Professional Documents
Culture Documents
50 Strategies Index Portfolio
Uploaded by
api-666002143Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
50 Strategies Index Portfolio
Uploaded by
api-666002143Copyright:
Available Formats
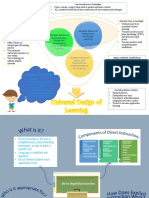
Class Environment
Strategy Description Steps
• Identify the langauges represented
• Pronounce and label common objects
Bilingual Books & Labels Respresentation validates students' home • Provide bilingual books
languages. They can use L1 knowledge to support
(16) their understanding of texts.
• Provide translations
• Explore key vocabulary in several languages
• Monitor us of bilingual resources.
• Establish classroom routines and expectations early
• Provide a print-rich environment
Combining and Scheduling Providing students with a variety of learning
• Strive for full implementation to meet the needs of all students
Strategies (50) formats: centers, technology, and small group
• Monitor and assess on a regular basis
• Use self-evaluation and reflection to improve your instruction
• Identify a language need
Games provide an opportunity to practice
• Model the game
language skills as well as language function
(giving directions or asking questions) and • Organize the pairs or groups
Communication Games (23) cooperative learning, and develop/reinforce • Guide the practice
concepts and break the ice. All games practice
communication skills. • Talk about the experience
• Assess the students' abilities to communicate orally
• Assign groups and build a team
Strategies for students to work together on an
assigned task. Each member has an assigned • Assign roles within the groups
Cooperative Learning (43) task. Instruction in team building and providing • Assign the task
intervention projects to ensure all students can
• Intervene to ensure full participation
participate.
• Report back to the class
• Find an age-appropriate project
• Set up the goals and parameters
Students research and share information from their • Make expectations clear
Culture Studies (36) own cultural history. • Plan the culminating activity
• Assess student growth and progress
• Add technology
• Identify skills to be practiced
These are places in a classroom where students
can engage in hands-on learning activities that • Introduce the centers
Learning Centers (22) allow them to experience a new skill. Centers all • Bring students up-the-date
EL students and others expand verbal interaction
• Assess student progress and understanding
and develop skills.
• Add technology
•Set up your room
Create a structured positive and nurturing •Establish routines
environment. ELs benefit from a routine
Predictable Routines and predictable structure. Knowing what to expect in •Model routines
Signals (1) routines and can focus more energy on the •Contextualize directions
instruction and less on what is expected. •Evalutate your use of routines and procedures periodically to identify areas that can
be improved.
•Identify the vocabulary
This approach in which language is made more •Collect visuals
understandable by displaying drawings or
Visual Scaffolding (4) photograph to connect with English words. Hard-
•Reproduce and organize visuals
copy and digital files can be used. •Engage the students
•Build the file of visuals
• Learn the language development levels of your students
• Look for technology to match both the language levels and academic needs of your
The use of technology in the classroom needs to students
Choosing Technology based be thought out and purposeful. Students need to • Choose technology that increases student interaction
learn 21st century skills and how to use technology
on Student Needs (9) to benefit learning. Technology enables students • Provide time for English language learners to use the technology
to work independently on skills. • Carefully monitor students as they use technology to determine if and when they are
confused or needing to advance in their use.
• Remember that technology should enhance learning
• Identify language objectives
A strategy that identifies the academic language •Identify and model problematic structures
Language Framework students need to be sucessful in a lesson and
•Plan an instructional sequence
Planning (34) plans supports using multiple methods. The
planning process is different depending on subject. •Assess and document student progress
•Add Technology
•Match strategies and curriculum
LSI supports students in becoming owners of their
learning. It provides strategies for reading, writing •Reflect on learning task approaches
Learning Strategy Instruction and other academic areas. Students learn self- •Model strategy use
monitoring skills and self-help approaches so they
(44) can be successful in school. Three types of •Practice the strategy
strategies: social/affective, metacognitive and •Make visuals for self-help
cognitive
•Assess to document strategy usage
Strategies Compiled from Herrell, A. L. & Jordan, M. (2015). 50 Strategies for Teaching English Language Learners (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN-13: 978-0133802450
Compiled by: Marnie Turman
Oral Language
Strategy Description Steps
• Plan the format of your questions ahead of time
Effective instruction depends on knowing what an •Plan everyone responds (ER) activities to encourage participation
Checking for Understanding (21) individual student understands. Teachers should check •Maintain visual contact with learners
for understanding on a regular basis.
