Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biomarkers Qualifications - A First Step Towards Companion Diagnostic Development Title
Uploaded by
endorengasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biomarkers Qualifications - A First Step Towards Companion Diagnostic Development Title
Uploaded by
endorengasCopyright:
Available Formats
Regulatory Feature
Biomarker qualification: a first step towards companion
diagnostic development
Biomarker qualification can be a first step towards companion diagnostic development. The European
Medicines Agency already has a biomarker qualification process and the US Food and Drug Administration is
developing one itself. The two agencies should find a way to harmonise their respective processes and propose
clear incentives for companies seeking to use them, say Sabah Malek, Sylvie le Gledic and Anne Dupraz-Poiseau.
Biomarkers have become a necessary tool submission, made by the Critical Path Evaluation and Research, which will evaluate the
during drug development, in both the pre- Institute’s Predictive Safety Testing submitter’s initial letter of intent (LOI) to make a
clinical and clinical settings. Drug developers Consortium, was reviewed between June determination on whether or not continuation
use these tools to objectively measure and 2007 and January 2008. The conclusion from of consultancy and advice is necessary. The LOI
evaluate normal biological processes, this pilot joint experience5 spurred the FDA contains a short summary of the drug
pathogenic processes, or biological responses and EMA to release their own guidance development tool, its proposed context of use,
to a therapeutic intervention1. Biomarkers are documents related to qualification of drug a brief overview of the available data and a
utilised to stratify patient populations, support development tools, which involves not only summary of future studies planned. A positive
efficacy claims, quantify drug benefit, identify traditional biomarkers, but also other qualification will allow drug development tools to
safety problems, measure toxicity and reduce methodologies, such as imaging, to assist be used by drug developers within regulatory
rs
clinical uncertainty. with drug development. The goal of these submissions without reconsideration and
fai
Along with the discovery and use of qualification programmes is to be confident reconfirmation if used within the qualified
biomarkers, advances in science are also that, once qualification has been granted, context. The specific US qualification process is
making it possible to provide tailored described in further detail in Table 1.
Af
regulators and drug developers will not need
treatments to patients – ie personalised to reconfirm utility of this tool when used in While the stated purposes of the EMA and
medicine, which aims to provide the right a similar manner, ie context for use. FDA guidance are very similar, the processes
treatment, to the right patient, at the right
y
The EMA was the first of the two agencies recommended by the two agencies for
or
dose and/or at the right time2. In some cases, to make a process available for companies or qualification differ (see Table 1).
especially where the biomarker’s assistance is consortiums to qualify novel methodologies for The major differences between these two
lat
required to make clinical decisions, companion drug development by publishing guidance in processes are as follows:
diagnostics (CDx) are being developed as a 20086. The term “methodologies”, according to • The EMA has separated qualification opinion
test. Biomarkers are indicators of drug effect from qualification advice, allowing one process
gu
the EMA, encompasses biomarkers, imaging
(normal biological and pathogenic processes as methods, or other drug development tools. to be public and the other to be confidential,
well as biological responses), whereas CDx are Since then, three biomarkers have been respectively. The FDA does not offer such an
Re
a test or an assay, developed for the biomarker qualified in the EU7. The FDA followed suit in option and once a qualification determination
measurement, to directly assist physicians in 2010 by publishing its own guidance document8. is reached, this is made public for comments.
making treatment decisions. Next generation This guidance is still in draft form and, to date, The FDA wants to make this information
rip
sequencing, system biology and proteomics are its finalisation has not been announced. public to encourage scientific innovation and
just some of the areas where innovation is speed up the availability of safe and effective
The EMA and FDA processes
Sc
occurring and making the development of products. To promote this idea, the FDA
CDx more commonplace. The qualification process through the EMA is recommends the creation of collaborative
Like most areas of scientific innovation, the done via either Committee for Medicinal groups to undertake the development of
©
regulatory landscape surrounding biomarkers Products for Human Use (CHMP) qualification these drug development tools and go
has not caught up with the use. Regulators advice or CHMP qualification opinion. through this qualification process.
would like to ensure that the results of an Depending on the available biomarker • The EMA guidance specifically encourages
assessment can be relied upon to have a supportive studies, it is either an opportunity to submitters to apply in parallel to the FDA
specific interpretation and application in drug receive guidance on the submitted plan for and the EMA. The EMA specifies that both
development and regulatory decision making. future studies (biomarker qualification advice) agencies will then communicate and meet
Traditionally, biomarkers were validated or to obtain a qualification opinion. The latter is with the applicant together – made possible
through scientific debate, consensus, and based on the review of final protocols, study by a confidentiality agreement between the
standing the test of time3. Using this process, reports and supportive data to establish the FDA and the EMA – to maximise the
it could take years for biomarkers to be use of a defined novel methodology for a chance of scientific consensus. The FDA
widely accepted by the scientific community. specific purpose in drug development. The final draft guidance does not mention this
Regulatory authorities have now realised the goal of both (qualification advice and opinion) is parallel qualification opinion.
benefit and need for an accelerated process to lead to a proposed innovative development • An essential difference is the fact that the
to enable advances in drug development and method (ie qualified biomarker) that is FDA does not specify that any fees are
expedite the availability of safe and effective considered an acceptable regulatory standard associated with its qualification process,
products4. In 2007, the US Food and Drug for the claimed used in a defined context for whereas the EMA will charge sponsors
Administration and European Medicines drug development. The specific EU qualification scientific advice and follow-up fees. These
Agency announced a joint biomarker process is described in further detail in Table 1. fees are unfortunately not negligible and
qualification review of seven nephrotoxicity The FDA’s qualification process is under the can be burdensome on many sponsors
biomarkers. This flagship biomarker responsibility of the agency’s Center for Drug (see Table 1).
12 November 2011 www.scripregulatoryaffairs.com © Informa UK Ltd 2011
Regulatory Feature
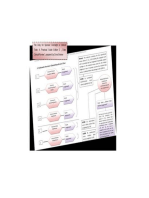
Table 1: Comparison of the European Medicines Agency and US Food and Drug Administration qualification
processes
European Medicines Agency US Food and Drug Administration
Scope Address innovative drug development methods and tools Identify new tools to aid in drug development. Help bring
(novel methodologies for a specific purpose in drug new products to the patients faster
development)
Purpose CHMP qualification opinion: Acceptability of the specific use Qualification process for drug development tools intended
of a defined novel methodology for a specific purpose in for use in multiple drug development programmes or
drug development therapeutic areas
or
CHMP qualification advice: Advice on future protocols and
studies planned for qualification purposes of an individual
methodology/tool
Approach Consultancy and collaboration between CHMP and Consultancy and collaboration between FDA and other
individual companies individuals or companies
Agency enforcement Voluntary basis Voluntary basis
Fees Full scientific advice fee (>€75,000 ($105,000)) & follow-up No cost
rs
advice fee (>€37,000). Usual 90% fee reduction for small
and medium-sized enterprises
fai
Qualification team Specialised group of experts appointed by the CHMP, named Creation of a specialised group named “qualification review
“qualification team”, led by a co-ordinator and composed of a team” composed of Center for Drug Evaluation and Research
Af
minimum of five members. The experts are identified based review staff from various relevant disciplines with expertise
on technology supporting the development of the novel appropriate to review of the submission
methodology
y
or
Procedure Main steps of the procedure: Pre-qualification: voluntary exploration data submission to
1. Letter of Intent determine if drug development tool development is
2. Assignment of an EMA scientific administrator (initial worthwhile
lat
validation step) Main steps of the procedure:
3. Appointment of the co-ordinator and the qualification 1. Letter of Intent
gu
team 2. Drug development tool briefing package and initial meeting
4. Preparatory meeting 3. Drug development tool investigation and development
Re
5. Evaluation of data and discussions 4. Submission of a formal qualification package
6. List of questions sent to applicant 5. Review of qualification package. For more controversial
7. Scientific advice working party review qualification decisions, CDER may decide to hold public
8. CHMP adoption of qualification advice and discussion of discussions.
rip
qualification opinion 6. Qualification decision by CDER
9. Public consultation (six weeks/only for qualification 7. FDA will put the new determinations as a draft guidance
opinion) and will use comments to develop a final guidance
Sc
10. Adoption of final CHMP qualification opinion No timelines are mentioned in the guidance document
Precise timelines are given in the guideline
©
Public status Qualification opinion: Open to public (public consultation) Public consultation is not systematic prior to qualification
prior to final qualification, publicly available once qualified (CDER may hold public discussions for controversial drug
Qualification advice: Confidential document development tools). Once qualification determination is
confirmed, it is made open systematically to the public
Output CHMP qualification opinion and scientific assessment Statement for qualification: conclusion regarding the
CHMP qualification advice on future protocols and studies to adequacy of the submitted data to support the drug
be further performed for qualification purposes of a specific development tool’s qualification and context of use
tool/methodology
• Process timelines are not given in the FDA the draft guidance document (“Why CDER is apparent that this biomarker measurement
guidance, whereas the precise number of developing a Qualification Process”?). It would during commercialisation of the targeted
days is specified for each step in the EMA have been interesting for the EMA and the therapy is needed for a safe and effective use
guidance. The submitter is able to use these FDA to align the proposed definitions and of the drug. In these cases, the further
timelines to plan for the biomarker and explanation in their guidances, if only for development of a CDx becomes a necessity.
drug development programmes when this harmonisation purposes. For both therapeutic and CDx developers,
information is transparent. there are many steps to be covered for the
• Finally, many definitions (ie qualification, Significance for diagnostic developers CDx development (beyond the qualification of
biomarker, etc) are provided by the FDA, The benefits of the biomarker measurement the related biomarker), which are still unclear
along with explanations for the purpose of during clinical studies are in some instances so (eg need for co-approval or not, when to
© Informa UK Ltd 2011 www.scripregulatoryaffairs.com November 2011 13
Regulatory Feature
introduce CDx in drug development/clinical Directive is currently under revision and the IVD processes. In addition, the fee associated with
trial, labelling requirements, etc). Unfortunately, classification will be reviewed. It is planned that, the process in the EU is another barrier that
neither the FDA nor the EMA offers much among other new requirements, CDx technical might discourage this process.
support for these stakeholders currently to files will have to be reviewed by notified bodies, In general, to foster innovation and
bridge the biomarker qualification to CDx/ the certification organisations that member state encourage developers to utilise the biomarker
drug co-development. national authorities designate to carry out one qualification process in the EU and US, it
The FDA does not attempt to make a or more of the conformity assessment would be beneficial to find a way to harmonise
connection between biomarkers and CDx procedures described in the annexes of the both processes (from the EU and the US) and
development within its various guidance various medical device directives. This should to propose clear incentives. This would be key,
documents. There is no mention of CDx in the bring more robustness to CDx development as biomarker qualification can be a first step
current draft guidance on qualification of drug but it will not solve all issues related to the towards CDx development.
development tools or a reference to needed interactions between drug and CDx
biomarkers within their recently released regulatory authorities. References
guidance document on CDx9. 1. Biomarkers Definitions Working Group (2001),
In the most recent EMA reflection paper Conclusion Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred
related to pharmacogenomics biomarkers, Biomarkers have the potential to allow drug definitions and conceptual framework, Clinical
development programmes to move forward at Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 69, 89-95
diagnostic tests are discussed but rather briefly,
a rapid pace, especially now that regulators 2. Lawson E, Lebon L et al, Activities to Improve the
with no detailed information. In addition, this Regulatory Framework for Companion Diagnostics
refection paper is limited to genetic biomarkers have taken steps to lay out the framework for
Step Up, Scrip Regulatory Affairs, 16 November 2010
and does not apply to all potential biomarkers. their qualification. As illustrated, there are
3. Goodsaid F, Frueh F, Biomarker Qualification Pilot
rs
However, it does at least recognise the value of today well defined biomarker qualification Process at the US Food and Drug Administration,
determining diagnostic performance and clinical processes in the EU and in the US. The EMA
fai
AAPS Journal, 2007, 9(1), E105-E108,
validity. Furthermore, it concludes with a brief guidance specifically encourages submitters to www.aapsj.org/view.asp?art=aapsj0901010
description of the development and use of apply in parallel to the FDA and the EMA. 4. Goodsaid F, Frueh F, Strategic Paths for Biomarker
Af
CDx during drug development10. However, differences between both processes Qualification, Toxicology, 2008, 245, 219-223,
might make that difficult, namely the lack of http://bit.ly/rM2vuK
There are other developmental issues that
harmonised definitions between both sides, 5. EMA, Final Conclusions on the Pilot Joint EMEA/FDA
need to be addressed as CDx become
y
the fees associated with the EMA process, the VXDS Experience on Qualification of
or
increasingly necessary. The first is that there are Nephrotoxicity Biomarkers, London, 22 January
no criteria that can be utilied to distinguish lack of timelines on the FDA side and the key
2009, EMEA/679719/2008 Rev 1,
issue of data confidentiality and intellectual
lat
when the development of a CDx is necessary. http://bit.ly/u5EJQG
Not all biomarkers will be further developed property. In the EU, nine biomarker 6. EMA, Qualification of Novel Methodologies for Drug
as CDx, therefore it is important to be able to qualification requests were made in 2010, Development: Guidance to Applicants,
gu
make this distinction. according to the EMA’s annual report12. Since 22 January 2009, EMEA/CHMP/
Since development of CDx and targeted the flagship submission, however, the EMA has, SAWP/72894/2008,http://bit.ly/sXi5RJ
Re
therapeutics involves both the in vitro to date, only qualified two other biomarkers. 7. Qualification of novel methodologies and biomarkers,
For the FDA, the qualification process has EMA website, http://bit.ly/rzezt7
diagnostic and pharmaceutical industry, both
not yet been finalised or utilised. Despite this, 8. FDA, Draft guidance for industry, Qualification
regulatory divisions will have to interact in
rip
Process for Drug Development Tools, October
order to ensure that safe and effective devices there are currently more than 100 drugs that
2010, http://1.usa.gov/997GCf
are allowed on the market. specify biomarkers on various sections of their 9. FDA, Draft guidance for industry and FDA staff, In
labelling (ie indications for use, dosage and
Sc
For the FDA, harmonisation and interactions Vitro Companion Diagnostic Devices, 14 July 2011,
between the divisions within the agency will administration, boxed warning, etc). In fact, the http://1.usa.gov/mXrNZP
be easier given the fact that all the divisions FDA has aggregated these drugs and published 10. EMA reflection paper on methodological issues
©
dealing with these products are under the this in a table on its website13. While the associated with pharmacogenomic biomarkers in
responsibility of the FDA. There are, however, biomarker qualification guidance is in line with relation to clinical development and patient
other operational challenges that the FDA will the FDA’s vision – to foster innovation – many selection, 9 June 2011, EMA/446337/2011,
of those in industry will most likely prefer to http://bit.ly/pFe9FR
face given the differences between these
11. Directive 98/79/EC of the European Parliament
divisions. Some examples of these differences discuss qualification in connection with a
and of the Council of 27 October 1998 on in vitro
are the binding/non-binding nature of certain submission, which would be subject to diagnostic medical devices, OJ, 7 December1998,
submissions and the development of disclosure regulations. Many developers might L331, 1-37
formalised procedures. choose this option also because of intellectual 12. EMA Annual Report 2010, 28 June 2011,
In Europe, harmonisation and interactions for property issues, which can pose a disincentive EMA/306870/2011, http://bit.ly/vggMiuf
drug and CDx regulatory co-approvals will be a to enter the public qualification process with 13. Table of pharmacogenomic biomarkers in drug
major challenge. This is mostly due to the fact the FDA. Therefore, to encourage the use of labels, FDA website, http://1.usa.gov/uf7jlC
that while the EMA reviews and approves the public qualification process, the FDA might
targeted therapeutics, the majority of IVD need to consider providing clarification on Sabah Malek, Sylvie le Gledic and Anne Dupraz-
Poiseau all work at Voisin Consulting Life Sciences,
technical files, including most CDxs, do not need what type of information it will make public in whose main office is based in Boulogne, France, and
to be reviewed by any regulatory authority at order to protect intellectual property. which specialises in regulatory strategy for healthcare
present time under In Vitro Diagnostics Directive Academics might find the FDA and the products. The authors would like to thank their
98/79/EC11. The CE marking of these IVDs that EMA biomarker qualification process helpful colleagues Mihaela MacNair and Patrick Larcier
for their contribution. Mrs Malek and Mrs MacNair
allows the product to be marketed across during the discovery stage. However, these are based in the firm’s US office in Cambridge,
Europe is today under the responsibility of the institutions usually do not have resources to Massachusetts. Website: www.voisinconsulting.com.
manufacturer (self-certification). The IVD handle these different and complex regulatory Email: dupraz@voisinconsulting.com.
14 November 2011 www.scripregulatoryaffairs.com © Informa UK Ltd 2011
You might also like
- ADMET for Medicinal Chemists: A Practical GuideFrom EverandADMET for Medicinal Chemists: A Practical GuideKatya TsaiounNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers, Diagnostics and Precision Medicine in the Drug Industry: Critical Challenges, Limitations and Roadmaps for the Best PracticesFrom EverandBiomarkers, Diagnostics and Precision Medicine in the Drug Industry: Critical Challenges, Limitations and Roadmaps for the Best PracticesNo ratings yet
- Week 2: Post-Marketing Regulation of Pharmaceutical Products LearningDocument4 pagesWeek 2: Post-Marketing Regulation of Pharmaceutical Products LearningNics PedrezuelaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Regulatory Approval Process - Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesModule 2 - Regulatory Approval Process - Lecture NotesyvssmanjunathNo ratings yet
- Integration of Biomarkers Data in Clinical TrialsDocument5 pagesIntegration of Biomarkers Data in Clinical TrialsSUMAN CHAUDHURINo ratings yet
- Evolving Regulatory Perspectives On Digital Health Technologies For Medicinal Product DevelopmentDocument11 pagesEvolving Regulatory Perspectives On Digital Health Technologies For Medicinal Product DevelopmentNot 8No ratings yet
- The FDA and Worldwide Current Good Manufacturing Practices and Quality System Requirements Guidebook for Finished PharmaceuticalsFrom EverandThe FDA and Worldwide Current Good Manufacturing Practices and Quality System Requirements Guidebook for Finished PharmaceuticalsNo ratings yet
- 8837 FNLDocument10 pages8837 FNLcarNo ratings yet
- 2020 09 H PP EuropaBio Patient-EngagementDocument6 pages2020 09 H PP EuropaBio Patient-Engagementqichen0818No ratings yet
- Celerion Biomarkers Unlocking-Value 093013Document3 pagesCelerion Biomarkers Unlocking-Value 093013SUMAN CHAUDHURINo ratings yet
- Goldsmith 1998Document3 pagesGoldsmith 1998Carlita LuzónNo ratings yet
- New Drug Application Content and Review Process For Clinical Pharmacology and BiopharmaceuticsDocument16 pagesNew Drug Application Content and Review Process For Clinical Pharmacology and BiopharmaceuticsAnki0391No ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics Modelling As A Fundamental Tool To Support Accelerated AccessDocument20 pagesBiopharmaceutics Modelling As A Fundamental Tool To Support Accelerated AccessMaria Rey RicoNo ratings yet
- The Path from Biomarker Discovery to Regulatory QualificationFrom EverandThe Path from Biomarker Discovery to Regulatory QualificationNo ratings yet
- Drug Development Process-1Document12 pagesDrug Development Process-1Ima AnNo ratings yet
- Biotherapeutics MTG Seoul August 2010 FINAL 4jan 2012 PDFDocument21 pagesBiotherapeutics MTG Seoul August 2010 FINAL 4jan 2012 PDFJosé Carlos Solís SuárezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Development ChapterDocument20 pagesClinical Development ChapterPooja Ramit KapoorNo ratings yet
- BMM 10Document3 pagesBMM 10Kumar ChaithanyaNo ratings yet
- Guidance To Industry and Reviewers - Exploratory IND Studies PDFDocument16 pagesGuidance To Industry and Reviewers - Exploratory IND Studies PDFcool BunnNo ratings yet
- Federal Register / Vol. 65, No. 251 / Friday, December 29, 2000 / NoticesDocument23 pagesFederal Register / Vol. 65, No. 251 / Friday, December 29, 2000 / NoticesBabbooNo ratings yet
- CR023 Module 6 - REV0Document28 pagesCR023 Module 6 - REV0Sony M NidhiryNo ratings yet
- Regulated Bioanalytical Laboratories: Technical and Regulatory Aspects from Global PerspectivesFrom EverandRegulated Bioanalytical Laboratories: Technical and Regulatory Aspects from Global PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Fit For Purpose Method DevelopmentDocument17 pagesFit For Purpose Method DevelopmentjakekeiNo ratings yet
- Perspective: Implementing The U.S. FDA Guidance On Pharmacogenomic Data SubmissionsDocument5 pagesPerspective: Implementing The U.S. FDA Guidance On Pharmacogenomic Data SubmissionsVeronica BalanNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument11 pagesReviewNoonNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Reliance For Regulatory Decision MakingDocument13 pagesGuidelines On Reliance For Regulatory Decision MakingABDELA RARINo ratings yet
- From Laboratory To Patient The Journey of A Medicine Assessed by EMADocument26 pagesFrom Laboratory To Patient The Journey of A Medicine Assessed by EMAmegakibNo ratings yet
- Drug Design and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesDrug Design and DevelopmentMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Comparazione Tra L'iter Di Approvazione Di Farmaci Da Parte Di EMA e FDADocument7 pagesComparazione Tra L'iter Di Approvazione Di Farmaci Da Parte Di EMA e FDAbeneNo ratings yet
- Nonclinical Safety Assessment: A Guide to International Pharmaceutical RegulationsFrom EverandNonclinical Safety Assessment: A Guide to International Pharmaceutical RegulationsWilliam J. BrockNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines Ecbs 2001Document52 pagesClinical Guidelines Ecbs 2001Ajay KumarNo ratings yet
- From Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance To ICH M10: Labcorp Drug DevelopmentDocument5 pagesFrom Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance To ICH M10: Labcorp Drug Developmentlamouna.lamittaNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Conducting Clinical Trials Based On Drugs Medical Products Good Clinical PracticeDocument44 pagesGuidance For Conducting Clinical Trials Based On Drugs Medical Products Good Clinical PracticeMostafa SalahNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Affairs in Biotech IndustryDocument29 pagesRegulatory Affairs in Biotech IndustryG.Bhavana 4GM20BT018No ratings yet
- Guidelines On Bio Similar SDocument201 pagesGuidelines On Bio Similar Sbhanu99No ratings yet
- Drug Approval Manuscript India PDFDocument10 pagesDrug Approval Manuscript India PDFardhanputraNo ratings yet
- Drug Approval Manuscript India PDFDocument10 pagesDrug Approval Manuscript India PDFardhanputraNo ratings yet
- Food Control System Assessment Tool: Dimension D – Science/Knowledge Base and Continuous ImprovementFrom EverandFood Control System Assessment Tool: Dimension D – Science/Knowledge Base and Continuous ImprovementNo ratings yet
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesFrom EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Regulatory AffairsDocument14 pagesRegulatory AffairsSiddarth Reddy100% (2)
- Technology Trends in Drug Discovery and Development: Implications For The Development of The Pharmaceutical Industry in AustraliaDocument29 pagesTechnology Trends in Drug Discovery and Development: Implications For The Development of The Pharmaceutical Industry in Australiagallu35No ratings yet
- Prodrug Design: Perspectives, Approaches and Applications in Medicinal ChemistryFrom EverandProdrug Design: Perspectives, Approaches and Applications in Medicinal ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Georgirene D. Vladutiu, PH.DDocument9 pagesGeorgirene D. Vladutiu, PH.DfdablogNo ratings yet
