Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microecon
Microecon
Uploaded by
Feane LamasanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microecon
Microecon
Uploaded by
Feane LamasanCopyright:
Available Formats
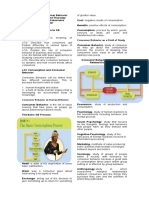
CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
A study of how individuals make decision to spend THE ORDINAL UTILITY THEORY
their available resources (time, money and effort) - Also called indifference theory; utility is not
or consumption related aspects (What they buy? measureable but can only be ranked or
When they buy?, How they buy? etc.). compared.
Broadly the study of individuals, or organizations - Indifference curve – different combinations of
and the processes consumers use to search, select, two goods that can be consumed that yield the
use and dispose of products, services, experience, same level of satisfaction or utility. A series of
or ideas to satisfy needs and its impact on the indifference curve is called and indifference
consumer and society. map.
FACTORS AFFECTING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
CULTURE – influence varies from country to country THEORY OF PRODUCTION AND COST
SOCIAL FACTORS – norms of behavior in social Production Function – technical relationship
groups between the firms and its output.
PERSONAL FACTORS – lifestyle, occupation, age Output = f(Inputs)
PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS – individual behavior Fixed Inputs – quantity is not changed by the
Customers - specific in terms of brand, company, or firm regardless of its reasons.
shop. It refers to person who customarily or Variable inputs – quantities can readily be
regularly purchases particular brand, purchases changed like labor and raw materials
particular company‘s product, or purchases from Production period:
particular shop. o Very short-run period – immediate
Consumer - person who generally engages in the period
activities - search, select, use and dispose of o Short-run period – some inputs used by
products, services, experience, or ideas. firms are fixed while others a variable.
The study of consumer behaviour helps everybody o Long-run period – all the inputs used in
as all are consumers. It is essential for marketers to production of the firm are variable units
understand consumers to survive and succeed in THE LAW OF DIMINISHING MARGINAL
this competitive marketing environment. The RETURNS
following reasons highlight the importance of - Successive unit of variable inputs are added to
studying consumer behaviour as a discipline. fixed inputs.
The reason to study consumer behaviour is because Average product (AP): AP = TP / Labor
of the role it plays in the lives of humans. Most of Marginal product (MP): MP = TP / L
the free time is spent in the market place, shopping
or engaging in other activities.
Utility – degree of satisfaction per unit of
consumption
CARDINAL UTILITY THEORY
- Utility is measurable. Utils is the unit of
measurement for satisfaction.
LAW OF DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY
- Marginal (extra or additional); one consumes
more and more of a particular good, marginal
utility decreases. It is more of a psychological
law and forms the basis of a download sloping
demand curve.
You might also like
- New Product Development Process of FMCG ProductDocument9 pagesNew Product Development Process of FMCG ProductChanduChandranNo ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter 3Document21 pagesExercises Chapter 3Katia Ibrahim100% (1)
- Market Segments and Consumer Behavior: Buying RolesDocument2 pagesMarket Segments and Consumer Behavior: Buying Rolessweet sunshineNo ratings yet
- Marketing FundsDocument2 pagesMarketing FundstohhweexinNo ratings yet
- Principles of MarketingDocument2 pagesPrinciples of MarketingBianca Jane GaayonNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Principles of Marketing - Week 8Document4 pagesQ3 - Principles of Marketing - Week 8Glaiza PerezNo ratings yet
- KMBN MK01 Unit 1 & 2Document19 pagesKMBN MK01 Unit 1 & 2Sudhanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument156 pagesUntitledMARION KERUBONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Foundations of Consumer BehaviourDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - The Foundations of Consumer BehaviourMariam KhailanyNo ratings yet
- The Theoryof Consumer Behavior: Applied Economics 12Document11 pagesThe Theoryof Consumer Behavior: Applied Economics 12Jannah EnrileNo ratings yet
- Buyer Behavior By: M Rafeeq Unit-I Importance of Studying Consumer BehaviorDocument12 pagesBuyer Behavior By: M Rafeeq Unit-I Importance of Studying Consumer BehaviorMohd RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Industrial Buyer BehaviorDocument22 pagesChapter Three Industrial Buyer BehaviorMingizem BirhanNo ratings yet
- CB - Module1 - Notes by Vivek SirDocument18 pagesCB - Module1 - Notes by Vivek SirDeepak Kumar DebdasNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document44 pagesCH 1Yeshambel EwunetuNo ratings yet
