdes Victoria UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Java 8 Features Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesJava 8 Features Cheat Sheetsafimido100% (1)
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in MathcadDocument6 pagesEigenvalues and Eigenvectors in MathcadZlata TrbovicNo ratings yet
- Statistics - Python PDFDocument16 pagesStatistics - Python PDFNguyen H. Tinh100% (1)
- B.tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AI) 2022 23 RevisedDocument35 pagesB.tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AI) 2022 23 RevisedJobs GlbitmNo ratings yet
- Data Wrangling Cheat SheetDocument1 pageData Wrangling Cheat Sheetcuneyt noksanNo ratings yet
- SciPy Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSciPy Cheat Sheetcuneyt noksanNo ratings yet
- Python SciPy Cheat Sheet Linear Algebra PDFDocument1 pagePython SciPy Cheat Sheet Linear Algebra PDFTech and HacksNo ratings yet
- Cheat PythonDocument8 pagesCheat PythonhectordelosriosdiazNo ratings yet
- NumpyGUIA PYTHON-03Document1 pageNumpyGUIA PYTHON-03Danilo ZanichelliNo ratings yet
- Importing Data Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Pickled Files Exploring Your DataDocument1 pageImporting Data Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Pickled Files Exploring Your DatalocutoNo ratings yet
- Pandas: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelyDocument1 pagePandas: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelySofia HerreraNo ratings yet
- Using Matlab With Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageUsing Matlab With Python Cheat SheetMete ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Numpy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Inspecting Your Array Sorting ArraysDocument1 pageNumpy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Inspecting Your Array Sorting ArraysLourdes Victoria UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Spacy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Spans VisualizingDocument2 pagesSpacy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Spans VisualizingAarthi MuthuswamyNo ratings yet
- Matplotlib: Matplotlib Is A Python 2D Plotting Library Which ProducesDocument1 pageMatplotlib: Matplotlib Is A Python 2D Plotting Library Which Producesyama kenezonoNo ratings yet
- Pandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationDocument1 pagePandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationlocutoNo ratings yet
- Numpy Training For BeginnersDocument41 pagesNumpy Training For BeginnersHarish ReddyNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12 Cs em Atp Practical Hand Book 215961Document29 pagesNamma Kalvi 12 Cs em Atp Practical Hand Book 215961Vignesh VarunNo ratings yet
- Pandas Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePandas Cheat Sheetcuneyt noksanNo ratings yet
- Data WranglingGUIA PYTHON-05Document1 pageData WranglingGUIA PYTHON-05Danilo ZanichelliNo ratings yet
- C Program To Find Transpose of A MatrixDocument1 pageC Program To Find Transpose of A MatrixVishwas ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PandasGUIA PYTHON-04Document1 pagePandasGUIA PYTHON-04Danilo ZanichelliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NumpyDocument17 pagesIntroduction To NumpyNavyaNo ratings yet
- 55-102 NumpyDocument48 pages55-102 NumpyRap ImaginNo ratings yet
- Fast I - O in Java in Competitive Programming - GeeksforGeeksDocument1 pageFast I - O in Java in Competitive Programming - GeeksforGeekssurafelhnsNo ratings yet
- التعلم العميقDocument192 pagesالتعلم العميقMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- FDS Lab Manual (1-3) PDFDocument17 pagesFDS Lab Manual (1-3) PDFHepziba JNo ratings yet
- Python For Data Science: Advanced Indexing Data Wrangling in Pandas Cheat Sheet Combining DataDocument1 pagePython For Data Science: Advanced Indexing Data Wrangling in Pandas Cheat Sheet Combining DatalocutoNo ratings yet
- WWW GeeksforgeeksDocument2 pagesWWW GeeksforgeeksTest accNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Python GeneratorsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Python GeneratorsjlbmdmNo ratings yet
- Y Er. Vishvas B. PrajapatiDocument16 pagesY Er. Vishvas B. PrajapatiKrupal PatelNo ratings yet
- Python Basic Level Interview Questions and Answers: Unpacking'Document22 pagesPython Basic Level Interview Questions and Answers: Unpacking'satyach123No ratings yet
- Practice GeeksforGeeks A Computer Science Portal For GeeksDocument9 pagesPractice GeeksforGeeks A Computer Science Portal For Geeksjeandanielflorestal70No ratings yet
- Tf LehrlingstrainingsDocument18 pagesTf Lehrlingstrainingsbernhard.schwarz2006No ratings yet
- 12th Computer Science One Marks Question Paper English Medium PDF DownloadDocument5 pages12th Computer Science One Marks Question Paper English Medium PDF Downloadrahmansadik643No ratings yet
- Erdal Dinc, Emine Baydan, Murat Kanbur, Feyyaz Onur: A, B B ADocument16 pagesErdal Dinc, Emine Baydan, Murat Kanbur, Feyyaz Onur: A, B B AAndrés F. CáceresNo ratings yet
- 2application of Matrices - 2020Document94 pages2application of Matrices - 2020Bảo Tín TrầnNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Its Applications: Tim Netzer, Andreas ThomDocument17 pagesLinear Algebra and Its Applications: Tim Netzer, Andreas ThomLuis FuentesNo ratings yet
- High Rise and EQDocument6 pagesHigh Rise and EQMaiwand KhanNo ratings yet
- GATE ME SP 2014 by NodiaDocument509 pagesGATE ME SP 2014 by NodiaRahul Kumar100% (2)
- Linear Algebra 2Document168 pagesLinear Algebra 2srkNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Optimization T2Document19 pagesLinear Algebra and Optimization T2Meenakshi JayarajNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram, Signal-Flow Graphs, Mason's RuleDocument84 pagesBlock Diagram, Signal-Flow Graphs, Mason's RulePro HackedNo ratings yet
- Topics in Linear AlgebraDocument2 pagesTopics in Linear Algebrab385319No ratings yet
- QRG CS PDFDocument424 pagesQRG CS PDFckvirtualize93% (15)
- Mathematical Modeling and ODEDocument44 pagesMathematical Modeling and ODESalma SherbazNo ratings yet
- Raffah and Abbott (2013a)Document11 pagesRaffah and Abbott (2013a)Paul AbbottNo ratings yet
- TUM MSCE Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesTUM MSCE Interview QuestionsAsad MalikNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1982 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument9 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1982 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Mec-103: Quantitative Methods (Assignment) : Section ADocument3 pagesMec-103: Quantitative Methods (Assignment) : Section AgociNo ratings yet
- 2021 Assignment 2Document3 pages2021 Assignment 2Saksham TiwariNo ratings yet
- MathDocument205 pagesMathamine menadNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Dept of MathsDocument65 pagesSyllabus Dept of MathsksanthiNo ratings yet
- TLP Global Motion Performance Analysis ProceduresDocument8 pagesTLP Global Motion Performance Analysis ProceduresTee Shi FengNo ratings yet
- Born Oppenheimer ApproximationDocument38 pagesBorn Oppenheimer Approximationmarce33236591No ratings yet
- Energies: A Nonlinear-Model-Based Observer For A State-of-Charge Estimation of A Lithium-Ion Battery in Electric VehiclesDocument20 pagesEnergies: A Nonlinear-Model-Based Observer For A State-of-Charge Estimation of A Lithium-Ion Battery in Electric VehiclesFatihNo ratings yet
- Design Code Calculations GCBDocument6 pagesDesign Code Calculations GCBmoganna73No ratings yet
- Math Solution IITKDocument9 pagesMath Solution IITKcombatps1No ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument395 pagesLinear AlgebraAbhisek Datta67% (3)
- B Tech in Dairy TechnologyDocument79 pagesB Tech in Dairy Technologypadma.ajaykumar1386No ratings yet