Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproductive System Quiz
Reproductive System Quiz
Uploaded by
Jason Colvin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Reproductive system quiz
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesReproductive System Quiz
Reproductive System Quiz
Uploaded by
Jason ColvinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Answer:
Vas deferens.
Drawia labelled diagram of the female reproductive system.
Answer:
Write ovo mar functions each of testis and ovary.
Answer:
Testes - Testes are the primary sexual organs in males. Two major functions oftestees are
* Testosterone production from Leydig cells,
+ Producion of sperm cells in seminiferous tubules.
(Ovary ~ Ovaries are the primary female sex organs, Two main functions of ovaries are
*+ Productions of female germ ces called eggs or oocytes
* Production of hormones ~ estrogens & progesterone which affect any of the female
secondary sexual characters & reproductive functions.
Describe the structure ofa seminiferous tubule
Answer:
The testis has about 250 compartments (Testicular lobules) which contain 1-3 highly coiled
‘seminiferous tubules. Each tubule s lined by 2 types of cells. Male germ cel (immature)
(spermatogonia) and Sertol ces.
‘Male germ cells form sperms by meiosis and Sertl cells provide nutrition to these germ calls
Male germ cells and Sertoli cells together form germinal epithelium. A seminiferous tubule is
‘Covered outside by a basement membrane.
Drawa labelled diagram of sperm.
Answer:
ama
embrane
Aerosorne
Nucleus cnttning
Heaa| ‘hrossuomal materia
ae ple
(energy s0ure fr set
What is oogenesis? Give a bret action of oogenesis
Answer:
Process of formation, development and maturation of haploid ovum or female gamete from
diploid germinal cel ofthe ovary.
Celis of the germinal epithelium of ovary undergo repeated mitotic dwisions to form diploid
Oogonia or gamete mother cels. They are formed inthe ftal ovary in large number by mitotic
isin from primary oocyte,
4. Corpus luteum: It secretes the hormone progesterone, which prepares the uterus for
implantation. if implantation fails the corpus luteum becomes inactive and degerverates.
‘fan embryo gets implanted, the corpus luteum continues to secrete progesterore until
the fourth month f pregnancy, after thatthe placenta takes over this function.
Endometriunm I icthe micous membrane lining the uterus, which becomes
Drogressively thicker and more glandular and has an incressed blood supply in the latter
part of the menstrual cycle. Ths prepares the endometrium for implantation of the
‘embryo, but if this does not occur much ofthe endometrium breaks down andis lost in
_menstruation. if pregnancy i established the endometrium becomes the decidua, which
Isshed after birth,
-Acrosome: A membranous 53 at or near the front of a sperm that assists in penetration
ofthe egg, The acrosome contains enzymes, which are released when the sperm,
contacts the egg pror to fertiisation, The enzymes break down the outer layers Of the
28g to permit entryot
the sperm,
‘Sperm tat The tall sa fine vibrating posterior portion ofthe sperm which helps in
‘swimming, This abity to swim (called motility is essential for male fetity as the sperm
hhasto svi up the vagina canal, cervix and cervical canal to reach tothe ovtim,
5. Fimbriae: They help: inthe collection of ovum after ovulation,
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Electrocardiogram ReviewDocument4 pagesElectrocardiogram ReviewJason ColvinNo ratings yet
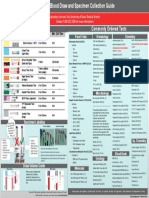
- LTD Order of Blood Draw and Specimen Collection Guide - Blank - Copy - Id - 7441067Document1 pageLTD Order of Blood Draw and Specimen Collection Guide - Blank - Copy - Id - 7441067Jason ColvinNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument4 pagesHealth AssessmentJason ColvinNo ratings yet
- TccccardDocument1 pageTccccardJason ColvinNo ratings yet