Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conditional 1
Uploaded by
ionut petcuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditional 1
Uploaded by
ionut petcuCopyright:
Available Formats
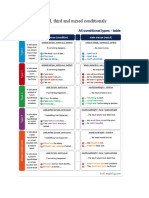
There are three types of conditional sentences with IF ("If") in English.
In all, the conditional sentence
(the one with "if") is a secondary sentence that depends on a main one.
The main clause can be at the beginning, or it can follow the secondary one (conditional with "if").
Conditional 1
The conditional of type 1 expresses a real and possible condition.
In this type, in the secondary sentence the predicate is present, and in the main one we have will +
short infinitive.
Examples:- I will go to the sea if the weather is good.
- If I leave now, I will arrive home at 8 o'clock.
- I will stay at home if it rains.
Instead of "will" we can have other modal verbs, such as can, may, etc.
- If you want, you can borrow my book.
- If it is cloudy, it is possible to rain.
IF can be replaced by provided (that), providing, supposing, suppose, in case.
- What will we do if he is late?
- What shall we do, assuming he is late?
Should + infinitive can be used instead of Present Simple, when the secondary (conditional) action is
possible, but improbable. This type of secondary is often combined with the imperative.
In this case, "should" is translated as: in case that, if it were to happen that.
- If she rings up, tell her I'm out. - If he calls, tell him I'm not at home.
- If she should ring up, tell her I'm out. - If he calls, tell him I'm not at home.
Conditional 2
The type 2 conditional expresses an unlikely condition and refers to a hypothetical situation.
In the secondary sentence the predicate is in the simple past tense, and in the main one we have the
construction would + infinitive.
Examples: - I would go to the sea if the weather was good.
- If he came home, his mother would be very happy.
- I would stay at home if it rained.
Although the simple past form of the verb "to be" (a fi) for the 1st person and the 3rd person singular
is "was", in the case of the conditional, the form "were" is used for all persons
- If I were in your place, I would be calmer.
- He would buy this house if he were rich.
Instead of "would", we can have other modal verbs, such as "might" or "could".
- If you worked and earned more, you could buy that car.
- He could have problems if he wasn't careful.
Conditional 3
The conditional of type 3 expresses an action in the past (which did not happen) that could have been
possible, if a certain condition had been fulfilled.
In the secondary sentence the predicate is in the past perfect tense, and in the main one we have the
construction would + have + the participle (the third form of the verb).
Examples:. - I would have gone to the sea if the weather had been good.
- If he had known the truth, he would have acted differently.
- I would have stayed at home if it had rained.
Instead of "would", we can have other modal verbs, such as "might" or "could", thus we have the
constructions: might + have + participle or could + have + participle.
- If he had gone to the garden, maybe he would have met Mary.
- If he had graduated high school, he could have gone to college.
Other peculiarities of IF conditionals
• In addition to the three types of conditional in English, we can also find conditional 0 (present +
present) and mixed conditionals (a combination of conditionals of type 2 and 3).
- If the temperature drops below 0 degrees, the water freezes. (certain thing)
- If he had followed my advice, he would have a happy marriage today.
- If he wasn't so friendly, she wouldn't have befriended him.
"if not" can be replaced with "unless".
- I won't go shopping if you don't come with me.
- I wouldn't have come if you hadn't invited me.
The conditional circumstantial sentence can be replaced by a conditional circumstantial complement,
which can be introduced by "but for".
- If she hadn't helped him, he would have been in another country.
Usually, in the main sentence that is the regent of a conditional, we find the modal verb "will" in
various tenses (will / would / would have), it can be replaced by other modal verbs. These modal
verbs bring different nuances compared to "will".
"Will" shows the highest degree of possibility among modal verbs.
- If her brother is good, she will be very happy.
"May / might" shows all possibility, but to a lower degree than will.
- If it were cloudy, it might rain.
"Can / could" shows ability.
- If he had been there, he could have helped them.
In addition to expressing a condition, the conditional can also refer to a promise or a warning,
especially in the case of type 1 conditional.
- If you behave nicely, I will buy you a toy.
- If you don't work hard, you will be fired.
You might also like
- Conditional Sentences ExplainedDocument4 pagesConditional Sentences ExplainedAntonio GarcíaNo ratings yet
- BachillerDocument5 pagesBachillerFatima VazquezNo ratings yet
- The Briefest English Grammar and Punctuation Guide Ever!From EverandThe Briefest English Grammar and Punctuation Guide Ever!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- If ClauseDocument3 pagesIf Clauseliziana zaharieNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument3 pagesConditional SentenceRegina MagdaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument6 pagesConditional Sentencesmigue714100% (1)
- Conditional SentencesDocument8 pagesConditional SentencesShabnam Fatima NathaniNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ExplainedDocument2 pagesConditionals ExplainedFlorencia Custo BlanchNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Guide - Types, Structures & UsageDocument6 pagesConditionals Guide - Types, Structures & UsageAnca ȘtefănescuNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalscat FNo ratings yet
- MaribelDocument24 pagesMaribelmdiazb01No ratings yet
- If clauses & conditional sentences explainedDocument21 pagesIf clauses & conditional sentences explainedAngélica Lizeth Cervantes GonzálezNo ratings yet
- The 'Zero' Conditional: 1. FormDocument14 pagesThe 'Zero' Conditional: 1. Formhima67No ratings yet
- Understanding Conditional SentencesDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Conditional SentencesManal CherifNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Conditional (Open Condition)Document4 pagesType 1 Conditional (Open Condition)Hung TranNo ratings yet
- English Condition PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish Condition PDFBiglolo BiglalaNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesType 2 Conditional SentencesIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- S6 ConditionalsDocument20 pagesS6 ConditionalsPedro FERREIRANo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument3 pagesConditional SentenceLiwanto LeeNo ratings yet
- Conditional Schue LerDocument14 pagesConditional Schue LerraimodNo ratings yet
- Situations and Their Consequences. We Will Study The Use of Following WordsDocument6 pagesSituations and Their Consequences. We Will Study The Use of Following WordsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 0,1,2,3Document6 pagesConditionals 0,1,2,3seherNo ratings yet
- The Zero Conditional: If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result)Document6 pagesThe Zero Conditional: If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result)Daniel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Isi Conditional SentenceDocument9 pagesIsi Conditional SentencenurhalizaatikaNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Conditional Sentences in EnglishDocument6 pages5 Types of Conditional Sentences in EnglishShaistaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionalsChalmers SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Conditionals: Zero ConditionalDocument2 pagesGrammar: Conditionals: Zero ConditionalfatimaNo ratings yet
- Third Conditional WorksheetDocument6 pagesThird Conditional WorksheetHatice AydinNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 1Document22 pagesConditionals 1Olguita H. PastorNo ratings yet
- Aptis DocumentsDocument31 pagesAptis DocumentsElenaNo ratings yet
- Lectia 3Document5 pagesLectia 3Tavy92No ratings yet
- Type 1 Conditional Sentences Are Used To Talk About Real and Possible SituationsDocument10 pagesType 1 Conditional Sentences Are Used To Talk About Real and Possible SituationsSadia AminNo ratings yet
- All Conditionals - Mixed Conditionals, Alternatives To If', InversionDocument4 pagesAll Conditionals - Mixed Conditionals, Alternatives To If', InversionKiara QuispeNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument6 pagesConditional SentencesMuhammad Uzair QadirNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument3 pagesMixed ConditionalsRodriguez Banda Guillermo A0% (1)
- Conditional Clause and Main ClauseDocument22 pagesConditional Clause and Main ClauseTita RashidaNo ratings yet
