Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Negligence Workshop 7 Duty of Care
Negligence Workshop 7 Duty of Care
Uploaded by
Benlotte Jnr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views6 pagesThe document discusses negligence law and the duty of care. It outlines three tests to determine if a duty of care is owed: [1] Donoghue v Sturgeon's test of foreseeability and proximity, [2] the three-stage Caparo test of foreseeability of harm, proximity, and whether it is fair to impose a duty, and [3] precedent cases where a duty of care has already been established for certain relationships. It also discusses exceptions for liability for omissions and acts of third parties.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses negligence law and the duty of care. It outlines three tests to determine if a duty of care is owed: [1] Donoghue v Sturgeon's test of foreseeability and proximity, [2] the three-stage Caparo test of foreseeability of harm, proximity, and whether it is fair to impose a duty, and [3] precedent cases where a duty of care has already been established for certain relationships. It also discusses exceptions for liability for omissions and acts of third parties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views6 pagesNegligence Workshop 7 Duty of Care
Negligence Workshop 7 Duty of Care
Uploaded by
Benlotte JnrThe document discusses negligence law and the duty of care. It outlines three tests to determine if a duty of care is owed: [1] Donoghue v Sturgeon's test of foreseeability and proximity, [2] the three-stage Caparo test of foreseeability of harm, proximity, and whether it is fair to impose a duty, and [3] precedent cases where a duty of care has already been established for certain relationships. It also discusses exceptions for liability for omissions and acts of third parties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
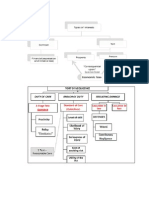
NEGLIGENCE WORKSHOP 7
DUTY OF CARE
Breach of a legal duty to take care by the defendant resulting in *
1 damage to the claimant.
HOW TO DETERMINE DUTY AT CARE BEING OWED
Test 1 – Donoghue u Sturgeon
Foreseeability – Taker reassemble care to avoid acts 1
omissions while can reasonably furze would injure your
neighbour.
Proximity – Persons who are soo closely and directly
affected by the act.
New care / Approach in ascertaining “Duty of Care”
Caparo u Dickman (3 stage approach)
Note that, where a precedent has been established, there’s no
need to apply this.
3 stage test. No Precedent then
a) Foreseeability of harm – Objective man test. Reasonably
foreseeable that the * take of care would cause the claimant
harm.
b) Proximity – Closeness between the defendant and claimant.
Very important eg: where * arumed responsibility for the
claimant (care of kk / witness)
c) It must be fair / just/ reasonable to impose * * - At the
courts * looking at the whole circumstance (socially,
politically and economically) – In effect, policy consideration
in the area of.
Floodgate and Deterrence
Insurance and Defensive *
The approach in Caparo is confirmed in the case of Robinson v
cliet constable
Example of established precedent
1. Road user to ouer road users
Nettleship v Weston – aidriver owes a duty of care to otuer
road users not to cause them physical injury by careless
driving
Apply task – In the case of BW US
2. Carsidy v Ministry of Health and Medical protesimals owe a
duty of care to patients once the7y have accepted them for
treatment.
Apply Task – In the care of BW v Dr. * Medical Negligence.
3. Robinson V Cliet Constable – Police owes a duty of care to
the public to protect them from reasonably foreseeable
physical injury when carrying out an arrest. But owes no
duly to respond to emergency calls – Alexandrou x Oxford.
Liability for Omission
General Rule: No duty is imposed on a mere failure to act – Smith
v Little woods * is liability impose on those who cause injury /
damage.
Eg: No legal obligation to * by rescue Jomeme drowing. In the
case of KK, there was no legal * to try to rescue BW.
Exception – There is no duty imposed on a mere failure to act
except.
1. Statue imposes such a duty or (Don’t worry)
2. Where the defendant * responsibility for the claimant or
3. Where the defendant created the risk or
4. Where there’s a * duly or
5. The de has * control over the claimant
Omisms and the emergency services
1. Ambulance – Kent v Griffiths on acceptance of an
emergency call, the ambulance service owes a duty of care
to * within a reasonable time.
Duty might not be bereaved where
a. Exercise their * to deal with a more * emergency
2. The hire Brigade – Owes NU duty of care to attend a hire but
if they do, they owe a duty not to make a situation worse * a
positive act.
- Capital and Countries U *
3. The Police – Owes, No duty to respond to emergency calls –
Alexandrou u *
Liability for Acts of 3rd Parshes
General Rule – Smith v Little woods, these is no * duty is
imposed an a twelve to present a 3rd party occurring learn to
another.
Eg: No duty imposed an MCC to present S.J from causing harm
to B.W
Exception
Look at the act of the 3rd party
1. Sufficient proximity between defendant and claimant
2. Sufficient proximily between defendant and 3rd party
3. The defendant created the danger
4. The risk was on the defendant premises
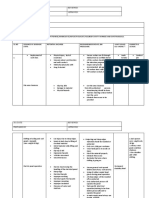
Apply Task 1 – Identify who owes the claimant a duty of care,
tort, *
1. Parties – Ben Williams (BW) (Claimant)
Possible defendant – Sophia Jennings (S.J)
- BW v SJ - *
- Torts- General Negligence
- Loss – Personal injury to back (back pain), **************
- Properly damage – Damage to car repair / replacing it
- Consequential economic loss * directly by personal injury.
2. BW v KK (Witness)
Tort – General Negligence
Tort – Personal injury - * back injury couring a slipped disc
in his * spine as a result of pulling BW out of the car. Hence,
* contributed to this pain.
- Consequential economic tors
BW v Northern Ambulance
3. Tort- General Negligence
Tort – Personal injury, * of his sipplied disc, cause as a result
ambulance service arriving lare and GEL.
4. BW v Dr *
Tort – Clinical / Medical Negligence
Tort – Personal injury - * in both legs as a result of surgery
performed by Dr. G. and CEL.
CEL – O rooter for the last 4 years but has been unable to
work since the accident. Tort income and job.
You might also like
- First Year Torts OutlineDocument16 pagesFirst Year Torts Outlinenicole_huddlest6741No ratings yet
- Law of TortDocument27 pagesLaw of TortLydia AzmiNo ratings yet
- Torts OutlineDocument67 pagesTorts OutlineBeeBeeTwo100% (2)
- Table of Upper Limb MusclesDocument4 pagesTable of Upper Limb MusclessuperdobbyNo ratings yet
- Negligence ChecklistDocument5 pagesNegligence ChecklistFifi Jarrett100% (1)
- Torts I Negligence Study Guide TXDocument7 pagesTorts I Negligence Study Guide TXLaw Student 101100% (1)
- Tort Law NotesDocument28 pagesTort Law NotesThomas Ranco SuNo ratings yet
- Contractor Weekly Hse Report Blank With DefinitionsDocument4 pagesContractor Weekly Hse Report Blank With DefinitionsGonzalo Davila100% (2)
- Causation & RemotenessDocument5 pagesCausation & RemotenessABDOULIENo ratings yet
- Liability For OmissionsDocument4 pagesLiability For OmissionsMahdi Bin MamunNo ratings yet
- Torts MADocument10 pagesTorts MAMaanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 - Negligence - Breach of DutyDocument13 pagesWorksheet 3 - Negligence - Breach of DutyBrian PetersNo ratings yet
- Roc and A Hard PlaceDocument1 pageRoc and A Hard PlaceKarlo Marco CletoNo ratings yet
- Business Law - Tort NotesDocument9 pagesBusiness Law - Tort NotesnovypooNo ratings yet
- In Time Of Emergency: A Citizen's Handbook On Nuclear Attack, Natural DisastersFrom EverandIn Time Of Emergency: A Citizen's Handbook On Nuclear Attack, Natural DisastersNo ratings yet
- Torts Outline1Document32 pagesTorts Outline1Kasem AhmedNo ratings yet
- JSA Wall and Ceiling PanelsDocument5 pagesJSA Wall and Ceiling PanelsPAVANKUMAR67% (6)
- Torts & DamagesDocument16 pagesTorts & Damagesdorothy92105No ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 3 - Module 2Document22 pagesHealth: Quarter 3 - Module 2Mary Allysa DomingoNo ratings yet
- Advanced TortsDocument54 pagesAdvanced TortsLawstudent3100% (4)
- Ankle LectureDocument19 pagesAnkle Lecturegunawan crisNo ratings yet