- Regulatory RequirementsDocument6 pagesRegulatory RequirementsAmeeroddin Mohammad100% (1)
- Guidance For Industry: Qualification Process For Drug Development ToolsDocument22 pagesGuidance For Industry: Qualification Process For Drug Development ToolsVenkatesan CraNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Priority SettingDocument13 pagesApproaches To Priority SettingElla MaeNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Risk Management: Evidence-Informed Policies and Decisions, Considering Multiple FactorsFrom EverandFood Safety Risk Management: Evidence-Informed Policies and Decisions, Considering Multiple FactorsNo ratings yet
- Comparability Pathway For The Approval of Similar Biologics With Respect To Reference Biologics in Europe and BrazilDocument13 pagesComparability Pathway For The Approval of Similar Biologics With Respect To Reference Biologics in Europe and Brazil10 Adarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2017 12 01 FDA Predictive Toxicology RoadmapDocument16 pages2017 12 01 FDA Predictive Toxicology RoadmapTitanium PassariniNo ratings yet
- Biosimilares 2.0Document8 pagesBiosimilares 2.0Carlos Julio Nova LopezNo ratings yet
- Development and Approval of Combination Products: A Regulatory PerspectiveFrom EverandDevelopment and Approval of Combination Products: A Regulatory PerspectiveEvan B. SiegelNo ratings yet
- FDA CPGM CH 48 - Bio Research Monitoring - in Vivo Bio EquivalenceDocument40 pagesFDA CPGM CH 48 - Bio Research Monitoring - in Vivo Bio EquivalenceenticedNo ratings yet
- Craneetal 2019Document16 pagesCraneetal 2019บอส เลิศเกียรติรัชตะNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Efficacy Testing of Mosquito Repellents For Human SkinDocument37 pagesGuidelines For Efficacy Testing of Mosquito Repellents For Human SkinAbdul AnasNo ratings yet
- 02-10 2022 Pharm Healthcare Systems 2022 R2Document22 pages02-10 2022 Pharm Healthcare Systems 2022 R2Amira HelayelNo ratings yet
- 3 - 5 The Drug Development ProcessDocument10 pages3 - 5 The Drug Development Processaghanafissa5No ratings yet
- The Duty for Sponor Oversight in Clinical Trials: Practical Guide: 2nd Edition Clinical Data ReviewFrom EverandThe Duty for Sponor Oversight in Clinical Trials: Practical Guide: 2nd Edition Clinical Data ReviewNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics TitleDocument3 pagesPharmacokinetics TitleendorengasNo ratings yet
- Development of An Immuno-Based Colorimetric Assay For White Spot Syndrome VirusDocument6 pagesDevelopment of An Immuno-Based Colorimetric Assay For White Spot Syndrome VirusendorengasNo ratings yet
- A Simple and Rapid Immunochromatographic Test Strip For Detection of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) of ShrimpDocument6 pagesA Simple and Rapid Immunochromatographic Test Strip For Detection of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) of ShrimpendorengasNo ratings yet
- Rapid Detection of Shrimp White Spot Syndrome Virus by Real Time, Isothermal Recombinase Polymerase Amplification AssayDocument8 pagesRapid Detection of Shrimp White Spot Syndrome Virus by Real Time, Isothermal Recombinase Polymerase Amplification AssayendorengasNo ratings yet
- Biotech SOPDocument76 pagesBiotech SOPendorengasNo ratings yet
- A Simple Spectrophotometric Assay For The Measurement of Soluble Silica in WaterDocument3 pagesA Simple Spectrophotometric Assay For The Measurement of Soluble Silica in WaterendorengasNo ratings yet
- ECA QC Raw Mat 2015Document4 pagesECA QC Raw Mat 2015endorengasNo ratings yet
- Model CoA For Taq PolymeraseDocument3 pagesModel CoA For Taq PolymeraseendorengasNo ratings yet