- CondicionalesDocument2 pagesCondicionalesdavid sánchezNo ratings yet
- Grammar partsDocument8 pagesGrammar partsfirewyimer921No ratings yet
- Conditionals Zsófi MódraDocument3 pagesConditionals Zsófi MódraBácskay Balázsné ZsófiaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 1&2Document5 pagesConditionals 1&2Monica Adina BaneaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesSnakegreemNo ratings yet
- Zero, First, Second, Third and Mixed ConditionalsDocument4 pagesZero, First, Second, Third and Mixed ConditionalschelseaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument23 pagesConditionalsCarmen BugnarNo ratings yet
- The Four English Conditionals ExplainedDocument12 pagesThe Four English Conditionals ExplainedMariaNo ratings yet
- Conditional structuresDocument3 pagesConditional structuresSara Rios BroullonNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechDocument22 pagesActive and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechTrịnh Quốc HiếuNo ratings yet
- The Use of The Suppositional Mood in Adverbial Clauses of Purpose and ConcessionDocument20 pagesThe Use of The Suppositional Mood in Adverbial Clauses of Purpose and ConcessionІра ПоворозникNo ratings yet
- Learn how to use the second conditionalDocument4 pagesLearn how to use the second conditionalPatri0% (1)
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument3 pagesMixed ConditionalsDASCALU ANANo ratings yet
- GRAMMARDocument11 pagesGRAMMARCristine Elizabeth Abude OritaNo ratings yet
- 1 and 2 ConditionalDocument4 pages1 and 2 ConditionalAnita P.No ratings yet
- GR ConmixedDocument20 pagesGR ConmixedJason WNo ratings yet
- Other PrepositionsDocument65 pagesOther PrepositionsjoseNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument9 pagesMixed ConditionalsLuis Rosique MartinezNo ratings yet
- Conditianal - If ClausesDocument15 pagesConditianal - If ClausesJbour LaithNo ratings yet
- How to Use Conditionals in English GrammarDocument2 pagesHow to Use Conditionals in English Grammarusuario4444No ratings yet
- Lesson On Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesLesson On Conditional SentencesMarina PeshovskaNo ratings yet
- English 7 Diagnostic Test 1st QuarterDocument3 pagesEnglish 7 Diagnostic Test 1st QuarterLexter Bryan DusaranNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Uses and FunctionsDocument3 pagesReservoir Uses and FunctionsJovie Ann RamiloNo ratings yet
- Layers of Atmosphere Worksheet Part IIDocument4 pagesLayers of Atmosphere Worksheet Part IILedam Emolotrab AdaipmilNo ratings yet
- Examen Parcial - Semana 4 INGLESDocument12 pagesExamen Parcial - Semana 4 INGLESClaudia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters of IndiaDocument5 pagesNatural Disasters of IndiaArnav Acharya WorldNo ratings yet
- Simple - Sentences Sample ESLlibrary PDFDocument38 pagesSimple - Sentences Sample ESLlibrary PDFJuanita Silva MontealegreNo ratings yet
- The InFluency Community - IdiomsDocument4 pagesThe InFluency Community - IdiomsEdgar Bonilla MuñozNo ratings yet
- Weather and Phrasal VerbsDocument23 pagesWeather and Phrasal VerbsElena GheorgheNo ratings yet
- X-Men Movies JumpChainDocument16 pagesX-Men Movies JumpChainSilva TNo ratings yet
- A Loetter To GodDocument14 pagesA Loetter To GodPooja PanditNo ratings yet
- En Plein Air Watercolor Expert Techniques and Simple Step by Step Projects For Creating Dynamic LandDocument155 pagesEn Plein Air Watercolor Expert Techniques and Simple Step by Step Projects For Creating Dynamic LandAnna Lara AbreuNo ratings yet
- Create terrifying undead with Animate Dead and Create Undead spellsDocument11 pagesCreate terrifying undead with Animate Dead and Create Undead spellsClawsfingerNo ratings yet
- Constructing a Hygrometer - Measure HumidityDocument4 pagesConstructing a Hygrometer - Measure HumidityNay Chi LwinNo ratings yet
- A Fictional Short Story Related To The Franklin Expedition - Khoi Ba NguyenDocument2 pagesA Fictional Short Story Related To The Franklin Expedition - Khoi Ba NguyenKhoi NguyenNo ratings yet
- CHE 436 MODULE 6 - Psychrometry (Humidification, Dehumidification, Cooling TowDocument48 pagesCHE 436 MODULE 6 - Psychrometry (Humidification, Dehumidification, Cooling TowEirell SandersNo ratings yet
- Pattern: If + Present Simple, Will + Base Verb USE: Shows A Likely or Possible Outcome That Will Probably Happen, If A Certain Condition Is MetDocument6 pagesPattern: If + Present Simple, Will + Base Verb USE: Shows A Likely or Possible Outcome That Will Probably Happen, If A Certain Condition Is MetSilverfoXX JackNo ratings yet
- Psychrometrics: Moist Air PropertiesDocument12 pagesPsychrometrics: Moist Air PropertiesMotaz H OthmanNo ratings yet
- Discover Xuong Giang TempleDocument11 pagesDiscover Xuong Giang Templekazu kabeNo ratings yet
- An African Thunderstorm Analysis All LevelsDocument3 pagesAn African Thunderstorm Analysis All LevelsAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Ccaa Hot Weather ConcretingDocument7 pagesCcaa Hot Weather ConcretingHussain ElarabiNo ratings yet
- Ad 2. Aerodromes Vanp Ad 2.1 Aerodrome Location Indicator and NameDocument21 pagesAd 2. Aerodromes Vanp Ad 2.1 Aerodrome Location Indicator and NameAyaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Semantic Roles Kel 3Document11 pagesSemantic Roles Kel 3Ahnas AttazqyNo ratings yet
- With Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western MountainsDocument3 pagesWith Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western Mountainshajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1463500318302336 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S1463500318302336 MainRafael QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Building ServicesDocument17 pagesBuilding ServicesNakul KordeNo ratings yet
- Checklist for maintaining resettlement homesDocument23 pagesChecklist for maintaining resettlement homesAmith PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Science 4-Q4-SLM12Document15 pagesScience 4-Q4-SLM12Ana ConseNo ratings yet
- تقرير ثرموداينمكDocument5 pagesتقرير ثرموداينمكاحمد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary BuildingDocument1 pageVocabulary BuildingKarl DitanNo ratings yet
- Hows The Soil? Maniyar Village Has Red Soil and Black Soil For Its Villages. (Document4 pagesHows The Soil? Maniyar Village Has Red Soil and Black Soil For Its Villages. (Chinmay KaranNo ratings yet
- I Is an Other: The Secret Life of Metaphor and How It Shapes the Way We See the WorldFrom EverandI Is an Other: The Secret Life of Metaphor and How It Shapes the Way We See the WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (26)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsFrom EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsNo ratings yet
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Learn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (47)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundFrom Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllFrom EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (83)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonFrom EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (136)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageFrom EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (425)
- On Speaking Well: How to Give a Speech with Style, Substance, and ClarityFrom EverandOn Speaking Well: How to Give a Speech with Style, Substance, and ClarityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageFrom EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (916)
- Everything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfFrom EverandEverything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (15)
- How to Tell a Story: An Ancient Guide to the Art of Storytelling for Writers and ReadersFrom EverandHow to Tell a Story: An Ancient Guide to the Art of Storytelling for Writers and ReadersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Writing That Works, 3rd Edition: How to Communicate Effectively in BusinessFrom EverandWriting That Works, 3rd Edition: How to Communicate Effectively in BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (29)
- How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingFrom EverandHow to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (26)
- The History of English: The Biography of a LanguageFrom EverandThe History of English: The Biography of a LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- How To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessFrom EverandHow To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (308)
- How to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneFrom EverandHow to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (115)