- Flaps in Head & Neck ReconstructionDocument78 pagesFlaps in Head & Neck Reconstructionkatnev100% (3)
- INTUBASIDocument45 pagesINTUBASIGusti Ngurah Andhika PNo ratings yet
- Tort Revision SheetsDocument11 pagesTort Revision SheetsSab SameemNo ratings yet
- Law of Tort NegligenceDocument20 pagesLaw of Tort NegligenceSophia AcquayeNo ratings yet
- Forearms Exercises PDFDocument11 pagesForearms Exercises PDFDeepak NaiduNo ratings yet
- All of TortDocument52 pagesAll of Tortkeerthi9999No ratings yet
- Negligence NotesDocument25 pagesNegligence NotesBaguma Patrick RobertNo ratings yet
- Tort Class Outline - NegligenceDocument21 pagesTort Class Outline - NegligenceAyman KhanNo ratings yet
- Laws1061 Torts-Summary LawcornersDocument10 pagesLaws1061 Torts-Summary LawcornersLandel SmithNo ratings yet
- Tort NegligenceDocument60 pagesTort NegligenceGautham SegarNo ratings yet
- NegligenceDocument9 pagesNegligencesheriyfNo ratings yet
- Law of Tort NotesDocument15 pagesLaw of Tort NotesfmsaidNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Intentional Torts: Sports Cases - There Is Implied Consent For Injuries Sustained in The Course of The GameDocument28 pagesChapter One: Intentional Torts: Sports Cases - There Is Implied Consent For Injuries Sustained in The Course of The Gamechiragr2No ratings yet
- 11 NegligenceDocument11 pages11 Negligencenatsu lolNo ratings yet
- 11 NegligenceDocument11 pages11 Negligencenatsu lolNo ratings yet
- 11 NegligenceDocument11 pages11 Negligencenatsu lolNo ratings yet
- 11 NegligenceDocument11 pages11 Negligencenatsu lolNo ratings yet
- Torts UpdateDocument11 pagesTorts UpdatechelseapulverNo ratings yet
- TortsDocument15 pagesTortsLaiba ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Duty of Care ContinuedDocument12 pagesDuty of Care Continuedfaiza3636No ratings yet
- An Overview of Tort Law 2009-2010Document31 pagesAn Overview of Tort Law 2009-2010erickyfmNo ratings yet
- 4 Tort Law 2017.2018Document22 pages4 Tort Law 2017.2018Constantin LazarNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Obligations To Act: 1. Duty To Warn / Duty To RescueDocument6 pagesAffirmative Obligations To Act: 1. Duty To Warn / Duty To RescueL.M. HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Internal Assessment - 1 Subject-Law of TortsDocument6 pagesInternal Assessment - 1 Subject-Law of TortsShreyaNo ratings yet
- Tort Law: Duty of CareDocument22 pagesTort Law: Duty of Carekeerthi99999No ratings yet
- Negligence - Duty of Care: Law of Torts I Lecturer: Christopher Gray E-Mail: What Is Negligence?Document4 pagesNegligence - Duty of Care: Law of Torts I Lecturer: Christopher Gray E-Mail: What Is Negligence?ABDOULIENo ratings yet
- Tort of NuisanceDocument3 pagesTort of NuisanceMamta Navneet SainiNo ratings yet
- Negligence: General PrinciplesDocument0 pagesNegligence: General PrinciplesDharshan SornalingamNo ratings yet
- Unit 31 - Negligence11Document14 pagesUnit 31 - Negligence11Manuela DedićNo ratings yet
- Law of Torts NotesDocument4 pagesLaw of Torts Noteslorriejason4No ratings yet
- Failure To Act As Negligent OmissionDocument4 pagesFailure To Act As Negligent OmissionAlex OkiriaNo ratings yet
- 406 - Torts CAN - FeileyDocument17 pages406 - Torts CAN - FeileyGeeth MpNo ratings yet
- TortsDocument73 pagesTortsladybird2310No ratings yet
- Breach of Duty of CareDocument46 pagesBreach of Duty of CareJavier LimNo ratings yet
- Law of Torts 2 CWDocument11 pagesLaw of Torts 2 CWabdallahnashaat3No ratings yet
- The Tortof NegligenceDocument19 pagesThe Tortof NegligenceTracey KandjimiNo ratings yet
- Omissions and Third Parties: Ms GallopDocument40 pagesOmissions and Third Parties: Ms GallopABDOULIENo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 - RemotenessDocument8 pagesWorksheet 5 - RemotenessBrian PetersNo ratings yet
