Professional Documents
Culture Documents
University of Manitoba Writing Sample.4
Uploaded by
Amos Tawiah AntwiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
University of Manitoba Writing Sample.4
Uploaded by
Amos Tawiah AntwiCopyright:
Available Formats
Annex 1: General Tenure Typology for Ghana
Types of Land
Tenure General characteristics of Public and Customary Land Tenure
Proportion (100%)
Total Land Area (23,854,000 Hectares) Administration
22
Public 5,247,800
20 Lands Commission: grants leases of
Compulsory Acquisition-powers of eminent domain 4,770,790 state land to applicants and these are
State Land registrable under deeds or title
registration.
Dual Relation- State takes over management- 2
Vested Land Customary owners retain ownership 477,080
Stool and Skin Lands Chiefs, Sub-chiefs and Family Head
78
Lands Commission on behalf of
Customary 18,606,120
Customary Owner
Family Lands
Characteristics of Customary Land Tenure
1. Paramount or Allodial Interest 3. Licence
Purchase by the stool
Gift made to the stool
Appropriation of unoccupied land by pioneers and
hunters of the stool land
Exclusive Possession
Use and Enjoyment § Long and Short Term Licence (sowing tenure/seasonal license)
Acquisition and
§ Heritability
Rights of Holder Right of Alienation § Alienation
Right of Proprietorship in Perpetuity
Right to Residual Proprietary Interest (Reversion)
2.The Usufructuary Interest or Customary
Freehold 4. Tenancies or Farming User rights
Right of Possession
Use and Enjoyment
Right of Alienation § Security and Quiet Enjoyment,
Rights of Holder § Right of Alienation
Right of Alienation § Heritability
Right to an Action in Trespass
Heritability of the Usufructuary Title
Rights to Compensation
§ Implied grant from a stool
Modes of Prospective stranger-tenant first be introduced to the village or headman
Acquiring § Express grant from a stool
with a customary drink. Generally, either bottle of schnapps or money or
Interest both, an amount offered.
§ Transfer from a stranger or from a subject to
another subject or from a subject to a stranger
§ Where there is failure of successor to whom the
property devolves after death of holder § Where there is adverse claim by the tenants against the landlord.
§ Abandonment § Where there is abandonment.
§ Where there is a breach of term especially where the term is s
Loss of Interest § Adverse claim condition.
§ Breach of term § Where there is a failure of the successor.
§ Forfeiture § When the farm falls into ruin, either by natural causes.
§ By consent of the usufructuary
2
§ Extinction by operation of legislation
2
Multiple Sources: Author (2016); Saravanan et al (2008)
28
You might also like
- LTD Palabrica NotesDocument20 pagesLTD Palabrica Notesjm0% (1)
- Sogie-Bill-Report-Group-2 2Document24 pagesSogie-Bill-Report-Group-2 2Quervy Mallari100% (2)
- Concept of Property Ownership PropertyDocument8 pagesConcept of Property Ownership PropertyJunjie Tebrero100% (6)
- Law 1.2Document6 pagesLaw 1.2gilldarc13No ratings yet
- Property PrelimsDocument10 pagesProperty PrelimsChristian Ivan Daryl DavidNo ratings yet
- IX. in Matrix Form, What Are The Different Kinds of Legal Easements? Provide The Legal Basis and Cite Their Respective CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesIX. in Matrix Form, What Are The Different Kinds of Legal Easements? Provide The Legal Basis and Cite Their Respective CharacteristicsSALMAN JOHAYRNo ratings yet
- LTD Palabrica NotesDocument20 pagesLTD Palabrica NotesDarla Grey0% (1)
- Columns Ni DeanDocument5 pagesColumns Ni DeanchrisNo ratings yet
- Agrarian Law Midterms 410Document10 pagesAgrarian Law Midterms 410Niel Robert UyNo ratings yet
- Property Lecture NotesDocument32 pagesProperty Lecture NotesKDNo ratings yet
- Succession ReviewerDocument45 pagesSuccession Revieweryh9jx48grwNo ratings yet
- S A. F P: Ienna Lores RopertyDocument5 pagesS A. F P: Ienna Lores RopertyMedj Broke Law StudentNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure DigestDocument88 pagesCivil Procedure DigestRodeleine Grace C. MarinasNo ratings yet
- Builder, Planter and Sower in Good FaithDocument6 pagesBuilder, Planter and Sower in Good FaithsamNo ratings yet
- OwnershipDocument11 pagesOwnershipcolleenNo ratings yet
- Sta. Rosa Development Vs CA and Juan Amante DigestDocument2 pagesSta. Rosa Development Vs CA and Juan Amante DigestJason BUENANo ratings yet
- Outline With WarrantyDocument107 pagesOutline With Warrantyelsielandia100% (1)
- Land Law - Lecture (2019)Document78 pagesLand Law - Lecture (2019)Sammy AlroubNo ratings yet
- Civil Law - Land TitlesDocument19 pagesCivil Law - Land TitlesfarNo ratings yet
- Creation of EasementsDocument6 pagesCreation of EasementsPhillip DoughtieNo ratings yet
- VOL. 168, DECEMBER 5, 1988 247: Caballes vs. Department of Agrarian ReformDocument12 pagesVOL. 168, DECEMBER 5, 1988 247: Caballes vs. Department of Agrarian Reformabo8008No ratings yet
- Rem 111 - Case Study - For SubmissionDocument25 pagesRem 111 - Case Study - For SubmissionventuristaNo ratings yet
- Case-Digests PartitionDocument5 pagesCase-Digests PartitionAllana NacinoNo ratings yet
- Land Titles and DeedsDocument43 pagesLand Titles and DeedskenNo ratings yet
- PROPERTY Notes (10/05/20) Chapter 2 Right of Accession Art 440. The Ownership of Property Gives The Art 445Document6 pagesPROPERTY Notes (10/05/20) Chapter 2 Right of Accession Art 440. The Ownership of Property Gives The Art 445Joms DevanoNo ratings yet
- Express EasementDocument9 pagesExpress EasementPhillip DoughtieNo ratings yet
- LTD Palabrica NotesDocument20 pagesLTD Palabrica NotesgianelleNo ratings yet
- Civ Chair - S DigestsDocument82 pagesCiv Chair - S Digestsruth sab-itNo ratings yet
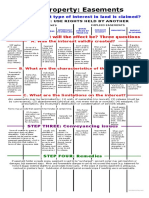
- Real Property: Easements: STEP TWO: What Will The Effect Be? Three QuestionsDocument1 pageReal Property: Easements: STEP TWO: What Will The Effect Be? Three QuestionsJulie GonzalezNo ratings yet
- CPAT Reviewer - Pledge, Mortgaage and AntichresisDocument5 pagesCPAT Reviewer - Pledge, Mortgaage and AntichresisZaaavnn VannnnnNo ratings yet
- Marven Fund. Property OwnershipDocument4 pagesMarven Fund. Property Ownershipmoveena abdullahNo ratings yet
- (REVIEWER) Credit Transactions - Lerma Philomatheia Tips PDFDocument7 pages(REVIEWER) Credit Transactions - Lerma Philomatheia Tips PDFAndrea RioNo ratings yet
- Agrarian Law - Premidterms (EH 410)Document3 pagesAgrarian Law - Premidterms (EH 410)Niel Robert UyNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - EasementDocument159 pagesGroup 5 - EasementJennifer Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Old Civil 13 UsteDocument50 pagesOld Civil 13 UsteTin TinNo ratings yet
- Property Midterm Notes CompilationDocument17 pagesProperty Midterm Notes Compilationjames lebronNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledpervez khanNo ratings yet
- Vda de Nazareno vs. Court of AppealsDocument14 pagesVda de Nazareno vs. Court of AppealsMa Roselle BathanNo ratings yet
- 10 Caballes v. DARDocument13 pages10 Caballes v. DARdos2reqjNo ratings yet
- SPL Midterm CoverageDocument28 pagesSPL Midterm CoverageZainne Sarip BandingNo ratings yet
- Up2020 - LTDDocument36 pagesUp2020 - LTDCG100% (1)
- LANDTITLES and Deeds Memory AidDocument12 pagesLANDTITLES and Deeds Memory AidRhic Ryanlhee Vergara FabsNo ratings yet
- Property, Succession, Obligations & Contracts and Special Contracts1Document56 pagesProperty, Succession, Obligations & Contracts and Special Contracts1girlNo ratings yet
- Agrarian Reform Law-Transcript-Capanas-MidtermsDocument26 pagesAgrarian Reform Law-Transcript-Capanas-MidtermsNiellaNo ratings yet
- 8 Up To 612 USUFRUCTDocument26 pages8 Up To 612 USUFRUCTJor LonzagaNo ratings yet
- Second Long ExamDocument11 pagesSecond Long ExamBeoyotch 1234No ratings yet
- Property Memory AidDocument8 pagesProperty Memory AidElaine TanNo ratings yet
- Automat and PNBDocument5 pagesAutomat and PNBKDNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Feliciano YambaoDocument9 pagesHeirs of Feliciano YambaoAngel Pagaran AmarNo ratings yet
- Real Property - Adverse PossessionDocument24 pagesReal Property - Adverse PossessionLewis Liu100% (2)
- Huron River BrochureDocument2 pagesHuron River Brochure05 ນ. ສຸພາພອນ ແກ້ວອຸດອນ 3EVANo ratings yet
- Property Reviewer ParasDocument17 pagesProperty Reviewer ParasRomena Luciano100% (7)
- 24 Vda de Naazareno V CADocument8 pages24 Vda de Naazareno V CAFlorieanne May ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bountiful Island: A Study of Land Tenure on a Micronesian AtollFrom EverandBountiful Island: A Study of Land Tenure on a Micronesian AtollRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Frimpong Jedidiah BoakyeDocument6 pagesFrimpong Jedidiah BoakyeAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- Supervisors SupportDocument2 pagesSupervisors SupportAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- Emerging Issues Related Land Tenure in GhanaDocument33 pagesEmerging Issues Related Land Tenure in GhanaAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument3 pagesReferenceAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument2 pagesInstructionsAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- waterAID 2009Document60 pageswaterAID 2009Amos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- UN-Habitat Land - Tenure - Security - in - Selected - CountriesDocument42 pagesUN-Habitat Land - Tenure - Security - in - Selected - CountriesAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- Ghana Land Tenure-Gfp ProjectDocument34 pagesGhana Land Tenure-Gfp ProjectAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- Building On Custom: Land Tenure Policy and Economic Development in GhanaDocument37 pagesBuilding On Custom: Land Tenure Policy and Economic Development in GhanaAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- KuntumensahDocument9 pagesKuntumensahAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- Boundary ConflictDocument14 pagesBoundary ConflictAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- RosterDocument3 pagesRosterAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- Policy Matters: Remembering Elinor OstromDocument126 pagesPolicy Matters: Remembering Elinor OstromAmos Tawiah AntwiNo ratings yet
- Animal Liberation: A Triangular Affair : Summum BonumDocument28 pagesAnimal Liberation: A Triangular Affair : Summum BonumAndreea Cătălina TacheNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument7 pagesResearch PaperRocelNo ratings yet
- Chiassoni SpaicDocument204 pagesChiassoni SpaicSofia ChicoNo ratings yet
- Four Moral Arguments in Proper Format #1 Abortion at 24 WeeksDocument2 pagesFour Moral Arguments in Proper Format #1 Abortion at 24 WeeksJannah Veron NuevasNo ratings yet
- British ValuesDocument3 pagesBritish ValuesThùy DungNo ratings yet
- Rawls On Liberty and Domination: Res Publica (2009) 15:397-413 DOI 10.1007/s11158-009-9102-6Document17 pagesRawls On Liberty and Domination: Res Publica (2009) 15:397-413 DOI 10.1007/s11158-009-9102-6Colton McKeeNo ratings yet
- Housing Discrimination Disclosure FormDocument2 pagesHousing Discrimination Disclosure Formnoah0firthNo ratings yet
- Tharoor, Are Human Rights UniversalDocument5 pagesTharoor, Are Human Rights UniversalMihaela SirițanuNo ratings yet
- rights:: I. According To PhilosphersDocument10 pagesrights:: I. According To PhilosphersBilawal MughalNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Comparative Human Rights PerspectiveDocument18 pagesSession 3 Comparative Human Rights PerspectiveAKSHAT KUMAR IPM 2019-24 BatchNo ratings yet
- Hve 111 Printed Full Note 2Document46 pagesHve 111 Printed Full Note 2Vaibhav DafaleNo ratings yet
- What Is The Meaning of Right To PrivacyDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Meaning of Right To PrivacyMark Rainer Yongis LozaresNo ratings yet
- Business and ConstitutionDocument6 pagesBusiness and ConstitutionMangesh KadamNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow Research ProposalDocument9 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow Research Proposaldivyavishal100% (1)
- Law As An Instrumentof Social ChangeDocument12 pagesLaw As An Instrumentof Social Changeaniket aryanNo ratings yet
- Convention On The Rights of Persons With DisabilitiesDocument20 pagesConvention On The Rights of Persons With DisabilitiesHabla GuateNo ratings yet
- G123QW2 Worksheet - Rights and ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesG123QW2 Worksheet - Rights and ResponsibilitiesZedrick Sam San JuanNo ratings yet
- Critically Examine The Importance of Ethics in International Relations and Elucidate With Suitable IlDocument2 pagesCritically Examine The Importance of Ethics in International Relations and Elucidate With Suitable IlNarendra GNo ratings yet
- Standarde Internationale Codul European de Etica Al Politiei PDFDocument45 pagesStandarde Internationale Codul European de Etica Al Politiei PDFRomeo EneNo ratings yet
- The Butler Opens With A Quote From Dr. Martin Luther King, JR, "Darkness Cannot Drive OutDocument3 pagesThe Butler Opens With A Quote From Dr. Martin Luther King, JR, "Darkness Cannot Drive OutRyan GreenbergNo ratings yet
- 2ndquarter Community Engagement Solidarity and Citizenship q2 LasDocument95 pages2ndquarter Community Engagement Solidarity and Citizenship q2 LasJeffrey LozadaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights of Vulnerable Groups With Refrence To WomenDocument164 pagesHuman Rights of Vulnerable Groups With Refrence To WomensanskarNo ratings yet
- HRHL FinalDocument28 pagesHRHL FinalGudipi JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Sociology of LawDocument10 pagesSociology of LawR. U. SinghNo ratings yet
- Notes On ConsequentialismDocument18 pagesNotes On ConsequentialismswapnilNo ratings yet
- National Human Rights CommissionDocument2 pagesNational Human Rights CommissionGaurav Prabhaker100% (1)
- BLO UMPAR ADIONG VsDocument2 pagesBLO UMPAR ADIONG VsAnaliza AlcoseroNo ratings yet
- Health LawDocument5 pagesHealth LawEunice NandyNo ratings yet
- Yiombi Thona, One of 100 Expats Making A Difference in KoreaDocument1 pageYiombi Thona, One of 100 Expats Making A Difference in KoreaEileenCahillNo ratings yet