Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitro Antiviral
Vitro Antiviral
Uploaded by
Saeha Noor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageRemdesivir and chloroquine were found to be highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, while ribavirin, penciclovir, and favipiravir required higher concentrations to be effective. Both remdesivir and chloroquine are approved for other diseases and could be explored further for treating COVID-19 patients. A molecular docking study also identified that ribavirin, remdesivir, galidesivir, tenofovir, and sofosbuvir tightly bind to the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2, indicating their potential for treating COVID-19.
Original Description:
Original Title
vitro antiviral
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRemdesivir and chloroquine were found to be highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, while ribavirin, penciclovir, and favipiravir required higher concentrations to be effective. Both remdesivir and chloroquine are approved for other diseases and could be explored further for treating COVID-19 patients. A molecular docking study also identified that ribavirin, remdesivir, galidesivir, tenofovir, and sofosbuvir tightly bind to the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2, indicating their potential for treating COVID-19.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageVitro Antiviral
Vitro Antiviral
Uploaded by
Saeha NoorRemdesivir and chloroquine were found to be highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, while ribavirin, penciclovir, and favipiravir required higher concentrations to be effective. Both remdesivir and chloroquine are approved for other diseases and could be explored further for treating COVID-19 patients. A molecular docking study also identified that ribavirin, remdesivir, galidesivir, tenofovir, and sofosbuvir tightly bind to the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2, indicating their potential for treating COVID-19.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
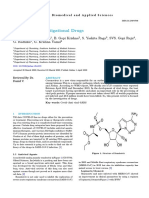
vitro antiviral potential of FAD-approved drugs, viz.
, ribavirin, penciclovir, nitazoxanide,
nafamostat, and chloroquine, tested in comparison to remdesivir and favipiravir (broad-spectrum
antiviral drugs) revealed remdesivir and chloroquine to be highly effective against SARS-CoV-2
infection in vitro (194). Ribavirin, penciclovir, and favipiravir might not possess noteworthy in
vivo antiviral actions for SARS-CoV-2, since higher concentrations of these nucleoside analogs
are needed in vitro to lessen the viral infection. Both remdesivir and chloroquine are being used
in humans to treat other diseases, and such safer drugs can be explored for assessing their
effectiveness in COVID-19 patients.
Several therapeutic agents, such as lopinavir ritonavir, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine,
have been proposed for the clinical management of COVID-19 (299). A molecular docking
study, conducted in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV-2 using
different commercially available antipolymerase drugs, identified that drugs such as ribavirin,
remdesivir, galidesivir, tenofovir, and sofosbuvir bind RdRp tightly, indicating their vast
potential to be used against COVID-19 (305). A broad-spectrum antiviral drug that was
developed in the United States, tilorone dihydrochloride (tilorone),
You might also like
- Vitro Antiviral Potential of FAD-approved Drugs, Viz.Document1 pageVitro Antiviral Potential of FAD-approved Drugs, Viz.garudaNo ratings yet
- Current Research in Green and Sustainable ChemistryDocument13 pagesCurrent Research in Green and Sustainable ChemistryRosnidar SumardiNo ratings yet
- Possible Treatment and Strategies For COVID-19: Review and AssessmentDocument16 pagesPossible Treatment and Strategies For COVID-19: Review and AssessmentAni RahayuNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0221 (20 Files Merged)Document33 pagesIMG - 0221 (20 Files Merged)Eurica CabilunaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Antimicrobial AgentsmiNo ratings yet
- Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: Rory J. Malek, Colin A. Bill, Charlotte M. VinesDocument21 pagesBiomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: Rory J. Malek, Colin A. Bill, Charlotte M. Vineszahraa ahmedNo ratings yet