- TORT 1 - NEGLIGENCE On Duty of CareDocument4 pagesTORT 1 - NEGLIGENCE On Duty of CareAlwani ArNo ratings yet
- Case Summaries TortsDocument8 pagesCase Summaries Tortssiwasna deoNo ratings yet
- Law of Tort Week 5.2Document16 pagesLaw of Tort Week 5.2Sophia AcquayeNo ratings yet
- Breach of DutyDocument9 pagesBreach of Dutyodahkasim100% (1)
- Pqs OmissionsDocument2 pagesPqs OmissionsKatie MarieNo ratings yet
- Wa0004Document13 pagesWa0004hypersingh69No ratings yet
- Pre Bar Tort OutlineDocument38 pagesPre Bar Tort OutlineBilly Alvarenga GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Torts IDocument25 pagesPresentation of Torts INuraqilah Shuhada100% (1)
- Negligence OutlineDocument10 pagesNegligence OutlinejohnNo ratings yet
- Gearench CatalogDocument86 pagesGearench Catalogmosallam123No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Nursing Care of Clients With Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument100 pagesUnit 4 Nursing Care of Clients With Musculoskeletal DisordersE. Tito Julianda SinagaNo ratings yet
- 11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pages11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemMira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CNo ratings yet
- RS Reba User ManualDocument63 pagesRS Reba User ManualRadu Nica0% (1)
- The Human Meniscus: A Review of Anatomy, Function, Injury, and Advances in Treatment: The Meniscus: Anatomy, Function, Injury and TreatmentDocument20 pagesThe Human Meniscus: A Review of Anatomy, Function, Injury, and Advances in Treatment: The Meniscus: Anatomy, Function, Injury and TreatmentLinggaNo ratings yet
- Ocular Blunt Trauma: Loss of Sight From An Ice Hockey InjuryDocument2 pagesOcular Blunt Trauma: Loss of Sight From An Ice Hockey InjuryShirakawa AlmiraNo ratings yet
- MSConnector DYNO Tds PDFDocument2 pagesMSConnector DYNO Tds PDFLeo AfrendraNo ratings yet
- Aseptic (Simple) Wound DressingDocument23 pagesAseptic (Simple) Wound DressingJohanna H DavidNo ratings yet
- And Wilt Thou Leave Me ThusDocument3 pagesAnd Wilt Thou Leave Me ThusRohana Fernando100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Use of Blood Warming Devices AABBDocument42 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Blood Warming Devices AABBBrandonHuangNo ratings yet
- Acute Management of Pelvic Ring Injuries: Kyle F. Dickson, MDDocument121 pagesAcute Management of Pelvic Ring Injuries: Kyle F. Dickson, MDSatrio Bangun NegoroNo ratings yet
- Main Sept 01Document59 pagesMain Sept 01Lindsey RobbinsNo ratings yet
- Implante Coclear Y Audición Residual: Cochlear Implant and Residual HearingDocument4 pagesImplante Coclear Y Audición Residual: Cochlear Implant and Residual HearingJosue Sanchez CruzNo ratings yet
- Who Killed Benny ParetDocument2 pagesWho Killed Benny Paretapi-294050189No ratings yet
- Operative Stabilization of Flail Chest Injuries: Review of Literature and Fixation OptionsDocument7 pagesOperative Stabilization of Flail Chest Injuries: Review of Literature and Fixation OptionsTommysNo ratings yet
- Question Chapter 12 ThalamusDocument8 pagesQuestion Chapter 12 ThalamusTrang BuiNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentTenzin Norzom NegiNo ratings yet
- K - 2 Secondary Survey Assessment (Anestesi)Document39 pagesK - 2 Secondary Survey Assessment (Anestesi)AndreAHutasoitNo ratings yet
- Chest PBLDocument2 pagesChest PBLRamish IrfanNo ratings yet
- Perineal HerniaDocument3 pagesPerineal Herniagogovet101No ratings yet
- P.E SbaDocument23 pagesP.E SbaSamanthaKhan33% (3)