•Provide adequate wait time
•Be aware of your body language
• Identify a language need
Games provide an opportunity to practice language • Model the game
skills as well as language function (giving directions or • Organize the pairs or groups
Communication Games (23) asking questions) and cooperative learning, and
develop/reinforce concepts and break the ice. All • Guide the practice
games practice communication skills. • Talk about the experience
• Assess the students' abilities to communicate orally
• Identify skills to be practiced
These are places in a classroom where students can • Introduce the centers
engage in hands-on learning activities that allow them to
Learning Centers (22) experience a new skill. Centers all EL students and
• Bring students up-the-date
others expand verbal interaction and develop skills. • Assess student progress and understanding
• Add technology
•Plan and gather materials
Unit vocabulary is previewed in L1 or L2. Concepts are • Introduce key vocabulary and concepts
presented using visuals. Concepts are reviewed after • Teach the lesson
Preview/Review (26) the lesson with students. Students are given
opportunities to learn the vocabulary in home language •Review vocabulary and concepts
or English. •Provide additional practice
•Assess and document students' interactions
• Introduce the question words
Similar to Think, pair share, student pairs read selected • Model each step of the strategy
text (paragraph or section) then answer "who, what,
where, when and how: questions. Partners discuss the • Model how to work with a partner
Read, Pair, Share (38) answers and find the answers in the selected text. ELs • Model the modifying of questions
partnered with strong English speakers provides • Pair the students
opportunities to practice and explore language skills in a
less stressful environment. •Discuss the assignment
• Assess to identify the need for additional instruction or guided practice
• Prepare the students for action
• List and review the steps
•Verbalize the action
Support supports in reading and writing by discussing •Allow for verbal practice
Reporting Back (14) and writing about learning experiences using content •Celebrate the achievements
vocabulary. •Review the vocabulary used
•Write the report
•Assess student progress and understanding
•Evaluate your use of reporting back
Skills Grouping
•Observe and document language levels
•Review needs for instruction
•Design and implement lessons
Skills grouping is used for short skills instruction.
Partner work provides verbal interaction. Studenst are Partner Work
Small Group and Partners (47) paired to complete a specific task. Peer tutoring a •Pair the students
strong student works with a classmate to acquire the •Identify and train potential tutors
skills.
•Match students
•Model the task
•Provide support and practice
•Share progress
•Identify the vocabulary
This approach in which language is made more •Collect visuals
understandable by displaying drawings or photograph to
Visual Scaffolding (4) connect with English words. Hard-copy and digital files
•Reproduce and organize visuals
can be used. •Engage the students
•Build the file of visuals
•Identify key vocabulary
Students make connections to past experiences, current •Teach the lesson or read the book
content, and vocabulary. Students introduce new
vocabulary and discuss and role-play. This strategy •Connect the vocabulary to past experiences
Vocabulary Role-Play (6) provides multiple exposures to the new vocabulary. •Plan ways to use the words
Multiple groups can be given the same words since •Give the students time to practice
groups will use vocabulary to create skits using different
context. •Perfrom the scenes
•Focus on multiple word meanings
Strategies Compiled from Herrell, A. L. & Jordan, M. (2015). 50 Strategies for Teaching English Language Learners (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN-13: 978-0133802450
Compiled by: Marnie Turman
Vocabulary & Comprehension
Strategy Description Steps
• Identify opportunities to use realia
This strategy uses real "concrete" objects to build
background knowledge and vocabulary. Real objects
allow students to see, feel, hear and smell the object •Collect realia
Realia Strategies (5) presented. Replica models and semi-concrete •Build a library of realia
(photographs or illustrations) may be used, however, •Use field trips as realia
they do not provide the same benefits as the real
"concrete" objects.