- Inhibition of The SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase by Natural BioactiveDocument13 pagesInhibition of The SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase by Natural BioactiveLuis MartinezNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Repurposing Therapeutics For Potential Treatment of Sars-Cov-2: A ReviewDocument19 pagesViruses: Repurposing Therapeutics For Potential Treatment of Sars-Cov-2: A ReviewJacqueline Rose Alipo-onNo ratings yet
- Farmakodinamik, Farmakokinetik Favipirafir Dan RemdesivirDocument9 pagesFarmakodinamik, Farmakokinetik Favipirafir Dan Remdesiviranggara apNo ratings yet
- Docking Study of Naringin Binding With COVID-19 Main ProteaseDocument8 pagesDocking Study of Naringin Binding With COVID-19 Main ProteaseLuis MartinezNo ratings yet
- In Silico Identification of Clinically Approved Medicines Against The Main Protease of Sars-Cov-2, Causative Agent of Covid-19Document17 pagesIn Silico Identification of Clinically Approved Medicines Against The Main Protease of Sars-Cov-2, Causative Agent of Covid-19Rakesh DavellaNo ratings yet
- 14 Antiviral TherapyDocument1 page14 Antiviral TherapyPhạm Ngọc MinhNo ratings yet
- Antivirales Orales de Primera Generación Contra El SARS CoV 2 ClinicalDocument21 pagesAntivirales Orales de Primera Generación Contra El SARS CoV 2 ClinicalCarmenNo ratings yet
- Farmakodinamik, Farmakokinetik FavipiravirrDocument7 pagesFarmakodinamik, Farmakokinetik Favipiravirranggara apNo ratings yet
- Favipiravir: A New and Emerging Antiviral Option in COVID-19Document8 pagesFavipiravir: A New and Emerging Antiviral Option in COVID-19Muhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Img 0144Document1 pageImg 0144Lân VũNo ratings yet
- Sars Cov 2 Tratamentos Artigo NatureDocument6 pagesSars Cov 2 Tratamentos Artigo NaturesandraNo ratings yet
- Article 3Document33 pagesArticle 3Ekhlass UddinNo ratings yet
- JMV 25729Document8 pagesJMV 25729Ahmed AllamNo ratings yet
- Img 0153Document1 pageImg 0153Lân VũNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy - 2020 - Barlow - Review of Emerging Pharmacotherapy For The Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019Document23 pagesPharmacotherapy - 2020 - Barlow - Review of Emerging Pharmacotherapy For The Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019Gaby VillasmilNo ratings yet
- Trials To Treat Covid.19 Pandemic by Drug Repurposing or Novel AgentsDocument4 pagesTrials To Treat Covid.19 Pandemic by Drug Repurposing or Novel AgentsHh FtNo ratings yet
- d41573 020 00016 0 PDFDocument2 pagesd41573 020 00016 0 PDFDema AlsouqiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledzahrah murni YusoffNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3748111Document23 pagesSSRN Id3748111jonabert2018No ratings yet
- Covid-19 Drug Therapy - Potential Options: Tim Smith, Pharmd, Bcps Tony Prosser, PharmdDocument4 pagesCovid-19 Drug Therapy - Potential Options: Tim Smith, Pharmd, Bcps Tony Prosser, PharmdMonicaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Epidemiology and Global HealthDocument5 pagesClinical Epidemiology and Global HealthSheppik TerimaNo ratings yet
- Identification of Existing Pharmaceuticals and Herbal Medicines As Inhibitors of Sars-Cov-2 InfectionDocument8 pagesIdentification of Existing Pharmaceuticals and Herbal Medicines As Inhibitors of Sars-Cov-2 Infectionxintong liuNo ratings yet
- Hugh J. Field and Erik de Clercq: Antiviral Drugs - A Short History of Their Discovery and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesHugh J. Field and Erik de Clercq: Antiviral Drugs - A Short History of Their Discovery and DevelopmentDedy FransiscusNo ratings yet
- Review Jurnal Target Obat: Kimia MedisinalDocument14 pagesReview Jurnal Target Obat: Kimia MedisinalNurkhalis BintangNo ratings yet
- Favipiravir: A New and Emerging Antiviral Option in COVID-19Document7 pagesFavipiravir: A New and Emerging Antiviral Option in COVID-19morteza salipiNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic Chemistry: MD Jawaid Akhtar TDocument9 pagesBioorganic Chemistry: MD Jawaid Akhtar TRetno Tri RahayuNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics Used in Treatment of COVID-19Document18 pagesTherapeutics Used in Treatment of COVID-19teapalmtreeNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Antiviral Therapy in Patients Hospitalized With Covid-19Document5 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Antiviral Therapy in Patients Hospitalized With Covid-19Central Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Favipiravir in The Treatment of Covid-19-Dr ErlinaDocument32 pagesFavipiravir in The Treatment of Covid-19-Dr ErlinaMuh JamalNo ratings yet