- LEARNING - Models Types - Tutorialspoint PDFDocument3 pagesLEARNING - Models Types - Tutorialspoint PDFThuraMinSweNo ratings yet
- Buyer Decision ProcessDocument83 pagesBuyer Decision ProcessSunil JoshiNo ratings yet
- MM Unit - IIDocument18 pagesMM Unit - IIHecbjtbbvNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 MinminDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 5 MinminLeones, Moanah A.No ratings yet
- Buying Behaviour Latest PDFDocument10 pagesBuying Behaviour Latest PDFmurarimishra17No ratings yet
- Introduction To Consumer BehaviorDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Consumer BehaviorMavieline Mae VillarinoNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Introduction: Consumer BehaviorDocument4 pagesUnit - I: Introduction: Consumer BehaviorrajeeevaNo ratings yet
- Marketing - 1-IntroDocument32 pagesMarketing - 1-IntroYogendra ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Marketing Chapter 2Document27 pagesPrinciple of Marketing Chapter 2Araceli PonterosNo ratings yet
- Study Note For Exam (Principles of Marketing)Document14 pagesStudy Note For Exam (Principles of Marketing)phoe_koNo ratings yet
- Marketing NotesDocument12 pagesMarketing NotesIl MulinaioNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Long QuestionDocument6 pagesFinal Exam Long Questionphoe_ko100% (1)
- MKTG Notes Week 1 With MCQDocument7 pagesMKTG Notes Week 1 With MCQSharavanan MNo ratings yet
- Conceptual: Session 1Document101 pagesConceptual: Session 1Advaita NGONo ratings yet
- MM Elec 02 Consumer BehaviorDocument3 pagesMM Elec 02 Consumer BehaviorAldrick BabatNo ratings yet
- Session ContentsDocument13 pagesSession ContentsMax CooperNo ratings yet
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR Didi Kartik Make inDocument8 pagesCONSUMER BEHAVIOUR Didi Kartik Make inVashu KatiyarNo ratings yet
- CB - Marketing ConceptDocument113 pagesCB - Marketing ConceptDr. Harshada Sushil Mulye (Asst. Prof.-General Management, Kharghar)No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Module-IDocument18 pagesConsumer Behaviour Module-Ijagan pawanismNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Theoretical Background: Marketing: MeaningDocument20 pagesChapter-3 Theoretical Background: Marketing: MeaningAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Consumer and Business Buyer Behaviour NotesDocument7 pagesConsumer and Business Buyer Behaviour NotesSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Subject - : Markering ManagementDocument70 pagesSubject - : Markering ManagementSamarth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introuction of The Study - (The Problem)Document13 pagesIntrouction of The Study - (The Problem)viral whatsapp statusNo ratings yet
- Sadia Tanin ID 111 141 251 - Internship Report On Bangladesh ICT Sector & Nascenia IT LimitedDocument11 pagesSadia Tanin ID 111 141 251 - Internship Report On Bangladesh ICT Sector & Nascenia IT LimitedMahamudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document23 pagesUnit 1Premendra SahuNo ratings yet
- CBBDocument22 pagesCBBshilpashinNo ratings yet
- Consumer Buying BehaviorDocument38 pagesConsumer Buying BehaviorzhazhanicolecondeNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour ExamDocument4 pagesConsumer Behaviour ExamMary Jane Sebial ManceraNo ratings yet
- Vijaya ProjectDocument77 pagesVijaya Projectsanjeevirm800No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior NotesDocument191 pagesConsumer Behavior NotesAnny MaharjanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Home Appliances in Salem City PDFDocument18 pagesA Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Home Appliances in Salem City PDFJessRaj DenisNo ratings yet
- A STUDY ON CUSTOMER ATTITUDE TOWARDS COLGATE TOOTHPASTE WITH REFERENCE TO COIMBATORE DISTRICT Ijariie7308 PDFDocument6 pagesA STUDY ON CUSTOMER ATTITUDE TOWARDS COLGATE TOOTHPASTE WITH REFERENCE TO COIMBATORE DISTRICT Ijariie7308 PDFRamana RamanaNo ratings yet
- A STUDY ON CUSTOMER ATTITUDE TOWARDS COLGATE TOOTHPASTE WITH REFERENCE TO COIMBATORE DISTRICT Ijariie7308 PDFDocument6 pagesA STUDY ON CUSTOMER ATTITUDE TOWARDS COLGATE TOOTHPASTE WITH REFERENCE TO COIMBATORE DISTRICT Ijariie7308 PDFzeeshanNo ratings yet
- A Study of Consumer Behaiour in Decatholon SportsDocument91 pagesA Study of Consumer Behaiour in Decatholon SportsDr Waseem CNo ratings yet
- Viviana Mall Is Closed Today and Tomorrow So I'm Not Gonna GoDocument81 pagesViviana Mall Is Closed Today and Tomorrow So I'm Not Gonna GotestNo ratings yet
- Chapter#1Document21 pagesChapter#1Đỗ Thanh HoaNo ratings yet
- Low Eeeeeee NGDocument16 pagesLow Eeeeeee NGCharissa MaeNo ratings yet
- Kata Prudvi RajuDocument73 pagesKata Prudvi RajuKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Consumer Behaviour StudentDocument25 pages1 Consumer Behaviour Studentbm jihanNo ratings yet
- Major Classic Consumer Buying Behaviour ModelsDocument10 pagesMajor Classic Consumer Buying Behaviour ModelsAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Application SynopsisDocument67 pages1.4 Application SynopsisChandru SivaNo ratings yet
- MS3 Midterms 1.b PDFDocument55 pagesMS3 Midterms 1.b PDFKirito ArjayNo ratings yet
- Final Document0Document296 pagesFinal Document0roshan soniNo ratings yet
- C.B Unit 5THDocument15 pagesC.B Unit 5THMasood ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour MM-4Document19 pagesConsumer Behaviour MM-4anujbeniwalNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Alissandrei Ann LacuataDocument92 pagesPrepared By: Alissandrei Ann LacuataJamaica Sañez TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviours ModelsDocument3 pagesConsumer Behaviours ModelsTanisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PEDocument1 pagePEFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- MODULE5Document10 pagesMODULE5Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Economic DevelopmentDocument25 pagesReviewer in Economic DevelopmentFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- OPMAN ReviewerDocument2 pagesOPMAN ReviewerFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- OpRes ReviewerDocument2 pagesOpRes ReviewerFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- BROCHUREDocument2 pagesBROCHUREFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - STSDocument3 pagesChapter 7 - STSFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chameleon 'S Tail: LinkDocument1 pageChameleon 'S Tail: LinkFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument2 pagesMarket StructuresFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- WR Group3Document22 pagesWR Group3Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Combined Results (2020-10-02 112205)Document538 pagesCombined Results (2020-10-02 112205)Apanar OoNo ratings yet
- Industrial MarketingDocument9 pagesIndustrial MarketingAditya0% (1)
- NauticaDocument4 pagesNauticaNishtha MahajanNo ratings yet
- Types of Financial DerivativesDocument14 pagesTypes of Financial DerivativesSolange TannouryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 5 SummaryNaveed AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-Part 1 Share Transaction Soal 1Document2 pagesChapter 11-Part 1 Share Transaction Soal 1Nicko Arisandiy0% (1)
- Economics 121: Introduction To Industrial Organization and Public Policy Professor Aaron EdlinDocument15 pagesEconomics 121: Introduction To Industrial Organization and Public Policy Professor Aaron EdlinMatthew RyanNo ratings yet
- Finance 100: Corporate Finance: Professor Michael R. Roberts Quiz 3 November 28, 2007Document8 pagesFinance 100: Corporate Finance: Professor Michael R. Roberts Quiz 3 November 28, 2007pvaibhyNo ratings yet
- Diez-Stephen-John-Critique 1Document3 pagesDiez-Stephen-John-Critique 1JaninaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan by AngeloDocument3 pagesMarketing Plan by AngeloSerial SleeperNo ratings yet
- CRM Section TwoDocument4 pagesCRM Section Twoyoumna yasser ismailNo ratings yet
- Customer & Product AuditDocument7 pagesCustomer & Product AuditWhenas WijayaNo ratings yet
- Export Pricing StrategiesDocument20 pagesExport Pricing StrategiesMahipalraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Role of Financial Markets and Institutions-1Document8 pagesChapter 01 Role of Financial Markets and Institutions-1مؤمن عثمان علي محمدNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply & Market EquilibriumDocument42 pagesDemand, Supply & Market EquilibriumnorynNo ratings yet
- Economics 101A (Lecture 26, Revised) : Stefano DellavignaDocument21 pagesEconomics 101A (Lecture 26, Revised) : Stefano DellavignaBagasNurWibowowNo ratings yet
- SML and CMLDocument18 pagesSML and CMLjeet_singh_deepNo ratings yet
- EquityDerivatives Workbook (Version-January2020)Document160 pagesEquityDerivatives Workbook (Version-January2020)Manish TandaleNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Week 5: Revenue Sharing With DistributorsDocument3 pagesAssignment For Week 5: Revenue Sharing With DistributorsGleynne MilloradaNo ratings yet
- New Product PricingDocument9 pagesNew Product PricingGeorgekutty Saju PooppillilNo ratings yet
- The Evening Star PatternDocument4 pagesThe Evening Star PatternFranciscoNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentdishan joelNo ratings yet
- ECON1010 Midterm 2013WDocument11 pagesECON1010 Midterm 2013WexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Current Status and Solutions To Reduce Logistics Costs in VietnamDocument4 pagesCurrent Status and Solutions To Reduce Logistics Costs in Vietnamgianggiang114No ratings yet
- Ukff3283 Course Plan 201910Document9 pagesUkff3283 Course Plan 201910Jayden YapNo ratings yet
- Advanced Macroeconomics Week 13 By: Dr. Wajahat AliDocument18 pagesAdvanced Macroeconomics Week 13 By: Dr. Wajahat Alighani khanNo ratings yet
- Promotion and Distribution ManagementDocument2 pagesPromotion and Distribution ManagementvamsibuNo ratings yet
- 157 PGTRB Commerce Study Material emDocument106 pages157 PGTRB Commerce Study Material emshareena ppNo ratings yet