Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Markets
Uploaded by
Carl's Aeto DomingoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Financial Markets
Uploaded by
Carl's Aeto DomingoCopyright:
Available Formats
FINANCIAL MARKETS
CHAPTER 1- FINANCIAL MARKETS -corporate & municipal bonds, corporate stocks,
commercial paper. (placed with the investors with the
-performs the essential function of transferring funds from assistance of Investment Bank)
economic players that have saved surplus to those who -has good connections: potential investors & knowledge
have a shortage of funds. of how to market securities.
LENDER- person/financial institution providing monetary DEBT VS. EQUITY
credit to the debtor. DEBT INSTRUMENTS- commitment on the part of issuer
BORROWER- person/entity that seeks funds from the to pay specific stream of cash flows to investor over a
lender. period until maturity, when the obligation ius discharged.
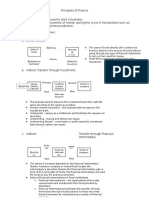
DIRECT FINANCE- lenders lend their savings directly to EQUITY- claims to share the net income and assets of
borrowers. business. Owner of equity receives dividends at specified
INDIRECT FINANCE- bank lends out depositors’ money to periods + receiving part of the business assets if goes
borrowers at a profit. bankruptcy. Investor= entitled to receive the leftover
after all other obligations have been paid.
FINANCIAL INSTITUTION-intermediaries/ physical location.
an establishment that completes and facilitates monetary MONEY MARKET-market for short term payments (year
transactions, such as loans, mortgages, and deposits. or less to mature). Exist for temporary investments-idle
FINANCIAL MARKETS- any place or system that provides fund. EX. Treasury Bills, Commercial Papers
buyers and sellers the means to trade financial CAPITAL MARKET- market for long term financial
instruments, including bonds, equities, the various instruments. Included in the capital market-issuances of
international currencies, and derivatives. securities and long term obligation by business and
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS- assets that can easily be government agencies.
converted into cash, which individuals can acquire. Ex. EX. Goverments Bonds, Corporate Bonds and Stocks
bonds
ASSYMETRIC INFORMATION- imbalance between two
CHAPTER 2- FINANCIAL SYSTEM (set of institutions) negotiating parties in their knowledge of relevant factors
FEATURES OF AN EFFECTIVE EFFECTIVE FINANCIAL and details. (side with more information enjoys a
SYSTEM competitive advantage over the other party)
FIDUCIARY SYSTEM- trust. Person with fiduciary duty has a
legal obligation to maintain that trust. ADVERSE SELECTION- problem created by assymetric
STRONG LEGAL INFRASTRUCTURE- set of transparent laws information, occurs before the transaction takes place,
that both parties to a financial institution regard as fair and leads to undesirable outcome.
protective of their interest. MORAL HAZARD- problem created by assymetric
SAFE, RELIABLE AND EFFICIENT PAYMENT SYSTEM- information, occurs after the transaction.
participants can make contractual payments; assured that
the funds get transferred to the right place on time at a INDIRECT METHOD OF FINANCE- intermediaries standing
relative cost. between the surplus unit and deficit unit.
DIRECT METHODS OF FINANCE DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS- receive funds (mostly in the
DIRECT FINANCE- surplus are directly transferred to deficit form of deposits) used to make loans.
unit without intermediaries EX. Commercial Banks
INDIRECT-with intermediaries FINANCE COMPANIES- acquires fund by selling
commercial papers and issuing stocks and bonds-lend
INVESTMENT BANK them to consumers and small businesses.
trading platform/s where the instrument is traded
CONTRACTUAL SAVINGS INSTITUTION- pension funds & and for getting the best terms for the customer.
life insurance companies.
COLLECTION OF INVESTMENT SCHEMES CHAPTER 3- THE SPECIAL ROLE OF COMMERCIAL BANKS
MUTUAL FUNDS- build portfolios or marketable assets.
Funds-offered and managed by large complexes that COMMERCIAL BANKS- bank that offers services to the general
provide a variety of funds and allow easy conversion from public.
one to another. ASSETS= LIABILITIES + NET WORTH (EQUITY
PRIVATE EQUITY FUNDS- Look for established corporations ASSETS:
that are not performing up to their best, acquire them, and • Cash
makes them private. (acquire existingly publicly traded • Securities
shares in target firm and converts to private ownership. • Core Loans (Business, Consumer, and Real Estate
HEDGE FUNDS- offer investment in professionally Loan)
managed portfolios and focus largely on marketable • Other Assets (Other Kinds of Loans, Bank Premises
instruments. and Bank Equipment, Real Estate Owned, and Misc.
