Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-Record To Report Overview
Uploaded by
Marycris CatayongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1-Record To Report Overview
Uploaded by
Marycris CatayongCopyright:
Available Formats
RECORD TO REPORT OVERVIEW
ROLES INITIAL APPROXIMATE RESOURCES:
Departmental Staff
Accountants
Office Managers
Business Managers
Program Assistants
OVERVIEW
This section provides an overview to the Record to Report process and the
related PeopleSoft modules.
In PeopleSoft we will have to adapt to new terminology as we transition from
SAMAS. In the Introduction to Chartfield class you will have been exposed to
some of the new terminology. On page two and three of this chapter is a quick
reference guide to the new Chartfield terminology. In PeopleSoft the correct
term for what we called in SAMAS a department ledger is general ledger.
The Record to Report process involves the General Ledger (GL), Project
Costing (PC), and the Asset Management (AM)) modules of PeopleSoft. Each
of these modules will receive data from other PeopleSoft modules, primarily
Accounts Payable (AP) and Purchasing (PO) as well as from other non-
PeopleSoft sources. Please see the flowchart on page four for a graphic
representation.
The GL module is the source for all financial reporting. It receives information in
the form of journal entries from all of the PeopleSoft modules mentioned in the
above paragraph as well as summarized information from other USF systems,
for example, GEMS for payroll data and OASIS for student information and
entries keyed online.
Record to Report is organized into five sections:
GL Inquiries and Reports
Journal Entry Inquiry
Non-Payroll Expenditure Transfers
Commitment Control Overview
Asset Overview and Inquiry
In the GL Inquires and Reports chapter we will show you how to run a general
ledger report and how to run an inquiry showing your departments activity.
When you run your departments general ledger you will see all activity has been
posted with a journal entry reference number. In the Journal Entry Inquiry
chapter we will show you how you can research a journal entry by using the drill
down to find the details about the entry.
Updated 7/10/03 Record to Report – Overview Page 1 of 4
In the Non-payroll Expenditure Transfers chapter we will review the new
procedures for submitting an expense transfer request.
In the Commitment Control chapter we will show you how to inquire for your
remaining spending authority (in SAMAS called unexpended available budget).
In the Asset Overview and Inquiry chapter we will show you how to look up
asset information you need to transfer or write off an asset.
Training for the Budget Transfers and Capital Projects chapters will be given in
separate sessions at a later time.
PeopleSoft applications are built on the concepts of the Business Unit and
SetID. The FAST team has used this concept to define USF’s business
environment within the PeopleSoft structure. Business Units and SetIDs are the
foundation that enables the flexibility while minimizing the administrative burden
of maintaining the system. SetIDs enable you to control how you share your
organizational data across the Business Units.
To further categorize the financial data with in the Business Units, PeopleSoft
uses Chartfields. PeopleSoft Chartfields are the fields that store your chart of
accounts and provide your system with the basic structure to segregate and
categorize transactional and budget data. Each Chartfield has its own attributes
for maximum efficiency and flexibility in recording, reporting and analyzing its
intended category of data.
PeopleSoft further segregates the financial data within the General Ledger
module through the use of ledgers. A ledger is a set of posted balances that
represents a set of books for a business unit. Ledgers store the posted net
activity for a set of Chartfield values by accounting period and by fiscal year.
Primarily they store actual, budget, forecast, statistical, or any other type of
data. For example the ACTUALS ledger has been defined for posting of daily
actual activity and additional ledgers have been defined for budgetary activity.
By using multiple fields each with their own attributes and meaning PeopleSoft
provides flexibility to your reporting. Rather than creating one value to represent
a complex string of information, Chartfields segregate the string into
components allowing you to combine the components multiple ways. Therefore
you can use combinations of components to define a unique string without
having to define a specific value for each string. This reduces the number of
values in your chart of accounts and can simplify maintenance.
GL is the owner of the Chartfields, however, since the Chartfields are used in all
of the modules to record transactions it is important to understand USF’s
design. All class participants should have completed the introduction to
Chartfields class prior to attending Record to Report. Below is a high-level
description of the Chartfields to be used by USF
Updated 7/10/03 Record to Report – Overview Page 2 of 4
Business Unit - Divides a business into logical units other than companies and
departments. The FAST team has defined the PeopleSoft General Ledger
module utilizing a single Business Unit for USF (USF01).
Operating Unit – Used to track financial activities by campus (Tampa, St Pete,
Sarasota, Lakeland) with the additional breakout of Health Sciences, FIPR and
Non-Operating (to be recorded at the University level).
Department – Used to track financial activity by organizational unit (generally
equivalent to the first four characters of the SAMAS account).
Account – Classifies the accounting nature of a transaction (equivalent to
general ledger and object code)
Fund Code – Primary structural unit for governmental accounting. Funds are
administered separately and maintained as a balanced set of accounts to be
used to present financial statements. (E&G, Auxiliary, Grants, etc)
Initiative –Used to track University funded initiatives and principle investigator
(PI) share of overhead rebates for Grants (current RO accounts).
Product – Used to track revenue and expenditures for specific activities.
Defined at the college or unit level.
Project ID/Grant – Used to track capital construction projects and grant activity.
Defined by facilities planning and grant management. (Will not be used by all
colleges or units, please refer to your specific area for guidelines)
NOTE: The information in this guide is based on certain assumptions:
Users have previously received training in PeopleSoft 8.4 navigation
Users have previously attended the Introduction to Chartfields training
Control tables have been set up with needed values prior to performing the
activities described in the sections to follow.
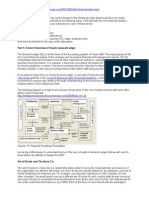
INPUTS - Subsidiary Systems / and Direct
Updated 7/10/03 Record to Report – Overview Page 3 of 4
Input
Accounts Payable *
*
*
Asset Management * *
* *
* *
Billing / Accounts Receivable * * >
* *
* *
Cash Deposits * * >
* *
* *
* > GENERAL LEDGER
*
* > Actual Data
Direct Journal Entry to G/L * * * * * * >
(Main Data
* Repository)
* >
* *
* *
OASIS System / Student Data * *
*
*
GEMS / Payroll Data *
Subsidiary Ledgers - Are "detailed" ledgers G/L: Repository of all summary data
Data will balance by Fund within General Ledger
Updated 7/10/03 Record to Report – Overview Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Overview of Financial Accounting in SAPDocument31 pagesOverview of Financial Accounting in SAPyashghodke83No ratings yet
- GL, AP, AR, Cash Journal and R3Document10 pagesGL, AP, AR, Cash Journal and R3sanjaypoptani.mclindiaNo ratings yet
- Record to Report: The End-to-End Financial Process CycleDocument4 pagesRecord to Report: The End-to-End Financial Process CycleDANIELNo ratings yet
- IS-U/FERC SAP’s Global Utilities Regulatory SolutionDocument9 pagesIS-U/FERC SAP’s Global Utilities Regulatory SolutionSelwyn Bausa Begata100% (1)
- SAP FICO Documents - SAP SIMPLE DocsDocument6 pagesSAP FICO Documents - SAP SIMPLE Docsrudy suryaNo ratings yet
- Peoplesoft Financials User Guide: Chart of AccountsDocument10 pagesPeoplesoft Financials User Guide: Chart of AccountsTin Zaw ThantNo ratings yet
- Budget ReportsDocument65 pagesBudget ReportsKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Parallel Accounting in New General LedgerDocument5 pagesParallel Accounting in New General LedgerbrcraoNo ratings yet
- Scenarios in SAP General Ledger AccountingDocument6 pagesScenarios in SAP General Ledger AccountingAmin raufiNo ratings yet
- Sap Unit 5 AccountingDocument18 pagesSap Unit 5 AccountingRatna Tri MharaniNo ratings yet
- SAP Accounting System Provides Structural Changes Management Tool Decision-Based International ApplicationsDocument7 pagesSAP Accounting System Provides Structural Changes Management Tool Decision-Based International ApplicationslazagasyNo ratings yet
- Set Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting SystemDocument10 pagesSet Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting Systemabebe kumelaNo ratings yet
- Financial Data MartDocument9 pagesFinancial Data Martvvnssatish0% (1)
- Financial Reporting in XBRLDocument56 pagesFinancial Reporting in XBRLEj BalbzNo ratings yet
- Bpcnw100 Ifrs Sp4 OverviewDocument44 pagesBpcnw100 Ifrs Sp4 OverviewVinutaNo ratings yet
- Fatimatus Zehroh - SUMMARY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM INFORMATION Unit 5&6Document8 pagesFatimatus Zehroh - SUMMARY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM INFORMATION Unit 5&6Fatimatus ZehrohNo ratings yet
- new gl segmentDocument9 pagesnew gl segmentDiego PazinNo ratings yet
- What's New in R12 Financials?: 1) Ledgers and Ledger SetsDocument4 pagesWhat's New in R12 Financials?: 1) Ledgers and Ledger SetsnmvelNo ratings yet
