Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Acute-Pain
Uploaded by
Marie CatapiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Acute-Pain
Uploaded by
Marie CatapiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
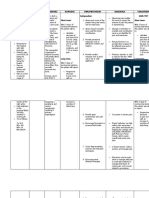
Name of patient: Patient J.M. Age: 15 years old Sex: Male Civil Status: Single Room: Emergency Room
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain related to Surgical Incision
Assessment Date: March 14, 2023 Intervention Date: N/A
Prepared by: Ma. Christina S. Mendoza Section/group no.: Sec 402, 3A CI/Supervisor: Mr. Vicente Baylon
Cues Nursing Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis
Subjective Cues Acute pain SCIENTIFIC Goal: Goal: Met
- Patient related to ANALYSIS:
stating a 7 out surgical incision Open After the 30
of 10 in pain secondary to appendectomy is After the 30 minutes shift,
scale post- a procedure minutes shift, the patient was
- Patient appendectomy done in the lower the patient will able to report a
characterize as evidence by right iliac, the be able to report relieve feeling
the sensation patient stating a surgeon makes a relieve feeling and a pain scale
of pain in the 7 out of 10 pain an incision and and a pain scale of 1.
incisional site scale while in the muscle layers of 1.
guarding is split to expose
Objective Cues position in the the peritoneum,
- One day post incisional site. after removing
apendectomy, the appendix and Objectives: Objectives:
with fresh whole procedure, 1. After nursing Independent Independent 1. MET. Patient
incisional the wound is intervention, Provide physical J.M. displayed
wound at the closed with patient J.M. will interventions Facial easiness, a
lower right stitches be able to - Massage Massage aid well relaxed and
quadrant of (Appendectomy: display facial (Effleurage) relaxation, comfortable
the iliac Procedure, easiness, hands, decrease muscle body, and his
region. preparation & relaxed arms, and tension, and vital signs were
- Facial risks comfortable feet. ease anxiety all in normal
Grimace 2018). Pain is a body, improved - Cold because the levels.
suggesting complex reaction well-being w/ compress physical contact
pain to tissue injury baseline level of around the related caring.
- Guarding during medical vital signs incisional (Berman et al.,
positioning in procedure that area, apply 2016)
the incisional invigorates 15 minutes
site to ease hypersensitivity at a time Reduces blood
pain of the central and do not flow to the
- Vital signs sensory system. apply ice specific area
shows: At the point directly on which can
BP: 140/100 when a patient the skin significantly
PR: 122 bpm goes through a reduce
RR: 28 bpm medical inflammation
procedure, and swelling
tissues and nerve that causes pain
endings are (John Hopkins
traumatized, Medicine, n.d.)
bringing an
incisional pain.
This trauma
overloads the
pain receptors
that send
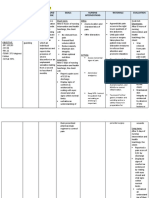
messages to the 2. Patient J.M. Provide cognitive- Distraction 2. MET. Patient
spinal cord, and his guardian behavioral therapy makes the J.M. and his
which becomes will be able to (CBT) person unaware guardian
overwhelmed, demonstrates - Distraction. of the pain only demonstrated
(Post-surgical the use of Facilitating for the amount well the use of
pain, n.d.). appropriate and/or of time and to appropriate
SITUATIONAL diversional providing the extent that diversional
ANALYSIS: activities and reading the distracting activities and
Herewith, the relaxation skills. material, activity holds his relaxation skills.
patient was television or her
admitted to the show, etc. “undivided”
hospital for - Guided attention.
appendicitis and imagery. (Berman et al.,
underwent open Involves 2016)
appendectomy the use of
recently. After 2- mental Guided imagery
days, patient ASL pictures or decreases and
reports pain in guiding the counteracts
the lower right patient to harmful effects
quadrant of the imagine of stress (e.g.,
iliac region and event muscle tension,
where the to distract activating the
incision was from the sympathetic
made for the pain nervous system,
appendectomy. and putting the
He rated pain client at risk for
with a 7 out of stress-related
10. In addition types of pain)
to , patient ASL (Berman et al.,
he has elevated 2016)
level of BP, RR,
and PR upon
assessment.
Facial grimace
and guarding
position in the
LRQ was noted.
Dependent
Dependent Opioid 3. MET. Patient
3. Patient J.M. - Administer analgesics for J.M. completely
will be able to analgesia moderate pain verbalize his
verbalize his as ordered are controlled relieve from
relief by the substances that pain
physician must be ordered
assigned by the physician,
this includes
drugs such as
codeine and
tramadol
(Berman et al.,
2016)
References:
Berman, A., Snyder, S. J., & Frandsen, G. (2016). Kozier & erb's fundamentals of Nursing: Concepts, processes and practice (10th ed.). Pearson
Australia.
Doenges, M. E., Moorhouse, M. F., & Murr, A. C. (2013). Nurse's pocket guide: Diagnoses, prioritized interventions, and rationales. Philadelphia,
PA: F.A. Davis
Franz, J. (n.d.). Post-surgical pain. Encyclopedia of Surgery. Retrieved September 14, 2021, from
https://www.surgeryencyclopedia.com/Pa-St/Post-Surgical-Pain.html.
John Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.). Ice packs vs. Warm Compresses for pain. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Retrieved September 20, 2021, from
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/ice-packs-vs-warm-compresses-for-pain.
Stone, R. (2021, February 4). Appendectomy. Ramsey Stone, M.D. Retrieved September 20, 2021, from
https://www.ramseystonemd.com/appendectomy.
The Health Line Team. (2018, September 29). Appendectomy: Procedure, preparation & risks. Healthline. Retrieved September 14, 2021, from
https://www.healthline.com/health/appendectomy#:~:text=During%20an%20open%20appendectomy%2C%20a,if%20your%20 appendix
%20has%20burst.
You might also like
- Or NCPDocument5 pagesOr NCPjelopigar921No ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain - NCPDocument3 pagesAcute Pain - NCPNovelyn PuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- NCP Breast CADocument3 pagesNCP Breast CAreeyahjonna100% (8)
- Subjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Chung Ching Pui: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNicholas Chung Ching Pui: Nursing Care PlanMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Orbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOrbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDersly LaneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Age: 60 Years OldDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Age: 60 Years OldLouise GudmalinNo ratings yet
- Demonstrate: Pain Coping TechniquesDocument4 pagesDemonstrate: Pain Coping TechniquesMae Therese B. MAGNO100% (1)
- Data Action Response: T - 37 °C PR - 95 BPM RR - 19 CPM BP - 120/80Mmhg Sp02-97%Document5 pagesData Action Response: T - 37 °C PR - 95 BPM RR - 19 CPM BP - 120/80Mmhg Sp02-97%Sheda BondNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainAshley Mae LopezNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocument8 pagesAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: SubjectiveDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: SubjectiveJonea Darlene JavierNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanice SolamilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PainDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Painjanmarc goreroNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeBiancaGabatinoAbarcaNo ratings yet
- NCP Post Op PainDocument2 pagesNCP Post Op PainLiz Liwag0% (1)
- NCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- NCP LeonilaDocument2 pagesNCP LeonilarhoinezaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis # 1 Acute Pain Related To Abdominal Incision.Document10 pagesNursing Diagnosis # 1 Acute Pain Related To Abdominal Incision.jhunanax100% (3)
- Nursing Process Care Plan Format: Patient Is A Non-SmokerDocument2 pagesNursing Process Care Plan Format: Patient Is A Non-SmokerDavid PerezNo ratings yet
- Painful Intramuscular Lipoma of The Infraspinatus Unusual Location and PresentationDocument4 pagesPainful Intramuscular Lipoma of The Infraspinatus Unusual Location and PresentationWewik PenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataDocument9 pagesClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Septic Arthritis NCPDocument3 pagesSeptic Arthritis NCPMae Therese B. MAGNO0% (1)
- NCP Breast CADocument3 pagesNCP Breast CAHannah Lacambra100% (1)
- Rheumatoid NCPDocument2 pagesRheumatoid NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORNo ratings yet
- Cyriax - Spine: by DR. Akshay A. Chougule (PT) Orthopaedic Manual TherapistDocument44 pagesCyriax - Spine: by DR. Akshay A. Chougule (PT) Orthopaedic Manual TherapistAishwarya Shah100% (1)
- NCP MastectomyDocument2 pagesNCP MastectomyDoc Duday100% (2)
- Carry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Document8 pagesCarry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Yosef OxinioNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres-ORDocument6 pagesPostoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres-ORMae Azores93% (99)
- All For Nov 14 Presentation FinalDocument13 pagesAll For Nov 14 Presentation FinalKristine JamilleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisGaming BoyNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSian Grace AsadaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainDyanne BNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2marohunkNo ratings yet
- ORAL KetamineDocument5 pagesORAL Ketaminerobo100% (1)
- Acute PainDocument9 pagesAcute PainVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainMimi Nacor100% (3)
- Preop Appendectomy NCPDocument3 pagesPreop Appendectomy NCPMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- NCP Total Hip ReplacementDocument11 pagesNCP Total Hip ReplacementDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Pain Dr. HenryDocument36 pagesPain Dr. Henryreagan setiawanNo ratings yet
- NCP-Acute Postpartum Perineal PainDocument2 pagesNCP-Acute Postpartum Perineal PainFrenzylane Diane CoralNo ratings yet
- OpstDocument5 pagesOpstNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation STO: (Goal Met)Document2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation STO: (Goal Met)Arian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation STO: (Goal Met)Document2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation STO: (Goal Met)Arian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Ii. NCP: Black, Et - Al. (2005) .Me Dical Surgical Nursing. 7 Edition - Elsevie R Pte LTD.P 927Document4 pagesIi. NCP: Black, Et - Al. (2005) .Me Dical Surgical Nursing. 7 Edition - Elsevie R Pte LTD.P 927Lecery Sophia Wong75% (4)
- Principles of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan:: Assessment/ Nursing Diagnosis Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan:: Assessment/ Nursing Diagnosis Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMonicaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Evaluation Objective of Care Intervention Rationale Subjective CuesDocument16 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Evaluation Objective of Care Intervention Rationale Subjective CuesRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-J P VDocument8 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-J P VMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Rafin NCP DS Pira orDocument6 pagesRafin NCP DS Pira orCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On: "Fracture Open III A, Complete Comminuted Displaced Femur Left"Document10 pagesNursing Care Plan On: "Fracture Open III A, Complete Comminuted Displaced Femur Left"Surkhali BipanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Pain Management in Anaesthesia Practice among Nurse AnaesthetistsFrom EverandAssessment of Pain Management in Anaesthesia Practice among Nurse AnaesthetistsNo ratings yet
- Pain Management for Clinicians: A Guide to Assessment and TreatmentFrom EverandPain Management for Clinicians: A Guide to Assessment and TreatmentCarl Edward NoeNo ratings yet
- Holistic Approach to Relieve Neck Pain, Back, and Shoulder Pain: An Effective Method for Pain ReductionFrom EverandHolistic Approach to Relieve Neck Pain, Back, and Shoulder Pain: An Effective Method for Pain ReductionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Lordosis Exercises - For Core and HipsDocument19 pagesLordosis Exercises - For Core and HipsRakesh MacherlaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Surgery Principles (PDFDrive)Document889 pagesPlastic Surgery Principles (PDFDrive)daxix89040No ratings yet
- Patients' Experience of Health Three Years After Structured Physiotherapy or Surgery For Lumbar Disc HerniationDocument8 pagesPatients' Experience of Health Three Years After Structured Physiotherapy or Surgery For Lumbar Disc HerniationsamNo ratings yet
- What Are The Steps in Paraffin Wax SpaDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Steps in Paraffin Wax SpaLezlie BenicoNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap From Rehab To Performance Sue FalsoneDocument297 pagesBridging The Gap From Rehab To Performance Sue FalsoneÁngel PerezNo ratings yet
- D. Cavitation A. Halo OrthosisDocument10 pagesD. Cavitation A. Halo OrthosisHakim Alhaady100% (1)
- PT1A - Salvadora, N. Assignment 1Document2 pagesPT1A - Salvadora, N. Assignment 1N.No ratings yet
- CASTDocument4 pagesCASTAlliah OrdanNo ratings yet
- SUZANN CAMPBELL, Textbook, Physical Therapy For ChildrenDocument3,253 pagesSUZANN CAMPBELL, Textbook, Physical Therapy For ChildrenFisioterapi KWarmadewa100% (5)
- Rodríguez-Hernández Et Al. - 2021 - Effects of Specific Virtual Reality-Based TherapyDocument15 pagesRodríguez-Hernández Et Al. - 2021 - Effects of Specific Virtual Reality-Based TherapyMARIA TERAPEUTANo ratings yet
- AC Joint InjuryDocument13 pagesAC Joint InjuryFarhan JustisiaNo ratings yet
- A Theoretical Model For Exercise Progressions As Part of A Complex Rehabilitation Programme DesignDocument3 pagesA Theoretical Model For Exercise Progressions As Part of A Complex Rehabilitation Programme DesignChrisNo ratings yet
- The Making of A Therapist: A Practical Guide For The Inner Journey (Norton Professional Books) - Louis CozolinoDocument5 pagesThe Making of A Therapist: A Practical Guide For The Inner Journey (Norton Professional Books) - Louis CozolinoxifojufaNo ratings yet
- DPT CurriculumDocument3 pagesDPT CurriculumDr. AtiaNo ratings yet
- Lateral EpicondilitisDocument6 pagesLateral EpicondilitisJacks CanalsNo ratings yet
- Fracture RehabilitationDocument43 pagesFracture Rehabilitationnanahossam12345No ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology ThesisDocument6 pagesExercise Physiology Thesiscarolinalewiswashington100% (1)
- Physical Therapy Resume PDFDocument3 pagesPhysical Therapy Resume PDFAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Sports Medicine - Brukner & Khan - Chapter 1Document10 pagesClinical Sports Medicine - Brukner & Khan - Chapter 1thithiNo ratings yet
- Direct Anterior Approach: Total Hip ArthroplastyDocument2 pagesDirect Anterior Approach: Total Hip ArthroplastyLéo ToaldoNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Gong's Mobilization Versus Scapular and Glenohumeral Mobilization in Subjects With Periarthritis of The ShoulderDocument4 pagesEffectiveness of Gong's Mobilization Versus Scapular and Glenohumeral Mobilization in Subjects With Periarthritis of The ShoulderInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: Vlad Costel MD Spitalul Clinic de Copii Doctor Victor GomoiuDocument46 pagesScoliosis: Vlad Costel MD Spitalul Clinic de Copii Doctor Victor GomoiuMada VisanNo ratings yet
- Humerus Anterolateral ApproachDocument15 pagesHumerus Anterolateral ApproachHussein SamhatNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitating The Athletic Horse (VetBooks - Ir)Document232 pagesRehabilitating The Athletic Horse (VetBooks - Ir)Saulo CardosoNo ratings yet
- DR Mohamed Hadinata Roslan MSCOst Final Thesis - Submission - BackupDocument75 pagesDR Mohamed Hadinata Roslan MSCOst Final Thesis - Submission - BackupHadinata RoslanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Neuro Assessment Intervensi Motor FunctionDocument295 pagesJurnal Neuro Assessment Intervensi Motor FunctionmadeNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain Numbness: Strain SciaticaDocument5 pagesLow Back Pain Numbness: Strain SciaticaCarol KayasNo ratings yet
- STOTT PILATES Warm Up Hip Rolls Merrithew®Document1 pageSTOTT PILATES Warm Up Hip Rolls Merrithew®melinda aniko szaboNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Adult Stroke Rehab and Recovery Ucm 485182Document117 pagesGuidelines For Adult Stroke Rehab and Recovery Ucm 485182Marcelo BenitezNo ratings yet
- Maja Roje Novak, MD, MS, Neurologist Croatia: Private Neurology ClinicDocument4 pagesMaja Roje Novak, MD, MS, Neurologist Croatia: Private Neurology ClinicHarsha SharmaNo ratings yet