•Assess by using realia
•Identify the independent reading levels of students
•Explain the program to the students
Advance Organizers (31) •Discuss the books in groups
•Add motivation over time
•Assess to monitor progress and plan instruction
•Demonstrate close reading when you read aloud
•Observe and document students' individual reading levels
•Choose short text with enough complexity to allow students to practice
comprehension strategies
•Prepare questions that engage students in reexaming texts and that support their
ability to meet the Common Core standards
•Document students' strengths and needs for reteaching
Close Reading (11) •Teach students how to ask important questions about the texts they read
•Incorporate rereading for gradually uncovering deeper meaning
•Relate texts to the students' past experiences
•Focus on observing and analyzing
•Provide experience using close reading in a wide variety of texts
•Constantly reflect on your institution and strive to improve your delivery, examples
and questioning
• Plan the format of your questions ahead of time
Effective instruction depends on knowing what an •Plan everyone responds (ER) activities to encourage participation
Checking for Understanding (21) individual student understands. Teachers should check •Maintain visual contact with learners
for understanding on a regular basis.
•Provide adequate wait time
•Be aware of your body language
•Identify the independent reading levels of students
•Explain the program to the students
Free Voluntary Reading (35) •Discuss the books in groups
•Add motivation over time
•Assess to monitor progress and plain instruction
Strategies Compiled from Herrell, A. L. & Jordan, M. (2015). 50 Strategies for Teaching English Language Learners (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN-13: 978-0133802450
Compiled by: Marnie Turman
Writing
Strategy Description Steps
Visuals to aid in the representation of ideas, text or •Identify the teaching purposes
connection. Graphic organizers help students with
writing a sequence of events or organizing •Explain the purpose
information. Organizers provide visual supports
Graphic Organizers (30) that enable students to make connections between •Involve students in contructing a graphic
events and characters. There are many types of
organizers to fit the need of students. - www. •Discuss the connections
teachervision.com/lesson-planning/graphic-
organizer •Provide additional practice using graphic organizers
•Identify key vocabulary
Students make connections to past experiences, •Teach the lesson or read the book
current content, and vocabulary. Students
introduce new vocabulary and discuss and role- •Connect the vocabulary to past experiences
Vocabulary Role-Play (6) play. This strategy provides multiple exposures to •Plan ways to use the words
the new vocabulary. Multiple groups can be given •Give the students time to practice
the same words since groups will use vocabulary
to create skits using different context. •Perfrom the scenes
•Focus on multiple word meanings
Strategies Compiled from Herrell, A. L. & Jordan, M. (2015). 50 Strategies for Teaching English Language Learners (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN-13: 978-0133802450
Compiled by: Marnie Turman
Assessment
Strategy Description Steps
•Identify an authentic project opportunity
Integrated Curriculum Project is a planning •Invoice students in project planning
approach n which knowledge and skills from •Relate the project to grade-level state standards and ESL standards
Integrated Curriculum several acadamic areas. These projects provide
•Identity the class goals
Projects (40) active learning opportunities for students. The
strategy focuses on vocabulary in multiple contexts •Establish working groups and their assignments
in authentic situations. •Integrate learning
•Integrate assessment to ensure effective instruction
•Group the students for instruction
Guided Reading is small group reading instruction
which provides skills instruction and coaching. •Begin the process
Running records are usined to determine reading
and skill acquisition. ELs benefit from instruction •Read aloud but not in unison
Guilded Reading (32) on self-monitoring for meaning and not just word •Pair students for additional practice
recognition. The small group activities consist of
reading, writing, vocabulary, phonics skills and •Teach minilessons based on student need
other literacy skills as needed.
•Assess on a regular basis
Strategies Compiled from Herrell, A. L. & Jordan, M. (2015). 50 Strategies for Teaching English Language Learners (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN-13: 978-0133802450
Compiled by: Marnie Turman
Home Connections
Strategy Description Steps
• Learn the language development levels of your students
• Look for technology to match both the language levels and academic needs of your
The use of technology in the classroom needs to students
Choosing Technology based be thought out and purposeful. Students need to • Choose technology that increases student interaction
learn 21st century skills and how to use technology
on Student Needs (9) to benefit learning. Technology enables students • Provide time for English language learners to use the technology
to work independently on skills. • Carefully monitor students as they use technology to determine if and when they are
confused or needing to advance in their use.