VENTURE CAPITAL FUNDS- focused on investing in and other assets.
assisting firms in the early stage of development. LIABILITIES:
(commonly in the high-tech and biotech sectors of the • Deposits
company. • Transaction Deposits
• Other Retail Deposits
• Wholesale Deposits (Managed Liabilities)
NET WORTH:
• A.K.A. Bank Capital
• Acts as cushion against losses in asset values
• Government Policies places the government as a
potential creditor of the bank.
PAYMENT SYSTEM AND MONEY
COMMERCIAL BANKS AND THE PAYMENT SYSTEM
BANK NOTES- transaction mediums
DEPOSITS- money held in a bank account
*Commercial Banks – provided the public with transaction
PRIMARY MARET- financial market which new issues of a
deposits that serve as payment media, augmenting coins,
security are sold to initial buyers.
and notes issues by governments and central banks.
SECONDARY MARKET- occurs when security that have
previously been issued are resold.
I. PAYMENT SYSTEM INFRASTRUCTURE
COMMERCIAL BANKS role- facilitate transactions that
TRADING PLATFORM
support the economy.
-Over the counter
FUND TRANSFER SYSTEMS:
-specialist system
A. CLEARING HOUSE- bankers’ establishment where
-electronic communications network.
checks & bills from member banks are exchanged, so
that net balances need be paid in cash.
BROKERS- serve the customer by executing trade
B. AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE
for the customer-customer submits an order to
ORIGINAL DIRECTORY FINANCIAL INSTITUTION
broker and the broker is responsible for finding the
➡ CLEARING HOUSE (Regulated by NACHA-National
Automated Clearing House Association) verifies and validates
➡ RECEIVING DEPOSITORY FINANCIAL INSTITUTION maturity and uses these funds to make loans or
acquire investments having another maturity.
ODFI- gathers ACH related orders VII. THE SAFETY NET AND REGULATORY POLICY
RDFI-reconcile bank accounts related to ACH -Commercial banks and other depository institutions are
transaction. among the most heavily regulated businesses in our
economy.
II. CREDIT AND STORED VALUE CARDS -It has long been recognized that difficulties faced by one
CREDIT CARD- bank advancing credit to buyer to bank can disrupt the payment system and in other ways spill
complete transaction instead of transferring funds over to other banks, and even disrupt the entire economy --
from the buyer’s transaction account. we call this today, systemic risk.
STORED VALUE CARDS- entitles the holder to make -To limit the scope of disruption, public policy over time has
purchases. These involve a certain maximum amount developed a so-called safety net for commercial banks.
that a holder can spend. -Central banks require such loans to be adequately
Credit Card Bill- must be made using a transfer from collateralized, to limit their loss exposure.
the buyer's transaction account.
SHADOW BANKING SYSTEM
III. PAYMENT MEDIA IN THE MONEY STOCK SHADOW BANKING - generally been used to denote
MEASUREMENT OF MONEY STOCK arrangements for intermediating credit outside traditional
Money Stock- available money in a specific place at a deposits and loans at commercial banks. EX. Investment
specific time. Banks
A. M1- currency + transaction accounts
B. M2- M1 + other components CHAPTER 4- PRICING OF FINANCIAL ASSETS
-cash, checking deposits, non-cash assets that cam VALUE OF SINGLE FUTURE PAYMENTS
easily be converted into cash. -Some financial assets provide their owner with a single cash
M1 is roughly one-sixth the size of (nominal) gross domestic payment at some specific date in the future.
product (GDP) M2 is approximately two-thirds the size of GDP. CASH PAYMENT - bills or coins paid by the recipient of goods
or services to the provider.
IV. VELOCITY (Turnover of Money)
𝐶𝐹 𝑛
-It represents the number of times the money stock 𝑃𝑉 =
(1 + 𝑖)𝑛
turns over each year for purchases of all final goods
and services (GDP).
VALUE OF A COUPON SECURITY
-If the velocity of money is stable - the public wishes to
COUPON BOND OR SECURITY- a type of bond that includes
hold money in proportion to its spending and income -
attached coupons and pays periodic interest payments
then a change in the money stock will translate into a
during its lifetime and its par value at maturity. These bonds
proportionate change in GDP.
come with a coupon rate, which refers to the bond's interest
per year.