- 21-30 SARS-CovDocument10 pages21-30 SARS-Covnadin changgiehNo ratings yet
- Ecprm 09 00577Document21 pagesEcprm 09 00577HETA JOSHINo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Ayurvedic TreatmentDocument29 pagesCovid 19 Ayurvedic TreatmentMIchelle SmithNo ratings yet
- Favipiravir: Pharmacokinetics and Concerns About Clinical Trials For 2019-Ncov InfectionDocument6 pagesFavipiravir: Pharmacokinetics and Concerns About Clinical Trials For 2019-Ncov InfectionJuan Felipe Herrera WilchesNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document18 pagesCovid 19teapalmtreeNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Publication by Student 1 (Signed)Document5 pagesResearch Paper Publication by Student 1 (Signed)Forensic MCQNo ratings yet
- Promising Research On Antiviral Medications Offers New Prospects For Sars-Cov-2 RecoveryDocument4 pagesPromising Research On Antiviral Medications Offers New Prospects For Sars-Cov-2 RecoveryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- QuinolonasDocument20 pagesQuinolonasAna NeryNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents and ChemotherapyDocument3 pagesAntimicrobial Agents and ChemotherapyDinakaranNo ratings yet
- Antivirus CovidDocument12 pagesAntivirus CovidAni RahayuNo ratings yet
- Treatment Options For Covid 19 The Reality and Challenges Shio Shin Jean Download 2024 Full ChapterDocument47 pagesTreatment Options For Covid 19 The Reality and Challenges Shio Shin Jean Download 2024 Full Chaptermari.artrip178100% (9)
- Davis ProjectDocument76 pagesDavis ProjectMuhammad SameerNo ratings yet
- Ribavirin, Remdesivir, Sofosbuvir, Galidesivir, and Tenofovir Against SARS-CoV-2 RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase (RDRP) A Molecular Docking Study PDFDocument6 pagesRibavirin, Remdesivir, Sofosbuvir, Galidesivir, and Tenofovir Against SARS-CoV-2 RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase (RDRP) A Molecular Docking Study PDFFercho MedNo ratings yet
- 218-Article Text-349-1-10-20200401 PDFDocument3 pages218-Article Text-349-1-10-20200401 PDFLeonardo de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Auto DockDocument7 pagesAuto Dockalealer2708No ratings yet
- D - O1a119203 - Wa Ode Yulianti Asrar JayaDocument19 pagesD - O1a119203 - Wa Ode Yulianti Asrar JayaWa Ode Yulianti Asrar JayaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy - 2020 - Jorgensen - Remdesivir Review of Pharmacology Pre Clinical Data and Emerging ClinicalDocument13 pagesPharmacotherapy - 2020 - Jorgensen - Remdesivir Review of Pharmacology Pre Clinical Data and Emerging ClinicalsankarNo ratings yet
- How Drug Repurposing Help in The Treatment of Covid-19 - 20231121 - 121232 - 0000Document1 pageHow Drug Repurposing Help in The Treatment of Covid-19 - 20231121 - 121232 - 0000Sartul singhNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument19 pagesResearch Articleshrooq sweilamNo ratings yet
- CovidDocument10 pagesCovidSufyan AliNo ratings yet
- Oral Antiviral Newsletter Yan Versi 2 - Dec 2021Document7 pagesOral Antiviral Newsletter Yan Versi 2 - Dec 2021YanMardianNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0753332222001172 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0753332222001172 MaingalancjammyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evaluation of Selected Pharmacological Treatments Used For Coronavirus (COVID-19) PandemicDocument5 pagesClinical Evaluation of Selected Pharmacological Treatments Used For Coronavirus (COVID-19) PandemicAbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Drug Therapy - Mar 2020 PDFDocument12 pagesCOVID 19 Drug Therapy - Mar 2020 PDFJean-Michel Tommy Luzayamo100% (1)
- Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Different Models and Treatment StrategiesFrom EverandCoronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Different Models and Treatment StrategiesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSaeha NoorNo ratings yet
- NspsDocument1 pageNspsSaeha NoorNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Revokation and Cancellation of An Offer Acceptance and ConsiderationDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Revokation and Cancellation of An Offer Acceptance and ConsiderationSaeha NoorNo ratings yet
- With SARS and MERSDocument1 pageWith SARS and MERSSaeha NoorNo ratings yet