- SAP General Notes 14nov2007Document8 pagesSAP General Notes 14nov2007api-3836423No ratings yet
- The Basic Activities in Glars:: U Ëc Invlvc Pingc C C Jrnalc Nric RMC A C IcDocument6 pagesThe Basic Activities in Glars:: U Ëc Invlvc Pingc C C Jrnalc Nric RMC A C IcgatchanessNo ratings yet
- Erp Fusion Reporting WPDocument10 pagesErp Fusion Reporting WPS.Nantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Accounting in New Accounting ModelDocument43 pagesPrinciples of Accounting in New Accounting ModelMudassar Nawaz100% (1)
- How To Read The Balance Sheet Summary Report: Step-by-Step GuideDocument4 pagesHow To Read The Balance Sheet Summary Report: Step-by-Step GuideAshima MishraNo ratings yet
- General Ledger AccuntingDocument186 pagesGeneral Ledger AccuntingAnkur GoyalNo ratings yet
- 130: What Are The Key Flexfields That Are Only Used in Oracle Applications by The Accounting Flexfield and No Other Flexfield?Document5 pages130: What Are The Key Flexfields That Are Only Used in Oracle Applications by The Accounting Flexfield and No Other Flexfield?Vidhi SethiNo ratings yet
- Business Consolidation (SEM-BCS) PDFDocument180 pagesBusiness Consolidation (SEM-BCS) PDFparivijjiNo ratings yet
- New General Ledger IntroductionDocument3 pagesNew General Ledger IntroductionManohar GoudNo ratings yet
- Tugas RangkumanDocument18 pagesTugas RangkumaniqbalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To AISDocument29 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To AISFatiha YusofNo ratings yet
- SAP AccountingDocument2 pagesSAP AccountingSultanNo ratings yet
- Posting PDFDocument22 pagesPosting PDFrahul sinhaNo ratings yet
- HFM Traning HITATHIDocument83 pagesHFM Traning HITATHIRakesh Jalla100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8John PaulNo ratings yet
- What Is SAP Finance ?what Business Requirement Is Fulfilled in This Module?Document4 pagesWhat Is SAP Finance ?what Business Requirement Is Fulfilled in This Module?Ananthakumar ANo ratings yet
- BTE (How To)Document16 pagesBTE (How To)emc_cefre1735No ratings yet
- Basic Configuration Settings For Implementing Asset Accounting in SAP 6.0Document5 pagesBasic Configuration Settings For Implementing Asset Accounting in SAP 6.0Jyotiraditya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO Course ContentsDocument10 pagesSAP FICO Course ContentsSagar Paul'gNo ratings yet
- The mySAP ERP Modules OverviewDocument17 pagesThe mySAP ERP Modules OverviewSubbireddy ChintapalliNo ratings yet
- Oracle SetupsDocument26 pagesOracle SetupsDaama ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Unit 9. Reconciliation Between Management Accounting and Financial Accounting Reconciliation Ledger Business ExampleDocument7 pagesUnit 9. Reconciliation Between Management Accounting and Financial Accounting Reconciliation Ledger Business ExampleItisham Nafis MuhammadNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument242 pagesAccountingzengys1312No ratings yet
- Financial Reporting and Management Reporting System NotesDocument7 pagesFinancial Reporting and Management Reporting System NotesJoana TrinidadNo ratings yet
- UML JournalDocument18 pagesUML JournalNisha MandaleNo ratings yet
- Sap FiDocument4 pagesSap FiNicky AugustineNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Industry Chart of AccountsDocument12 pagesHospitality Industry Chart of AccountsAgus Priyanto100% (7)
- New GLDocument30 pagesNew GLkalkikaliNo ratings yet
- Implement Subledger Accounting OptionsDocument36 pagesImplement Subledger Accounting OptionsRajesh ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Bpcnw10 Ifrs Overw Sp5Document41 pagesBpcnw10 Ifrs Overw Sp5YudhaPKusumahNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO Configuration GuideDocument3 pagesSAP FICO Configuration GuideChirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Structure & Master DataDocument10 pagesEnterprise Structure & Master DatapaiashokNo ratings yet
- 3 New GLDocument8 pages3 New GLChirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO ProcessesDocument21 pagesSAP FICO ProcessesGaurav Tipnis0% (1)
- General Ledger Manual: Draft Peoplesoft Version 8.9 January 17, 2007Document61 pagesGeneral Ledger Manual: Draft Peoplesoft Version 8.9 January 17, 2007PriyaNo ratings yet
- SAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyFrom EverandSAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Flight Training Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandFlight Training Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Mysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungFrom EverandMysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Siebel Incentive Compensation Management ( ICM ) GuideFrom EverandSiebel Incentive Compensation Management ( ICM ) GuideNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at A Glance IFRS 11 Joint ArrangementsDocument7 pagesIfrs at A Glance IFRS 11 Joint ArrangementsNoor Ul Hussain MirzaNo ratings yet
- Secretarial Practice: Std. Xii LMRDocument45 pagesSecretarial Practice: Std. Xii LMRaliffya rangwalaNo ratings yet
- Dendrite International: Group No-5 Alok Pratap Singh (23NMP05) Mohan Murari (23NMP19) Sudhansu Senapati (23NMP31)Document7 pagesDendrite International: Group No-5 Alok Pratap Singh (23NMP05) Mohan Murari (23NMP19) Sudhansu Senapati (23NMP31)Rahul NiranwalNo ratings yet
- Recognize Potential MarketDocument6 pagesRecognize Potential MarketBen ZerepNo ratings yet
- Makalah B.inggrisDocument15 pagesMakalah B.inggrisMuhammadnur AzizNo ratings yet
- L4M8Document3 pagesL4M8Shane SookrajNo ratings yet
- Company LawDocument11 pagesCompany LawAneshNo ratings yet
- University of London La3021 OctoberDocument6 pagesUniversity of London La3021 OctoberdaneelNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Research Paper PDFDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Management Research Paper PDFqqcxbtbndNo ratings yet
- Darkside of The Pools ReportDocument41 pagesDarkside of The Pools ReportdatasetNo ratings yet
- Anne Camille Mora - ResumeDocument1 pageAnne Camille Mora - ResumeIan Shain YapNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Economics Sample Paper 1 1Document18 pagesCBSE Class 11 Economics Sample Paper 1 1Smart shopNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Unit 3Document20 pagesEntrepreneurship Unit 3Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Walmart's Global Strategies CaseDocument9 pagesWalmart's Global Strategies CaseRandolph LeroyNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries and Worksheet PreparationDocument16 pagesAdjusting Entries and Worksheet Preparationcarlo bundalianNo ratings yet
- Project Report On The Genesis of Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL)Document44 pagesProject Report On The Genesis of Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL)swapnil panmandNo ratings yet
- Export Financing GuideDocument82 pagesExport Financing GuideRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Kctmo Rydon Grenfell Tower Newsletter May 2015Document35 pagesKctmo Rydon Grenfell Tower Newsletter May 2015TonyHatNo ratings yet
- Project Final - Corp. Law II 2022-23Document11 pagesProject Final - Corp. Law II 2022-23Lalbee SNo ratings yet
- 1570-1635319411751-Unit 02 Marketing Processes and PlanningDocument17 pages1570-1635319411751-Unit 02 Marketing Processes and Planningsathsaraniranathunga6No ratings yet
- What Jobs Can You Do With An Electrical Engineering DegreeDocument3 pagesWhat Jobs Can You Do With An Electrical Engineering DegreeImam d'SmartanNo ratings yet
- User Story For Purchase Inventory ManagementDocument3 pagesUser Story For Purchase Inventory ManagementAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting, Hilton, 7eDocument43 pagesManagerial Accounting, Hilton, 7eMohit Srivastava0% (3)
- Accounting IB Course OutlineDocument2 pagesAccounting IB Course OutlineEdwin Mudzamiri04No ratings yet
- Chapter Two The Economizing ProblemDocument13 pagesChapter Two The Economizing ProblemHannah CaparasNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Indonesian Consumer Online Shopping Behavior During The Covid-19 Pandemic: A Shopee Case StudyDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Indonesian Consumer Online Shopping Behavior During The Covid-19 Pandemic: A Shopee Case StudySiti Sarah Zalikha Binti Umar BakiNo ratings yet
- Murder at The MarginDocument5 pagesMurder at The MarginZara Khan100% (1)
- Operations Management Lesson 2 TransDocument6 pagesOperations Management Lesson 2 TransDianne TorresNo ratings yet
- Building Trust in the WorkplaceDocument4 pagesBuilding Trust in the WorkplaceCrinaNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumechantellrambergNo ratings yet