Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Prince Mulenga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views9 pagesUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Prince MulengaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
CANDIDATE NAME: MULENGA PRINCE
COMPUTER NUMBER:22102789
GROUP MEMBERS (COMPUTER NUMBERS:
1.MULENGA PRINCE #2102789
2.SIBESO ARTHUR #19002369
3 PINIFOLO JONATHAN #2101089
4,SIMBULE NATASHA, #22102087
5 PHIRI RACHEAL #2102157
6.MALILA GERALD #2100881
NAME OF LECTURER: MRS ZULU
TASK: ASSIGNMENT 1
DUE DATE: 11'* MARCH 2023
QUESTION ONE
Explain why most governments prefer the mixed economic system as opposed to market or
command economic systems. Word limit: 1000 (25 marks)
Economic systems
An economic system can be defined as the means by which a specific society or government uses to
organize and distribute the available scarce resources across a specified geographic region or
country. Economic systems are meant to regulate the factors of production, which include land,
labor, capital, aud entrepreneurship. There are four types of economie systems: 1)Mixed economic
system; (2)Command economic system; (3)Market economic system; and (4)Traditional economic
system.
‘Mixed economy system is a combination of traditional economy, market economy, and command
economy. The analysis of this definition means that in a command economy, government can step
into guide the factors of production and control of resources. Marker economy, this is all about
individual and businesses benefits and it is largely based on a fiee market economy with no forms
of government interference. In this type of system, there is little or no government interference, and
the market is controlled by the relationship between demand and supply. Resource allocation is
done through a price mechanism that is subject to the forces of demand and supply. Traditional
economy, this is based on the traditional values of the society. Most countries tend to adopt mixed
economic systems, and Zambia is one of those countries.
‘The primary reason why most governments prefer the mixed economic system over the market and
command economic systems is that te mixed economic system allows the government to intervene
in the economy where the market fails. This means providing those goods and services such as law
and order, education and healthy services that would have been under-provided if left to the market.
Through a mixed economic systems, the government is able to dictate what the producer should
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
produce and bring to the market. Producers are motivated by profit maximization and in a mixed
economy they are able to respond quickly to changes in consumer prefereuces. A mixed economic
system also allows the govemment to intervene in cases where there is inflation, for example by
controlling pricing or introducing subsides. According to Adain Smith, (1776). Hee believed that
without the involvement of government, a free market would create benefits only for consumers and
producers. This is critically dangerous, as it poses a high risk to the social welfare aspect.
‘The other reasons why governments prefer mixed economic systems is because of the following
merits.
Effectiveness: The fiee market has been said to have more efficiency in managing the economy.
The nature of the free market is that it isa self-regulated economy based on the laws of demand and
supply. It has the ability to cut costs and maximize profits, which in turn can lead to new
innovations and free up resources that can be utilized for production of goods that can benefit
society.
Resources: since the mixed economy contains features of both capitalism and socialism economy,
resources are used in the best possible way. The price mechanism, freedom of consumption, profit
motive, and occupation all contributes to the efficient allocation of resources.
Equality of control: in contrast to the command economy where government is fully in charge of
production factors, the mixed economy has less government control. This allows private enterprise
to invest their capital in different areas of their choice. It also gives the private market freedom to
operate, expand and grow their businesses.
Social welfare: Iu mixed economy, the major target is social welfare. Under this system both public
and private sectors work for the welfare of the people. A good example is corporate social
responsibilities. Some private enterprises do provide social amenities to the communities in areas
where they operate, like building schools, clinics, grading roads, providing transport through
donation of vehicles, ambulances to public hospitals, public schools, and in some cases ensuring
that areas where they are operating have basic needs such as clean water by drilling boreholes. The
locals benefits in this way from the private investments in their communities. To achieve this goal,
the governments provides an enabling business environment for these private enterprises to operate
smoothly. In some cases, the governments partners with the private enterprises to achieve the social
aim
Protection Of Business, Property And Individual Rights: The government prefers the mixed
economic system, becanse it is able to enforce Antitrust law, this type of law opposes monopolies,
‘musts, and other organization or practices that do not allow higher participation from potential
entrepreneurs
Its through this type of economy that goverment has the mandate to protect and ensure that private
and public businesses operate in such a manner that both businesses and individuals rights are fully
safeguarded through government agencies. For instance, Zambian govemmment do protect business
and peoples lives through Zambia Compulsory Standards Agency (ZCSA) by ensuring that all
products on the market comply with the Zambian standards, by doing so government is protecting
the lives of people from consuming counterfeited products, expired products.
