Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna Denaturation and Renaturation
Uploaded by
Soumyaranjan PatiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dna Denaturation and Renaturation
Uploaded by
Soumyaranjan PatiCopyright:
Available Formats
Denaturation of DNA:In the denaturation process, the hydrogen bonds between
two strands are broken giving rise to two single strands. The covalent bonds of DNA remain
unaffected.
Denaturation of DNA double helix takes place by the
following denaturating agents:
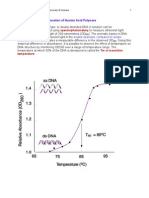
(i) Denaturation by Temperature:
If a DNA solution is heated to approximately 90°C or above there will
be enough kinetic energy to denature the DNA completely causing it to
separate into single strands. This denaturation is very abrupt and is
accelerated by chemical reagents like urea and formamide.The
chemicals enhance the aqueous solubility of the purine and pyrimidine
groups. This separation of double helix is called melting as it occurs
abruptly at a certain characteristic temperature called denaturation
temperature or melting temperature (Tm).It is defined as temperature
at which 50% of the DNA is melted.If several samples of DNA are
melted, it is found that the Tm is highest for those DNAs that contain
the highest proportion of G—C. Actually the value is used to estimate
the percentage of G—C in a DNA sample. In fact, the Tm of DNA from
many species varies linearly with G—C content.
This relationship between Tm and G—C content arises due to guanine
and cytosine form three hydrogen bonds when base paired, whereas
adenine and thymine form only two.
DNA Denaturation through NaOH Treatment
Apart from heating, chemical denaturation can also be achieved through the use of NaOH. A certain
concentration of NaOH can be used to denature DNA safely, often in as little as one minute. As the
concentration of NaOH used is reduced, the process will take longer -- but the DNA can still be fully
denatured.
DNA Denaturation through Salt .
A high concentration of salt will cause DNA to naturally denature, given the right concentration of
salt. DNA denaturation with salts are similar to denaturation through the use of organic solvents. In
general, DNA denaturation through salt cannot be renatured.
Effect of denaturation of DNA:
● Increased absorption of UV light at 260nm wavelengths. The rate of absorption is directly
proportional to the rate of denaturation
● Viscosity decreases, which reflects the physical change occurred in the DNA structure
What is Renaturation?
Renaturation is also known as annealing. When the temperature and pH return to optimum biological
level, the unwound strand of DNA rewind and give back the dsDNA.
If the DNA is not completely denatured, the renaturation process is fast and a one-step process, but
if the DNAs are completely denatured then the renaturation process occurs in a two-step process.
First complementary strands come together by random collision and then rewinding takes place
forming a double helix.
Renaturation occurs when the denatured DNAs are cooled in suitable conditions. Renaturation also
depends on temperature, pH, length and constituents of the DNA structure. The renaturation rate is
directly proportional to the number of complementary sequences present.
With renaturation, absorption of UV (260nm) decreases and viscosity increases again.
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesChemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsSherlock Wesley ConanNo ratings yet
- DNA Renaturation & HybridizationDocument3 pagesDNA Renaturation & HybridizationAqsa RaffaqNo ratings yet
- DR Tiang Report 1Document7 pagesDR Tiang Report 1KhAi EnNo ratings yet
- Hyperchromic EffectDocument7 pagesHyperchromic EffectvictorNo ratings yet
- Assigment ON HyperchromicityDocument13 pagesAssigment ON Hyperchromicityrag.1607No ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2Lloaana 12No ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of DNADocument5 pagesIsolation and Characterization of DNAgeorgiana0% (1)
- Genome ComplexityDocument24 pagesGenome ComplexityAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Habb - HBB 231 Notes - June 2024Document196 pagesHabb - HBB 231 Notes - June 2024AmandaNo ratings yet
- DNA STRUCTURE LectureDocument44 pagesDNA STRUCTURE Lectureevacarlina1721No ratings yet
- RDNA Lect Lecture Notes Mid Sem BTech IDDDocument146 pagesRDNA Lect Lecture Notes Mid Sem BTech IDDarpna sjsNo ratings yet
- DENATURATION AND RENATURATION of DNADocument4 pagesDENATURATION AND RENATURATION of DNAMillicent LanzuelaNo ratings yet
- 2 Okt 2019Document49 pages2 Okt 2019ElitaNo ratings yet
- Acid Hydrolysis of DNA Isolated From Allium Cepa and Analysis of DNA Components Using Qualitative Color Reaction TestDocument6 pagesAcid Hydrolysis of DNA Isolated From Allium Cepa and Analysis of DNA Components Using Qualitative Color Reaction Testmissy_macy11100% (1)
- 0532 HTMLDocument6 pages0532 HTMLyuNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 DNA Extraction and PCRDocument25 pagesLec 5 DNA Extraction and PCRSaif MohamedNo ratings yet
- Denaturation of Human HairDocument2 pagesDenaturation of Human HairDiosel Rezia PrazaNo ratings yet
- Bio Project-Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument21 pagesBio Project-Polymerase Chain ReactionS.AbiniveshNo ratings yet
- EthanolDocument8 pagesEthanolRohan Walking TallNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lecture 2 - DNA and Chromosome Structure PDFDocument58 pagesGenetics Lecture 2 - DNA and Chromosome Structure PDFMarlee SandersonNo ratings yet
- Hyperchromic Effect, and Reveals The Interaction Between The Electronic Dipoles in The StackedDocument3 pagesHyperchromic Effect, and Reveals The Interaction Between The Electronic Dipoles in The StackedrainabtNo ratings yet
- Biotech Group 5Document6 pagesBiotech Group 5CarminexxxNo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis and Blotting of DNADocument6 pagesElectrophoresis and Blotting of DNAAnkit GargNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument2 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionՏᗅႮRᗅBH ՏᗅiNiNo ratings yet
- s15 Miller Chap 8b LectureDocument19 pagess15 Miller Chap 8b LectureKartika FitriNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Identification of DNADocument13 pagesExtraction and Identification of DNAananyapandey6582No ratings yet
- Dna Rna 1Document27 pagesDna Rna 1ابوبكر خلف اللهNo ratings yet
- Duplichecker Plagiarism ReportDocument4 pagesDuplichecker Plagiarism Reportsouvikgh22No ratings yet
- 2 DNA ExtractionDocument1 page2 DNA ExtractionruelalmandresNo ratings yet
- DNA Denaturation: Biochemistry Department. Course Code:701 Instructor: Dr/OmneyaDocument16 pagesDNA Denaturation: Biochemistry Department. Course Code:701 Instructor: Dr/OmneyaAshik AdnanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 and 9 PDFDocument17 pagesExperiment 8 and 9 PDFKrizzi Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bio 101Document31 pagesBio 101SunflowerNo ratings yet
- Blotting Techniques ManishDocument56 pagesBlotting Techniques ManishAbdulati Abu RewillaNo ratings yet
- PCRDocument3 pagesPCRarian.boostani2002No ratings yet
- Diphenylamine TestDocument16 pagesDiphenylamine Testkenneth VonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory TechniquesDocument50 pagesLaboratory TechniquesmNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Manipulation: The Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument22 pagesNucleic Acid Manipulation: The Polymerase Chain Reactionamor_panopioNo ratings yet
- Cot CurvesDocument4 pagesCot CurvesVenkateswarlu Yadavalli100% (2)
- Preparation of Bacterial Genomic Dna and Concentration Determination of DnaDocument7 pagesPreparation of Bacterial Genomic Dna and Concentration Determination of DnaEbruAkharmanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Fourth EditionDocument17 pagesMolecular Biology: Fourth Editionفقوش عبودNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of DNADocument6 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of DNASamreen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- TRANSCRIPTIONDocument8 pagesTRANSCRIPTIONReizel GaasNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction: Principle, Technique and Applications in PathologyDocument11 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction: Principle, Technique and Applications in PathologyvellyezkaNo ratings yet
- Extraction of DNADocument3 pagesExtraction of DNASaksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dna Isolation From OnionDocument4 pagesDna Isolation From OnionHanz Christian Andrade Mendez100% (5)
- DNA-Au Colloid PreparationDocument6 pagesDNA-Au Colloid PreparationDAVID ROSAS VARANo ratings yet
- Internship Takara BioDocument4 pagesInternship Takara BioBhai Kabir singhNo ratings yet
- Genetics, Lecture 4, DNA Coiling and Re-Coiling (Slides)Document8 pagesGenetics, Lecture 4, DNA Coiling and Re-Coiling (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (1)
- Mol Gen 3 MeltingDocument29 pagesMol Gen 3 MeltingFriendlyGoodGirlNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Notes Class)Document1 page9.2 Notes Class)Bithiah BidsNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Lysis, SDS Page, Sequencing, ChromatographyDocument73 pagesAlkaline Lysis, SDS Page, Sequencing, ChromatographyShashwat Mishra100% (1)
- PCR: An Outstanding MethodDocument17 pagesPCR: An Outstanding MethodPriyaranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Ethanol PrecipitationDocument4 pagesEthanol PrecipitationPriyanka_1No ratings yet
- Southern BlottingDocument23 pagesSouthern BlottingAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- Biology Core Practical 6.1 DNA Amplification Using PCRDocument2 pagesBiology Core Practical 6.1 DNA Amplification Using PCRBenedicte Symcox100% (1)
- 10 - Basic Recombinant DNA TechniquesDocument77 pages10 - Basic Recombinant DNA TechniquesNguyenHongThamNo ratings yet
- IrrigationDocument6 pagesIrrigationSoumyaranjan PatiNo ratings yet
- WWW HorticulturegurujiDocument1 pageWWW HorticulturegurujiSoumyaranjan PatiNo ratings yet
- WWW HorticulturegurujiDocument3 pagesWWW HorticulturegurujiSoumyaranjan PatiNo ratings yet
- Euchromatin and HeterochromattinDocument4 pagesEuchromatin and HeterochromattinSoumyaranjan PatiNo ratings yet
- Precision CatalogDocument256 pagesPrecision CatalogImad AghilaNo ratings yet
- Essential Calculus Skills Practice Workbook With Full SolutionsDocument528 pagesEssential Calculus Skills Practice Workbook With Full SolutionsGerardo Navarro Sánchez94% (65)
- Ruhangawebare Kalemera Godfrey Thesis PDFDocument116 pagesRuhangawebare Kalemera Godfrey Thesis PDFYoobsan Tamiru TTolaaNo ratings yet
- Dna Adduct As Biomarker: Prof. Dr. Yahdiana Harahap, MS, AptDocument68 pagesDna Adduct As Biomarker: Prof. Dr. Yahdiana Harahap, MS, AptNadia AaqilahNo ratings yet
- Test09 Eoc Algebra2 ReducedDocument33 pagesTest09 Eoc Algebra2 ReducedkristymadimikeNo ratings yet
- Minimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerDocument2 pagesMinimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerIrish Nicole AlanoNo ratings yet
- Volvo Penta GensetDocument4 pagesVolvo Penta GensetafandybaharuddinNo ratings yet
- Qasr Al Sarab Desert Resort Location Map June2012Document1 pageQasr Al Sarab Desert Resort Location Map June2012Anant GârgNo ratings yet
- SAT Practice Test 10 - College BoardDocument34 pagesSAT Practice Test 10 - College BoardAdissaya BEAM S.No ratings yet
- Influence of Aesthetics Attributes of Brand Web Pages On Customer Brand EngagementDocument22 pagesInfluence of Aesthetics Attributes of Brand Web Pages On Customer Brand EngagementNOOR AKMA AIDANo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument14 pagesProject ReportNoah100% (7)
- Bchem 455 - Module 3Document42 pagesBchem 455 - Module 3WilliamNo ratings yet
- AppearancesDocument4 pagesAppearancesReme TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Asme Code Sec Ix Ma Appe 2004Document3 pagesAsme Code Sec Ix Ma Appe 2004Guillermo CamachoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Population EducationDocument4 pagesBasics of Population EducationLAILANIE DELA PENANo ratings yet
- Tabla9 1Document1 pageTabla9 1everquinNo ratings yet
- Flow Zone Indicator Guided Workflows For PetrelDocument11 pagesFlow Zone Indicator Guided Workflows For PetrelAiwarikiaar100% (1)
- LinkageDocument9 pagesLinkageHarshu JunghareNo ratings yet
- G10Mapeh Exam First QuaterDocument8 pagesG10Mapeh Exam First QuaterJonas LamcisNo ratings yet
- Kinder DLL Week 8Document15 pagesKinder DLL Week 8Jainab Pula SaiyadiNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani: Determination of Extreme Pressure, Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricants Using Four Ball TesterDocument10 pagesBITS Pilani: Determination of Extreme Pressure, Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricants Using Four Ball Testerakash chNo ratings yet
- Free Electron TheoryDocument8 pagesFree Electron TheoryNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- MSDS DowthermDocument4 pagesMSDS DowthermfebriantabbyNo ratings yet
- Discrete Wavelet TransformDocument10 pagesDiscrete Wavelet TransformVigneshInfotechNo ratings yet
- AIR Conditioner: Owner'S ManualDocument52 pagesAIR Conditioner: Owner'S Manualashley diazNo ratings yet
- EXCEL For Pump DesignDocument2 pagesEXCEL For Pump Designkad-7No ratings yet
- Ict 2120 Animation NC Ii Week 11 20 by Francis Isaac 1Document14 pagesIct 2120 Animation NC Ii Week 11 20 by Francis Isaac 1Chiropractic Marketing NowNo ratings yet
- Book Index The Art of Heavy TransportDocument6 pagesBook Index The Art of Heavy TransportHermon Pakpahan50% (2)
- Physics Unit 11 NotesDocument26 pagesPhysics Unit 11 Notesp.salise352No ratings yet
- Scholomance 1 GravitonDocument18 pagesScholomance 1 GravitonFabiano SaccolNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3From EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet