0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views4 pagesSchematic and Layout Verification Guide
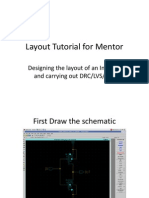
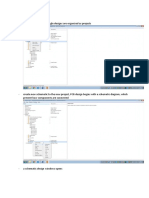
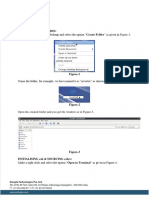
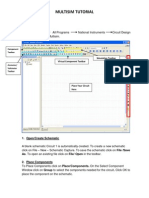
This document provides a tutorial on using the Calibre tool in Virtuoso software to verify connections between a schematic circuit and its corresponding layout. The tutorial walks through creating an inverter circuit schematic, generating the layout using MOS transistors, connecting all elements like the substrate and pins, placing labels, and finally using Calibre to check for any errors between the schematic and layout. The tutorial shows how Calibre can facilitate the connection verification process and speed up integrated circuit manufacturing.
Uploaded by
ergrCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views4 pagesSchematic and Layout Verification Guide
This document provides a tutorial on using the Calibre tool in Virtuoso software to verify connections between a schematic circuit and its corresponding layout. The tutorial walks through creating an inverter circuit schematic, generating the layout using MOS transistors, connecting all elements like the substrate and pins, placing labels, and finally using Calibre to check for any errors between the schematic and layout. The tutorial shows how Calibre can facilitate the connection verification process and speed up integrated circuit manufacturing.
Uploaded by
ergrCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd