Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aminoglycosides - Notes
Uploaded by
Anam Mir0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageAminoglycosides are a class of bactericidal antibiotics that are effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, though they work best against gram-negatives. They inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial ribosome. While hydrophilic and water soluble, they are not absorbed orally and must be administered parenterally. Their primary route of elimination is through the kidney, so renal impairment can cause nephrotoxicity due to accumulation. Resistance develops through enzymatic modification of the aminoglycoside.
Original Description:
Original Title
Aminoglycosides - notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAminoglycosides are a class of bactericidal antibiotics that are effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, though they work best against gram-negatives. They inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial ribosome. While hydrophilic and water soluble, they are not absorbed orally and must be administered parenterally. Their primary route of elimination is through the kidney, so renal impairment can cause nephrotoxicity due to accumulation. Resistance develops through enzymatic modification of the aminoglycoside.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageAminoglycosides - Notes
Uploaded by
Anam MirAminoglycosides are a class of bactericidal antibiotics that are effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, though they work best against gram-negatives. They inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial ribosome. While hydrophilic and water soluble, they are not absorbed orally and must be administered parenterally. Their primary route of elimination is through the kidney, so renal impairment can cause nephrotoxicity due to accumulation. Resistance develops through enzymatic modification of the aminoglycoside.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Aminoglycosides
generally considered to be bactericidal
effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms (although best activity
against gram-negative)
o commonly reserved for serious gram-negative infections
natural products or semisynthetic derivatives of the natural product
o characterised as glycoside substituted 1,3-diaminoinositols
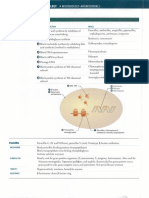
inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 16S unit within the 30S ribosomal subunit of
bacteria (near A-site)
o irreversible binding interaction
o conformational change to the A-site
o mis-reading of mRNA leads to formation of nonsense proteins, killing the bacteria
hydrophilic - water soluble
o multiple ionisable amine functionality with high pKa
o form acid salts at the basic nitrogens
o not absorbed via the oral route
o orally administered aminoglycosides have GItract antibacterial activity
primary route of elimination is through the kidney
o generally excreted unchanged by glomerular filtration
o patients with renal impairment exhibit potential for nephrotoxicity due to
accumulation in proximal tubular cells
o (also, ototoxicity – potential for hearing loss and loss of balance)
resistance is associated with N-acetylation, O-adenylation, O-phosphorylation
incompatibility with β-lactams as nucleophilic amino group of the aminoglycoside initiates
ring-opening of the β-lactam ring
You might also like
- Role of the Mediterranean Diet in the Brain and Neurodegenerative DiseasesFrom EverandRole of the Mediterranean Diet in the Brain and Neurodegenerative DiseasesNo ratings yet
- 9 AminoglycidesDocument41 pages9 AminoglycidesTasnim sarairehNo ratings yet
- Glycochemical Synthesis: Strategies and ApplicationsFrom EverandGlycochemical Synthesis: Strategies and ApplicationsShang-Cheng HungNo ratings yet
- Shakil 2007Document10 pagesShakil 2007Leila RaNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides KunjDocument17 pagesAminoglycosides KunjDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Agents: Methods of ResistanceDocument5 pagesAntibacterial Agents: Methods of Resistancenewguy927No ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides AbsorptionDocument6 pagesAminoglycosides AbsorptionBella Fikka GamilaNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument3 pagesGentamicindinaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Antibiotic Action, Class PPT IIDocument13 pagesMechanisms of Antibiotic Action, Class PPT IILarry TongNo ratings yet
- Saponins and Plant DefenseDocument6 pagesSaponins and Plant DefenseandrewalamNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors 2Document25 pagesProtein Synthesis Inhibitors 2AliImadAlKhasakiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Means Against LifeDocument13 pagesAntibiotics: Means Against Lifeshankul kumar100% (1)
- Aminoglycosides ResearchDocument12 pagesAminoglycosides Researchتارا للطباعة والترجمةNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides: Amlan GangulyDocument14 pagesAminoglycosides: Amlan GangulyAli Akand AsifNo ratings yet
- Antituberculur AgentsDocument16 pagesAntituberculur AgentsShiffali SinglaNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside - WikipediaDocument52 pagesAminoglycoside - WikipediaRustam LoharNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AntibioticsDocument13 pagesAntibacterial AntibioticsMuhamed ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Inhibitors of Cell WallDocument71 pagesBeta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Inhibitors of Cell WallAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside AntibioticsDocument36 pagesAminoglycoside AntibioticsGeneral InquiriesNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside: Systemic AminoglycosidesDocument47 pagesAminoglycoside: Systemic AminoglycosidesPawan PatelNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics IntroductiontoClassificationDocument16 pagesAntibiotics IntroductiontoClassificationFarida CitraNo ratings yet
- FungalDocument19 pagesFungalSparks Francis EzikaNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides, Macrolides, Chloramphenicol, LincomycinsDocument7 pagesAminoglycosides, Macrolides, Chloramphenicol, LincomycinsMello DiaxNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Amino-Glycosides Tetra-Cyclines Chloram - Phenicol Macrolides LincosamidesDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis Inhibitors: Amino-Glycosides Tetra-Cyclines Chloram - Phenicol Macrolides LincosamidesAnonymous elSqPhzKNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesAminoglycoside: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaawajahat100% (3)
- Mechanism of Action of Antibiotics: Subject:Pharmaceutical Microbiology DATE:18/09/2019Document12 pagesMechanism of Action of Antibiotics: Subject:Pharmaceutical Microbiology DATE:18/09/2019rubyNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument58 pagesProtein Synthesis InhibitorsmulatumeleseNo ratings yet
- First Bimonthly OralsDocument21 pagesFirst Bimonthly OralsKimberly Ann LeoragNo ratings yet
- Uc PDFDocument19 pagesUc PDFPenNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides: Official Reprint From Uptodate ©2021 Uptodate, Inc. And/Or Its Affiliates. All Rights ReservedDocument17 pagesAminoglycosides: Official Reprint From Uptodate ©2021 Uptodate, Inc. And/Or Its Affiliates. All Rights ReservedVanessa GomesNo ratings yet
- Identification of A Lactic Bacterium Strain Used For Obtaining A Pollen-Based Probiotic ProductDocument6 pagesIdentification of A Lactic Bacterium Strain Used For Obtaining A Pollen-Based Probiotic ProductAngela HernandezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Mcqs June 04Document7 pagesAntibiotic Mcqs June 04Subrahmanyam Sudi100% (4)
- Staphylococcus: S. Aureus Strains of IntermediateDocument9 pagesStaphylococcus: S. Aureus Strains of IntermediateRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- Improved Synthesis of A Cyclic Glutamine Analogue Used in Antiviral Agents Targeting 3C and 3Cl Proteases Including Sars-Cov 2 MDocument7 pagesImproved Synthesis of A Cyclic Glutamine Analogue Used in Antiviral Agents Targeting 3C and 3Cl Proteases Including Sars-Cov 2 Mnandigama chakradharNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument5 pagesCell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsFarhana Azmira AsmadiNo ratings yet
- Aminoglikosida Farkol 2 2023Document20 pagesAminoglikosida Farkol 2 2023ghazialghifariNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument2 pagesConclusionAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Actions of Benzimidazoles Against The Oral Anaerobes Fusobacterium Nucleatum and Prevotella IntermediaDocument9 pagesAntimicrobial Actions of Benzimidazoles Against The Oral Anaerobes Fusobacterium Nucleatum and Prevotella IntermediaoanapredaNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: Mechanism of ActionDocument9 pagesAminoglycoside Antibiotics: Mechanism of Actionprabhakaran payamNo ratings yet
- DP On AglDocument12 pagesDP On AglDeepikaNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Drugs: B.K. SatriyasaDocument56 pagesAntibacterial Drugs: B.K. SatriyasaVicNo ratings yet
- Lo Plus Senin Week 3Document4 pagesLo Plus Senin Week 3KesyaNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument12 pagesPharma NotesMayya FirdousNo ratings yet
- Kumar Et Al 2010 PDFDocument7 pagesKumar Et Al 2010 PDFrinifiahNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agent: DR Retno Budiarti M.Kes Microbiology Department FK UhtDocument43 pagesAntimicrobial Agent: DR Retno Budiarti M.Kes Microbiology Department FK UhtAlunaficha Melody KiraniaNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument2 pagesTuberculosisElle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside: Bactericidal Transport of Aminoglycoside S Through Bacterial Cell Wall and Cytoplasmic MembraneDocument2 pagesAminoglycoside: Bactericidal Transport of Aminoglycoside S Through Bacterial Cell Wall and Cytoplasmic MembraneNurwahidah Moh WahiNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Tasneem SmeratDocument78 pagesProtein Synthesis Inhibitors: Tasneem Smeratansam hirbaweNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: ProsthodonticsDocument4 pagesAnswer Key: ProsthodonticsBinayak UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Tawil et al. - 2010 - In depth study of a new highly efficient raw starch hydrolyzing α-amylase from Rhizomucor spDocument9 pagesTawil et al. - 2010 - In depth study of a new highly efficient raw starch hydrolyzing α-amylase from Rhizomucor spPedro MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- 16 57 RSC Adv L Methionine Based PhenolicDocument11 pages16 57 RSC Adv L Methionine Based PhenolickevinrogerNo ratings yet
- Iai 00120-23Document12 pagesIai 00120-23Robert StryjakNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antimicrobial TherapyDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Antimicrobial TherapyMERVENo ratings yet
- First Aid PharmacoDocument61 pagesFirst Aid PharmacogirNo ratings yet
- A Simple Method For Quantitative Determination of Polysaccharides in Fungal Cell Walls, Francois, Jean Marie, 2007Document6 pagesA Simple Method For Quantitative Determination of Polysaccharides in Fungal Cell Walls, Francois, Jean Marie, 2007deryhermawanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Furazolidone, Nalidixic Acidnorfloxacin, DapsoneDocument18 pagesUnit 3: Furazolidone, Nalidixic Acidnorfloxacin, DapsoneIshaani GargNo ratings yet
- Castillo 2013Document9 pagesCastillo 2013papahojaloveNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 pagesAntimicrobial AgentsErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (2)
- Mark Miguel P. Latras, RPHDocument11 pagesMark Miguel P. Latras, RPHLOLOLONo ratings yet
- Penicillin 140625060421 Phpapp01Document22 pagesPenicillin 140625060421 Phpapp01newtamil 2021No ratings yet
- AntimetabolitesDocument9 pagesAntimetabolitesAnam MirNo ratings yet
- Platinating Agents-1Document4 pagesPlatinating Agents-1Anam MirNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Date of Revision: October 12, 2018 Peer Review Date: March 1, 2017Document16 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Date of Revision: October 12, 2018 Peer Review Date: March 1, 2017Anam MirNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument30 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseAnam MirNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Fertility TestingDocument8 pagesPregnancy and Fertility TestingAnam MirNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus-Chronic ComplicationsDocument12 pagesDiabetes Mellitus-Chronic ComplicationsAnam MirNo ratings yet
- Asthma in Infants and ChildrenDocument25 pagesAsthma in Infants and ChildrenAnam MirNo ratings yet
- HypercalcemiaDocument12 pagesHypercalcemiaAnam MirNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Insipidus - NIDDKDocument9 pagesDiabetes Insipidus - NIDDKAnam MirNo ratings yet
- GI Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesGI Endocrine SystemAnam MirNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases For OSCE's (Pharmacy)Document13 pagesClinical Cases For OSCE's (Pharmacy)Anam MirNo ratings yet
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (39)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (83)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (267)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- I Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionFrom EverandI Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionNo ratings yet
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsFrom EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- The Fun Habit: How the Pursuit of Joy and Wonder Can Change Your LifeFrom EverandThe Fun Habit: How the Pursuit of Joy and Wonder Can Change Your LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- The Story of Philosophy: The Lives and Opinions of the Greater PhilosophersFrom EverandThe Story of Philosophy: The Lives and Opinions of the Greater PhilosophersNo ratings yet