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
‘Types of mixed economies:
‘The mixed economy may be classified in two categories namely:
Capitalistic mixed economy and Socialistic mixed economy
Capitalistie mixed economy: under this type of economic system, the ownership of various factors
of production are privately controlled, Government has no interference in this type of economic
system, the only thing government can attribute to this system is to ensure that rapid economic
growth. Government can achieve the economic growth under capitalistic economic system through
various ways such as cutting income taxes while adjusting social welfare payments like what the
Zambian government has been doing by increasing the Social Cash Transfer, increment of
Constituent Development Funds (CDF).
Socialistic economic system, government takes over the control of production activities, the forces
of demand and supply becomes the base for decision making. According to the theory of Karl
Mars, he believed that “low-income workers, ficed with these injustices, would inevitably revolt
against the wealthy bourgeoisie”. He clearly indicated the importance of equal distribution of goods
and services despite the class of any individual. The socialistic economy focuses umch on the
socioeconomic objectives where the profit motive is channeled to the welfare of the people
In conelusion, most governments prefer a mixed economic system as it enables them to balance
market forces with government intervention to promote economic efficiency, competition, social
welfare, stability, innovation, and social responsibility. A mixed economic system provides the best
of both worlds, allowing for economic growth while ensuring that the basic needs of citizens are
met.
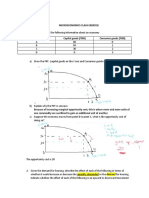
Question Two
A team consisting of three people is working on a big project, which involves manual entry of data
in a computer, with subsequent processing of these data and making a poster presentation.
‘Naturally, each member of the team has different abilities in performing either task. Adam can make
1 poster or 400 data entries in a day. Brenda can make 2 posters or 1200 data entries in a day.
Richard can make 3 posters or 900 entries ina day.
(a) In an event where each team member has access to their own personal computer, it means that
they are able to make data entries according to their capabilities,
1 Adam can make 1 poster or 400 data entries
2. Brenda can make 2 posters or 1200 data entries and
3. Richard can make 3 posters or 900 data entries,
‘This means that the total number of data entries made in a day will be 400+1200+900=2,500
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
Therefore, a total of 2,500 data entries will be made ina day
(b)According to the data given above that, Adam can make 1 poster a day, Brenda can make 2
posters aud Richard can make 3 posters a day. In the case that we should choose oue team member
to make posters, Richard would be chosen. Reason being that, the opportunity cost will be lower.
wwe would make three (3) posters at the cost of 900 data entries. As compared to the other two team
members Adam and Brenda
(©) The oppornmnity cost of Richard making 3 posters a day is 900 data entries and the opportunity
cost of making each poster a day will be 3 posters-900 data entries ~300 data entries
3 3
(@Adam can make 1 poster or 400 data entries in a day, and Brenda can make 2 posters or 1200 data
entries in a day. Therefore Adam would be selected, reason being that the opportunity cost of Adam
making 1 poster to make data entries is only 400. Meanwhile if Brenda is selected, the opportunity
cost of making 1 poster would be 2 posters=1200 data entries =600. Hence, it is more efficient to
assign Adam. 2 2
Parrett amelie
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
The points on the PPF curve represent efficient combinations of posters and data entries that the
team can produce. Points inside the curve represent inefficient conibinatious (e.g, the team is not
using all of their available resources), while points outside the curve are unattainable given the
team’s current resources and technology.
