0% found this document useful (0 votes)
395 views7 pagesEndocrine System Lab Worksheet Guide
The document is a lab worksheet for the endocrine system. It contains instructions to identify endocrine glands and hormones using an online anatomy software. It asks the student to identify endocrine structures, describe endocrine organ functions, and explain hormone actions and target tissues. The student must demonstrate understanding of the pituitary gland and its hormones, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, gonads and other endocrine functions.
Uploaded by
edwardCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
395 views7 pagesEndocrine System Lab Worksheet Guide
The document is a lab worksheet for the endocrine system. It contains instructions to identify endocrine glands and hormones using an online anatomy software. It asks the student to identify endocrine structures, describe endocrine organ functions, and explain hormone actions and target tissues. The student must demonstrate understanding of the pituitary gland and its hormones, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, gonads and other endocrine functions.
Uploaded by
edwardCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
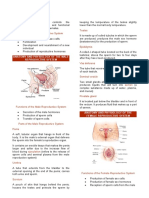
- Endocrine System Lab Worksheet: Provides instructions and questions for completing the endocrine system lab focusing on endocrine glands and corresponding hormone functions.
- Endocrine Organ Identification: Asks readers to identify endocrine organs based on their descriptions, focusing on location and function.
- Hormone Travel and Interaction: Explores how hormones travel and interact in the bloodstream with receptors and lists key hormones released from the pituitary gland.
- Target Organs for Hormones: Covers target organs involved in anterior and posterior pituitary hormone functions and outlines steroid effect on various body activities.
- Hormone Functions in Glands: Discusses hormone functions related to steroid production and secretion, adrenal cortex impact, and differences between primary and secondary endocrine functions.
- Adrenal Cortex and Pancreatic Cells: Elucidates the role of adrenal cortex in stress response and different cell types in the pancreas that produce hormones.
- Endocrine-Related Changes in Blood Pressure: Explains how endocrine peptides influence changes in blood volume and pressure via organs such as the heart.