V. LIQUIDITY PROVISION
LIQUIDITY - denotes providing readily available funds.
These funds can be used to make a purchase or to
discharge an obligation.
VI. DEALING WITH ASYMMETRIC INFORMATION
-Few businesses and almost no individuals have access to
direct forms of finance because they are characterized by
substantial informational symmetries. YIELD RATE- the anticipated return on an investment,
Maturity Transformation - occurs when a bank expressed as an annual percentage.
receives funds in the form of deposits having one COUPON RATE- represents the actual amount of interest
earned by the bondholder annually.
PAR / FACE VALUE- they represent how much a bond will MATURITY - the date on which the principal associated with
be worth at the time of the bond's maturity. a debt or bonds becomes due.
COUPON BOND RATE- the present discounted value of
future cash stream generated by a bond. if M represents Maturity and H the Holding period:
M > H = Price (interest rate) risk
SOLVING FOR YIELDS TO MATURITY M < H = Rollover (reinvestment) risk
Yield to Maturity (YTM) -refers to the rate of return the
investor will earn if the bond is held to maturity. RETURN VS YIELD
a. Price of the bond RETURN- financial gain or loss on an investment and is
b. Time left to maturity typically expressed as the change in the dollar value of an
c. Par Value investment over time.
d. Annual interest payments -also referred to as total return and expresses what an
DISCOUNT investor earned from an investment during a certain period.
-Acquisition cost is less than Face amount YIELD- income returned on an investment, such as the
-Yield rate is higher than Coupon rate interest received from holding a security.
PREMIUM -usually expressed as an annual percentage rate based on
-Acquisition cost is more than Face amount the investment's cost, current market value, or face value.
-Yield rate is lower than Coupon rate - includes investor earnings, such as interest and dividends
received by holding particular investments.
FORMULA Y- YIELDS TO MATURITY
𝐹𝑉 − 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒
𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑝𝑜𝑛 + 𝑛
𝑌𝑇𝑀 =
𝐹𝑉 + 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒
2
FIXED-RATE PAYMENT
FIXED-RATE PAYMENT - an installment loan with an
interest rate that cannot be changed during the life of the
loan.
Sample Solution:
MATURITY AND PRICE SENSITIVITY
-The longer the maturity of a bond, the more sensitive is its
price to change in interest rate.
-The price sensitivity of any bond INCREASES occurs at a
DECREASING RATE
YR < CR = BOND PRICE > FACE AMOUNT
HOLDING PERIODS VS MATURITIES
HOLDING PERIOD- the period of time the bond is owned
by an investor.
You might also like
- Real Estate Legal FictionDocument5 pagesReal Estate Legal FictionJoshua Sygnal Gutierrez100% (1)
- Financial Market ReviewerDocument9 pagesFinancial Market ReviewerBryan NograNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument32 pagesFinancial MarketsEmil BabiloniaNo ratings yet
- Party To Facilitate The Borrowing Activities BetweenDocument7 pagesParty To Facilitate The Borrowing Activities BetweenMikaela Amigan Evangelista100% (1)
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionsAdriana Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument4 pagesBusiness Finance ReviewerJanna rae BionganNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Introduction To Banking and Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesLecture - Introduction To Banking and Financial InstitutionsJessalyn Cabael100% (1)
- 3.5 - Solving Exponential Equations Using Logs, Applications Math 30-1Document14 pages3.5 - Solving Exponential Equations Using Logs, Applications Math 30-1Math 30-1 EDGE Study Guide Workbook - by RTD LearningNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Corporate Finance A Focused Approach 6th Edition PDFDocument29 pagesEbook PDF Corporate Finance A Focused Approach 6th Edition PDFjennifer.browne345100% (42)
- Bank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingFrom EverandBank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Continental CarriersDocument8 pagesContinental CarriersYaser Al-Torairi100% (3)
- Case StudyDocument28 pagesCase StudyXyza Faye Regalado100% (1)
- Chaper 8 - FinmarDocument3 pagesChaper 8 - FinmarNathalie GetinoNo ratings yet
- FinMar ReivewerDocument16 pagesFinMar ReivewerChealseah MerceneNo ratings yet
- HHHJJDocument6 pagesHHHJJNiks MonzantoNo ratings yet
- MAS2 - Group 1Document6 pagesMAS2 - Group 1Cheese ButterNo ratings yet
- 01 Role of Financial Markets and Institutions GRCDocument13 pages01 Role of Financial Markets and Institutions GRCJohanna Nina UyNo ratings yet
- Fin 12 Notes (Ch2 Updated)Document4 pagesFin 12 Notes (Ch2 Updated)Kaycee StylesNo ratings yet
- FNDC ModulesDocument2 pagesFNDC ModulesJessa LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 1.1 Financial Intermediation: Market FailuresDocument3 pagesChap 1 1.1 Financial Intermediation: Market FailurestrangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Finanacial Markets and InstitutionsDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Finanacial Markets and InstitutionsChincel G. ANINo ratings yet
- Finance Part 2Document6 pagesFinance Part 2Justine PascualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 - Money and The Financial SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 23 - Money and The Financial SystemTumblr_userNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Role of Financial Markets and Institutions - GRC Role of Financial Markets and Institutions Chapter ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLecture Notes - Role of Financial Markets and Institutions - GRC Role of Financial Markets and Institutions Chapter ObjectivesGabrielle VizcarraNo ratings yet
- What Are Financial MarketsDocument5 pagesWhat Are Financial MarketsJasmine FalibleNo ratings yet
- 1-Marketing Financial Products - An IntroductionDocument43 pages1-Marketing Financial Products - An IntroductionKartik BhartiaNo ratings yet
- Banking Reviewer - CruzAR PDFDocument36 pagesBanking Reviewer - CruzAR PDFruby vinluanNo ratings yet
- FINMAR Chapter 1 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesFINMAR Chapter 1 (Reviewer)Charisse VisteNo ratings yet
- Banking and Finance ReviewerDocument6 pagesBanking and Finance ReviewerDe Villa, Ivy JaneNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument17 pagesBusiness Finance ReviewerkassyvsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Financial System and MarketsDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Indian Financial System and MarketstayaisgreatNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesFinancial Markets Midterm ReviewerFiona Erica ComplitadoNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions: ReadingsDocument10 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions: ReadingsQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- FM 2 - Old EdDocument3 pagesFM 2 - Old Edgojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - ReviewerDocument11 pagesFinancial Markets - ReviewerOne DozenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2Nursyahidah SafwanaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Financial SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 1 - Financial SystemMiera FrnhNo ratings yet
- Finance Part 2 PDFDocument5 pagesFinance Part 2 PDFJustine PascualNo ratings yet
- CH 10 NotesDocument11 pagesCH 10 Notesravideva84No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Financial MarketsDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Financial MarketsHoy HoyNo ratings yet
- Fin Mar SemisDocument5 pagesFin Mar SemisDomondon Dianna Mae T. BSA 1ANo ratings yet
- Financial System - Can Cause Positive Effect To The Economy. LikeDocument3 pagesFinancial System - Can Cause Positive Effect To The Economy. LikeGlensh Reigne CarlitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Banks & Other Financial Intermediaries: 19 PersonsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Banks & Other Financial Intermediaries: 19 PersonsMary.Rose RosalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2Farapple24No ratings yet
- Chap 2-3 - 4 - 5 LTTCDocument24 pagesChap 2-3 - 4 - 5 LTTCQuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Overview of Financial SystemDocument2 pagesNotes On The Overview of Financial SystemjeanneNo ratings yet
- Chapter - OneDocument30 pagesChapter - OneMagix SmithNo ratings yet
- Module 1-3 - FMDocument4 pagesModule 1-3 - FMryokie dumpNo ratings yet
- 121 - Notes Q3Document8 pages121 - Notes Q3Tricia KiethNo ratings yet
- Bonds Are Debentures. Whenever A Bond IsDocument1 pageBonds Are Debentures. Whenever A Bond Iskate trishaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency: Overview of The Financial SystemDocument12 pagesEfficiency: Overview of The Financial SystemErika Anne Jaurigue100% (1)
- Banking Chapter 1Document7 pagesBanking Chapter 1Shasharu Fei-fei LimNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document54 pagesChap 2Yeshiwork GirmaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - : Debt Instrument - Contract That Specifies How and When A Borrow Must Repay A LenderDocument2 pagesFinancial Markets - : Debt Instrument - Contract That Specifies How and When A Borrow Must Repay A LenderLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- Bus. Finance Lecture Ch. 12Document16 pagesBus. Finance Lecture Ch. 12Camille BigataNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL-MARKETS Prelims RevDocument13 pagesFINANCIAL-MARKETS Prelims RevJasmine TamayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Acctg235Document21 pagesChapter 5 Acctg235Ronnel Villaceran SaysonNo ratings yet
- Fin EnvDocument26 pagesFin EnvLaiba KhanNo ratings yet
- FINMAR Chapter 1 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesFINMAR Chapter 1 (Reviewer)Lazarae De DiosNo ratings yet
- Basics of Commercial BankingDocument59 pagesBasics of Commercial BankingRhea PaboralinanNo ratings yet
- Bond Markets NotesDocument3 pagesBond Markets NotesCrizza AngelaNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Midterm Reviewer 1Document13 pagesCapital Market Midterm Reviewer 1geverachristinemaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument3 pagesFinancial MarketsAbmel DreamerNo ratings yet
- Promissory NoteDocument2 pagesPromissory NotemarjoriefacuriNo ratings yet
- Pefindo'S Corporate Default and Rating Transition Study (1996 - 2010)Document21 pagesPefindo'S Corporate Default and Rating Transition Study (1996 - 2010)Theo VladimirNo ratings yet
- The Usury LawDocument6 pagesThe Usury LawNoreen T� ClaroNo ratings yet
- FinMgt1Finals Regular 2019Document7 pagesFinMgt1Finals Regular 2019Franz Ana Marie CuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Time Value of MoneyDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Time Value of MoneyAhmed FathelbabNo ratings yet
- 1966 - Morris - The Balance of Payments CrisesDocument11 pages1966 - Morris - The Balance of Payments Crisesrogue_lettuceNo ratings yet
- Disclaimer: Paper 6E: Global Financial Reporting Standards 1Document34 pagesDisclaimer: Paper 6E: Global Financial Reporting Standards 1Shashank 45No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Annual Cash Flow AnalysisDocument54 pagesChapter 5 Annual Cash Flow AnalysisShudipto PodderNo ratings yet
- Day 4 Master Class CS Krishna Sharan Mishra Corporate Restructuring PDFDocument83 pagesDay 4 Master Class CS Krishna Sharan Mishra Corporate Restructuring PDFsmchmpNo ratings yet
- 1 1meaningDocument21 pages1 1meaningadtyshkhrNo ratings yet
- PSimple Interest PDFDocument9 pagesPSimple Interest PDFEi HmmmNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Study Material 2019-20Document16 pagesIncome Tax Study Material 2019-20Ayush MittalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4 AnswersDocument1 pageProblem Set 4 Answerssandrae brownNo ratings yet
- MCMP Const. vs. Monark, Nove. 10, 2014Document12 pagesMCMP Const. vs. Monark, Nove. 10, 2014Elaine GuayNo ratings yet
- Acceptance of Public DepositsDocument29 pagesAcceptance of Public DepositsSukirti ShikhaNo ratings yet
- Icfai2008 - 1307514033 Security AnalysisDocument17 pagesIcfai2008 - 1307514033 Security AnalysisJatin GoyalNo ratings yet
- Classification, Rescheduling, Write OffDocument17 pagesClassification, Rescheduling, Write OffismailabtiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Food InflationDocument14 pagesProject Report On Food Inflationishan6488No ratings yet
- Shubhrakanti Nag: Financial Planning Report ForDocument60 pagesShubhrakanti Nag: Financial Planning Report ForRakesh IndianNo ratings yet
- Principles of Islamic Economics: © DR Muhammad Hamidullah Library, IIU, Islamabad. Http://iri - Iiu.edu - PKDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Islamic Economics: © DR Muhammad Hamidullah Library, IIU, Islamabad. Http://iri - Iiu.edu - PKHami KhaNNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument16 pagesChapter TwoHananNo ratings yet
- Ethiopias Banking Sector 2019 20Document41 pagesEthiopias Banking Sector 2019 20AsniNo ratings yet
- CH 4 In-Class Exercise 2 (Solutions)Document3 pagesCH 4 In-Class Exercise 2 (Solutions)Zenni T XinNo ratings yet
- Interest Free BankingDocument19 pagesInterest Free BankingSameer ShafqatNo ratings yet
- 61 - Javellana Vs LimDocument1 page61 - Javellana Vs LimBibi JumpolNo ratings yet