Question three
a) Assume that farmers in a given area are able to switch back and forth between potato and wheat
production depending on market conditions. Similarly, consumers tend to regard potatoes and
heat as substitutes. As a result, the demand and supply of Potatoes are highly seusitive to
changes in both potato and wheat prices. Demand and supply functions for Potatoes are as,
follows:
Q
Qs
430 - 25P + 12.5PW + 0.2Y, (Demand)
100 + 75P- 25PW- 12.5PL+10R, (Supply)
(A)To determine the demand and supply of Potatoes, we need to substitute the given values (PW =
K4, Y= K7, 500 billion, PL= K8, and R= 20 inches) in the demand and supply functions as follows:
Demand: Qp = -1,450 — 25P + 12.5(4) + 0.2(7500) = 100 - 25P
Therefore, Qo = 100 - 25P
Supply: Qs = -100 + 75P— 25(4) - 12.5(8) + 10(20) =- 100 + 75P
Therefore, Qs =-100 + 75P.
(2) To calculate the surplus or shortage of Potatoes, we need to compare the quantity demanded
(Qo) and quantity supplied (Qs) at different prices:
At P=K1:
Qo = 100 — 25(1.50)
Qn= 62.5 million medas
Q
Q
Qo - Qs = 62.5 — 12.5 = 50 million medas (Shortage)
Therefore, at the price of 1.50 there is a shortage of 50 million medas, as the quantity demanded is
‘more than the quantity supplied.
100 + 75(1.50)
2.5 million medas
AtP=K2
Qo = 100 — 25(2)
0 million medas
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
100 + 75(2) = 50 million medas
Qo - Qs =50-S0=0
Therefore, at the price of 2 there is no shortage or surplus, as the quantity demanded is equal to the
quantity supplied. Meaning that at the price of 2 and the quantity of 50, market is in equilibrium.
AtP=K2.50
Qo = 100 - 252.50)
Qo- 37.5 million medas
Qs =-100 + 75(2.50) = 87.5 million medas
Qo - Qs = 37.5 — 87.5 =-50 million medas (Surplus)
Therefore, at the price of 2.50 there is a surplus of 50, as the quantity demanded is less than the
quantity supplied.
(3)To caleulate the market equilibrium price and quantity, we need equate the Qo to the Qs and
solve for P: Qo = Qs
100 —25P =-100 + 75P
100 + 100 = 75P + 25P
200 = 100P.
k2
Substitute P = K2 back info either the demand or supply equation fo get Q: Q = 100 - 25(2) = 50
tillion medas of potatoes. Therefore, the market equilibrium price is K2 and the equilibrium
quantity is 50 million medas of potatoes.
(4) Price elasticity = PED -(% change in quantity demanded) when price changes from K2 to K1.5
(Cochange in price)
AtP=K150 PED= (62.5 -50) 2 = 12.5 x2=25 -PED-
(1.5-2)50 — -0.50 50 -25
PED=-1 unit elastic this occurs where price and quantity demanded change by the same proportion
1 unit elastic
AtP=K2; PED =(50—50)2=0x2 =PED=0 Perfect inelastic
(2-2) 50 0x50 0
PED = 0 (Perfectly inelastic) Whatever the % change in price there is no change in quantity
demanded. Price elasticity is then said to be perfectly inelastic
AtP=K2.50; PED = Qo—Qix Py
P,—Py
=37.5-50) 2
(2.5-2) 50 25
PED=-1 (unit elastic) this occurs where price and quantity demanded change by the same
proportion. In this state price is said to be unity elastic.
=1 unit elastic
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
(S)Determinate of price elasticity of demand and supply
Demand;
1. The number and closeness of substitutes
2. Proportion of income spent spent on goods
3. The number of users ofa commodity
Supply;
1. Production time period
2. Availability of factors of production
Question Four
a). Suppose there is a new residential area in town, The area is composed exclusively of flats and is
populated by low-income residents. The people who live in the area tend to stay in that area
because (1) they cannot afford to live in other areas of the town, (2) they prefer to live with people
of their own ethnic group, or (3) there is discrimination against them in other areas of town. Rents
paid are a very high percentage of peoples' incomes
(1) the demand will be relatively inelastic. The argument is based on the fact that the residents in this
area have few substitutes as they are unable to move to other areas for the fear of being discriminated
Additionally, these residents are already paying a high rentals and since accommodation is a necessity,
a slight inctease in rentals may not have a luge impact on the demand
(2) The supply of flats in such an area is likely to be relatively inelastic. Reason being that investors
that invest in housing are mostly after profit maximization and seeing that the area is populated with
low-income residents. Hence, they intend to shun investing in such areas which is resulting in
decrease of supply
8)
(Price)P
D
Equilibrium price and quantity
Q
(quantity)
Both demand and supply curves are showing a steep slope as they are both relatively inelastic.
b) (1)The introduction ofa subside on rental paid by residents in the area would mean that they get
to spend less on their income on rentals. This will now increase the demand for apartments in the
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
‘SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
area which will cause the demand curve to shift to the right resulting in a new market equilibrium
as there will be more demand than supply.
b) 2) Analyze the results of this program. Show the results on the graph and explain what will result
(Price) D2
4 Lz s
Pat
Pi
Nv 50
a @ (quantity)
The residents get to gain more fiom the introduction of subsides which has made a positive impact of
their rentals causing the demand curve to shift to the right
(b) (The introduction of the subsidy on the side of the supplier, will mean that the developers or
suppliers get to spend less on the cost of building new flats. This program is going to shift the supply
curve to the right as developers are now on incentives to enable them build more flats.
P
(price) s
Pl ~ /*
P2
NN D
Q
ae (quantity
Therefore, Tenants gain from this program for paying lower rentals and they have more disposable
incomes. Developer or suppliers also gains from this program as they receive subsidy for building
uew flats. The government will now incur a cost by paying building subsidies.
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA
INSTITUTE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
SOB 1115: MICROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT 1
References
Adam Smith, (1776). An inquiry into the nature and causes of wealth of Nations. Edinburg!
Scotland. W.Strahan and T. Cadell, Landon.
Sanford Tkeda: (1996). Dynamics of the Mixed Economy: Toward a Theory of
Interventionism London: Routledge 1997
"social democracy". Jason P. Abbot. Routledge Encyclopedia of Intemational Political
Economy. Ed. R. J. Barry Jones. Taylor & Francis, 2001. 1410
Schiller, Bradley. The Micro Economy Today, MeGraw-Hill/rwin, 2010. "Mixed economy.
Tawney, R. H. (1964). Equality. London: Allen and Unwin. ISBN 0-04-323014-8
Jump up Crosland, A (1977). The Future of socialism. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press
ISBN 0-8371-9586-1
David Begg, Gianluigi Vernasca, Stanley Fischer and Rudiger Dombusch ISBN-13
9780077129521 ISBN-10 0077129520
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Solutions EXERCISE 1Document7 pagesSolutions EXERCISE 1Prince MulengaNo ratings yet
- Business Environment Assignment 1 Solution-6Document1 pageBusiness Environment Assignment 1 Solution-6Prince MulengaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledPrince MulengaNo ratings yet
- Business Environment Assignment 1 Solution-5Document1 pageBusiness Environment Assignment 1 Solution-5Prince MulengaNo ratings yet
- Economic SystemsDocument9 pagesEconomic SystemsPrince MulengaNo ratings yet
- Sob 1115 Assignment One SolutionsDocument10 pagesSob 1115 Assignment One SolutionsPrince MulengaNo ratings yet
- Economic SystemsDocument9 pagesEconomic SystemsPrince MulengaNo ratings yet