Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols
Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols
Uploaded by
RALPH REPOLLO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThis document defines key terms related to alcohols, ethers, thiols and their reactions. It explains that a diol contains two hydroxyl groups, a glycol has hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbons, and dehydration of an alcohol eliminates a water molecule. It also defines ethers, cyclic ethers, thiols, mercaptans and disulfides. Additionally, it summarizes common reactions like acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols, and oxidation of primary, secondary and thiols.
Original Description:
Original Title
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND THIOLS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key terms related to alcohols, ethers, thiols and their reactions. It explains that a diol contains two hydroxyl groups, a glycol has hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbons, and dehydration of an alcohol eliminates a water molecule. It also defines ethers, cyclic ethers, thiols, mercaptans and disulfides. Additionally, it summarizes common reactions like acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols, and oxidation of primary, secondary and thiols.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesAlcohols, Ethers and Thiols
Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols
Uploaded by
RALPH REPOLLOThis document defines key terms related to alcohols, ethers, thiols and their reactions. It explains that a diol contains two hydroxyl groups, a glycol has hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbons, and dehydration of an alcohol eliminates a water molecule. It also defines ethers, cyclic ethers, thiols, mercaptans and disulfides. Additionally, it summarizes common reactions like acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols, and oxidation of primary, secondary and thiols.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
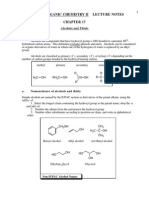
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS, AND THIOLS
DIOL - A compound containing two -OH (hydroxyl) groups.
GLYCOL - A compound with hydroxyl (-OH) groups on adjacent carbons.
DEHYDRATION - Elimination of a molecule of water from an alcohol. In the dehydration of an alcohol,
OH is removed from one carbon and an H is removed from an adjacent carbon.
ETHER - A compound containing an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms.
CYCLIC ETHER - An ether in which the ether oxygen is one of the atoms of a ring.
THIOL - A compound that contains an -SH (sulfhydryl) group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
MERCAPTAN - A common name for any molecule containing an -SH group. Mercaptan, which literally
means “mercury capturing.”
DISULFIDE - A compound containing an (-S-S-) group.
ACID-CATALYZED DEHYDRATION OF AN ALCOHOL - When isomeric alkenes are possible, the major
product is generally the more substituted alkene.
OXIDATION OF A PRIMARY ALCOHOL - Oxidation of a primary alcohol by potassium dichromate gives
either an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid, depending on the experimental conditions.
OXIDATION OF A SECONDARY ALCOHOL - Oxidization of a secondary alcohol by potassium dichromate
gives a ketone.
ACIDITY OF THIOLS - Thiols are weak acids, with pKa values of approximately 10. They react with strong
bases to form water-soluble thiolate salts.
OXIDATION OF A THIOL TO A DISULFIDE - Oxidation of a thiol gives a disulfide. Reduction of a disulfide
gives two thiols.
You might also like
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument27 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ethershgp9ms5gjcNo ratings yet
- Chap IV - Etherepox - ThiolsulfidesDocument36 pagesChap IV - Etherepox - Thiolsulfideshelia.jafari2No ratings yet
- Ethers and Epoxides - Thiols and SulfidesDocument31 pagesEthers and Epoxides - Thiols and SulfidesZulkifly TamsanNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature - : Ol. Other Substituents Are Named and Numbered As Done in AlkanesDocument7 pagesNomenclature - : Ol. Other Substituents Are Named and Numbered As Done in AlkanesGulshan BatraNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones&CarboxylicacidDocument13 pagesAldehydes, Ketones&CarboxylicacidDUHA GORASHINo ratings yet
- Oxygen Containing Organic CompoundsDocument9 pagesOxygen Containing Organic CompoundsmNo ratings yet
- 18: Ethers and Epoxides Thiols and Sulfides: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionDocument30 pages18: Ethers and Epoxides Thiols and Sulfides: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionEileen EunJung KimNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Chemistry Important Chapter - Halo Alkanes and Alkyl HalidesDocument16 pagesJee Main Chemistry Important Chapter - Halo Alkanes and Alkyl HalidesTest Practice100% (1)
- Ether: Navigation Search AetherDocument7 pagesEther: Navigation Search AetherMuhammad Wahyu Nugraha0% (1)
- AlcoholsDocument15 pagesAlcoholsNikolina RajkovačaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Ethers For Students (Ch1)Document37 pagesAlcohols and Ethers For Students (Ch1)hamzh al-harbiNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument10 pagesAldehydes and Ketonesnivasan aNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of AlcoholDocument4 pagesPhysical Properties of AlcoholrhiNo ratings yet
- Jee-Aldehyde Ketone & Carboxylic Acid Chem XiiDocument72 pagesJee-Aldehyde Ketone & Carboxylic Acid Chem Xiiswastik aroraNo ratings yet
- Go 3 Alcohol, Ether, AminesDocument13 pagesGo 3 Alcohol, Ether, Aminescikaifa100% (1)
- Final ScriptDocument6 pagesFinal ScriptKresley GamayNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 1Document13 pagesAlcohols 1Suresh VedpathakNo ratings yet
- F334 - What's in A Medicine?Document11 pagesF334 - What's in A Medicine?Becky Tenney100% (1)
- Unit 11 Alcohols Ethers Thiols UST Template 1Document31 pagesUnit 11 Alcohols Ethers Thiols UST Template 1Daniel BalubalNo ratings yet
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocument5 pagesAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem U-2 AlcoholDocument33 pagesOrganic Chem U-2 Alcoholsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- 16 Hydroxyl compound-24-STDDocument38 pages16 Hydroxyl compound-24-STDManh Doan DucNo ratings yet
- Organic ReagentsDocument11 pagesOrganic ReagentsChinmaya Singh100% (1)
- CH 20Document8 pagesCH 20adafgsdfgNo ratings yet
- EsterificationDocument3 pagesEsterificationKhris Sy-HandumonNo ratings yet
- ALDEHYSES (Autosaved)Document46 pagesALDEHYSES (Autosaved)az713511No ratings yet
- EthersDocument27 pagesEtherssafiabarkat5No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones-DSVOLDocument107 pagesAldehydes and Ketones-DSVOLMERCY ATUYANo ratings yet
- CH 17Document18 pagesCH 17MirjanaNo ratings yet
- CHM 102 - Alcohols-2Document7 pagesCHM 102 - Alcohols-2Philip OkunoyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.4 Alcohol, Ether & EpoxidesDocument52 pagesChapter 2.4 Alcohol, Ether & Epoxides0JTINGNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry-Non-Metals OxygenDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry-Non-Metals OxygenMarvin IdigaNo ratings yet
- Chem 102. EthersDocument24 pagesChem 102. Etherskeanna.samaniegoNo ratings yet
- L4 GgOxidising Alcohols 8-12-21Document19 pagesL4 GgOxidising Alcohols 8-12-21boobooNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The Alcohols Alcohols: Monohydric C H OHDocument23 pagesChemistry of The Alcohols Alcohols: Monohydric C H OHAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 HydrocarbonsDocument19 pagesChapter3 Hydrocarbonssyaz lianaNo ratings yet
- Vijendra Pal SinghDocument54 pagesVijendra Pal SinghVijendra Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenols and EthersDocument13 pagesAlcohol Phenols and EthersShivaanee SK100% (1)
- EthersDocument16 pagesEthersajay gudlaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry PPT - Ch. 22 - 11th Grade - II TERM - DeC'23Document138 pagesOrganic Chemistry PPT - Ch. 22 - 11th Grade - II TERM - DeC'23Ana Pamela MejiaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument17 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsSohamNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument16 pagesAlcoholsNirvaniNo ratings yet
- AldehydeDocument29 pagesAldehydeJan michael ChivaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument21 pagesCarboxylic AcidNischal AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument41 pagesUnit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and EthersPoovaraahan RaghuveeranNo ratings yet
- Lectures 19-22 (LB) Alcohols-Phenols-EthersDocument61 pagesLectures 19-22 (LB) Alcohols-Phenols-Ethersvintu pvNo ratings yet
- Organic Functional GroupsDocument8 pagesOrganic Functional GroupsScientology1No ratings yet
- Structure of Aldehydes: Aldehyde, Any of A Class ofDocument13 pagesStructure of Aldehydes: Aldehyde, Any of A Class ofBellaPeruchaNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilDocument13 pagesHsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilFathima NithinshaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsDocument11 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsLana Arsyad100% (2)
- Reaction Mech For Ether and EpoxidDocument59 pagesReaction Mech For Ether and Epoxidlorraine_cuaNo ratings yet
- Ethers 22Document22 pagesEthers 22waleed734445No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDocument81 pagesChapter 23 Functional GroupsYudi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument20 pagesClass 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidsst06082005No ratings yet
- Ethers and Epoxides Thiols and SulfidesDocument18 pagesEthers and Epoxides Thiols and SulfidesTrescia Mae EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Definitions Topic 4.2.1 Alcohols OCR A Chemistry A LevelDocument2 pagesDefinitions Topic 4.2.1 Alcohols OCR A Chemistry A LevelCHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Alcohol: Boiling Points and Water SolubilitiesDocument4 pagesAlcohol: Boiling Points and Water SolubilitiesChelsea ManioNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document32 pagesCH 18Dimas MitraNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CPH Review QuestionsDocument1 pageChapter 8 CPH Review QuestionsRALPH REPOLLONo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - The Self As A Product of Modern Society Among Other Constructions (Journal 2)Document5 pagesActivity 2 - The Self As A Product of Modern Society Among Other Constructions (Journal 2)RALPH REPOLLONo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument6 pagesNuclear ChemistryRALPH REPOLLONo ratings yet
- Significance of EnvironmentDocument1 pageSignificance of EnvironmentRALPH REPOLLONo ratings yet