• Remember that technology should enhance learning
•Identify the langauges represented
• Pronounce and label common objects
Bilingual Books and Labels Respresentation validates students' home • Provide bilingual books
languages. They can use L1 knowledge to support
(16) their understanding of texts. • Provide translations
• Explore key vocabulary in several languages
• Monitor us of bilingual resources.
•Identify the independent reading levels of students
•Explain the program to the students
Free Voluntary Reading (35) •Discuss the books in groups
•Add motivation over time
•Assess to monitor progress and plain instruction
• Find an age-appropriate project
• Set up the goals and parameters
Students research and share information from their • Make expectations clear
Culture Studies (36) own cultural history. • Plan the culminating activity
• Assess student growth and progress
• Add technology
Strategies Compiled from Herrell, A. L. & Jordan, M. (2015). 50 Strategies for Teaching English Language Learners (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN-13: 978-0133802450
Compiled by: Marnie Turman
You might also like
- Element Checklist For MYP Unit Planners: Does The Unit Include The Following?Document8 pagesElement Checklist For MYP Unit Planners: Does The Unit Include The Following?Shantha KundapuraNo ratings yet
- Amt in A Nutshell - ExplainedDocument2 pagesAmt in A Nutshell - ExplainedMis El100% (2)
- NYU Teacher Curriculum Template Hindi UrduDocument16 pagesNYU Teacher Curriculum Template Hindi UrdumusicpamNo ratings yet
- Immersion Teaching Strategies Observation Checklist: The Bridge: From Research To PracticeDocument4 pagesImmersion Teaching Strategies Observation Checklist: The Bridge: From Research To PracticepmakmakNo ratings yet
- Comparitive of Methods 2Document4 pagesComparitive of Methods 2EWLIZABETH ESPIRITUNo ratings yet
- FIELD STUDY 2 LEARNING EPISODE 11 Delivering My Lesson PlanDocument13 pagesFIELD STUDY 2 LEARNING EPISODE 11 Delivering My Lesson PlanJayrel Fabrero100% (1)
- Mikel Murillo - Jan 11 2018Document2 pagesMikel Murillo - Jan 11 2018api-424444999No ratings yet
- Unit Seven-Communicative Activities PDFDocument41 pagesUnit Seven-Communicative Activities PDFEdher QuintanarNo ratings yet
- Domain 1 Artifacts 4 Column - TeachersDocument4 pagesDomain 1 Artifacts 4 Column - Teachersapi-384069095No ratings yet
- Approaches To Learning: ThinkingDocument4 pagesApproaches To Learning: ThinkingjorbelocoNo ratings yet
- Evaluating MYP Rubrics in WORDDocument11 pagesEvaluating MYP Rubrics in WORDJoseph VEGANo ratings yet
- Pedagogy Primary jhs-1Document9 pagesPedagogy Primary jhs-1Jennifer kyeremehNo ratings yet
- Teaching ApproachesDocument3 pagesTeaching Approachesapi-546696759No ratings yet
- Santrock Claimed That Mental Processes of Experts Can Help The Teachers Guide The Students Into Becoming More Effective LearnersDocument6 pagesSantrock Claimed That Mental Processes of Experts Can Help The Teachers Guide The Students Into Becoming More Effective LearnersDavid Espartero Jr.No ratings yet
- 8.5 5d Framework Version 4.5 v3 2Document4 pages8.5 5d Framework Version 4.5 v3 2Liidia_gNo ratings yet
- Ri Activities For Year 4Document10 pagesRi Activities For Year 4DONORICH JOSEPH ANSONNo ratings yet
- Teaching-Learning - Assessment Strategies Towards Higher Order Thinking SkillsDocument129 pagesTeaching-Learning - Assessment Strategies Towards Higher Order Thinking Skillsglizel diamalNo ratings yet
- Tla HotsDocument129 pagesTla HotsFREDELITA PAMPLONANo ratings yet
- Language Teaching MethodsDocument20 pagesLanguage Teaching MethodsAhmadNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocument11 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of TeachingKa NaNo ratings yet
- Instructional ApproachesDocument3 pagesInstructional Approachesapi-549234739No ratings yet
- Australia Teacher GuidelinesDocument5 pagesAustralia Teacher GuidelinesKromuel AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Learning ExamplesDocument4 pagesApproaches To Learning ExamplesRituparna BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Eseg5053 Teaching Methodology: Assignment Guidelines and RubricsDocument4 pagesEseg5053 Teaching Methodology: Assignment Guidelines and RubricsDiana ManafNo ratings yet
- Tefl-Lesson PlanDocument30 pagesTefl-Lesson PlanMaulidea PutriNo ratings yet
- John Sorenson - Oct 24 2017Document2 pagesJohn Sorenson - Oct 24 2017api-407913601No ratings yet
- Lexs EvaluationDocument2 pagesLexs Evaluationapi-390615454No ratings yet
- PP ATL ListDocument4 pagesPP ATL ListMegyes VivienNo ratings yet
- SawyerDocument6 pagesSawyerapi-357419171No ratings yet
- PSTM (Midterm)Document10 pagesPSTM (Midterm)MONICA VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- ATL Skills Framework Extract From MYP From Principles Into PracticeDocument8 pagesATL Skills Framework Extract From MYP From Principles Into PracticePerihan SayedNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Planning Process enDocument1 pageCollaborative Planning Process enapi-380030046No ratings yet
- 2020 - Science - LimanAnthony - Instructional Design in Learning ScienceDocument43 pages2020 - Science - LimanAnthony - Instructional Design in Learning ScienceChetan VasaveNo ratings yet
- IdteacherstandardsDocument12 pagesIdteacherstandardsapi-487852288No ratings yet
- Presentation Section5 FarajnezhadDocument39 pagesPresentation Section5 FarajnezhadHadeer Abd El AzizNo ratings yet
- Health Education Reviewer WEEK 7 (Mendoza Jocie AngelDocument4 pagesHealth Education Reviewer WEEK 7 (Mendoza Jocie AngelJocie Angel PUNZALAN MendozaNo ratings yet
- Summer Institute Guide To Facilitation Math.2018Document30 pagesSummer Institute Guide To Facilitation Math.2018David WalkeNo ratings yet
- AICLE PPT Unit3Document20 pagesAICLE PPT Unit3Leticia Martinez ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Development of School Based Remedial Reading ProgramDocument87 pagesDevelopment of School Based Remedial Reading ProgramMARYNILLE JOY DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Continuum PracticeDocument18 pagesContinuum PracticeSaid HbadNo ratings yet
- Remedial EnrichmentDocument22 pagesRemedial EnrichmentNor Diwiyana Binti Mohamed Nor IPGKRMNo ratings yet
- Group Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomDocument9 pagesGroup Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomSAVIRA MARETTANo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Training Facilitation Cur 532Document26 pagesPowerpoint Training Facilitation Cur 532api-357806953No ratings yet
- Module 6 The Teaching Profession 1Document9 pagesModule 6 The Teaching Profession 1Maria Alexandrea Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Levels of Practice #6 - Curriculum, Instruction and AssessmentDocument2 pagesLevels of Practice #6 - Curriculum, Instruction and AssessmentLanguages CoordinationNo ratings yet
- AMT Explained PDFDocument1 pageAMT Explained PDFbranwell COGO100% (1)
- Assessment RubricDocument2 pagesAssessment Rubricapi-394899778No ratings yet
- Academic Conversations S JCC Day 3Document34 pagesAcademic Conversations S JCC Day 3Maryjane Bailo Lamela100% (1)
- Perbandingan PBL Dengan Kaedah TradisionalDocument30 pagesPerbandingan PBL Dengan Kaedah TradisionalSamrul YoNo ratings yet
- The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityDocument11 pagesThe Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityLeany AurelioNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document26 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2Andrea Nicole BalaresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - HPGD1103 - E-Tutorial - Part1 - January 2023Document28 pagesLecture 1 - HPGD1103 - E-Tutorial - Part1 - January 2023Ihwanor AsrafNo ratings yet
- Communication - I. Communication Skills: Approaches To Learning - (Atl Skills)Document4 pagesCommunication - I. Communication Skills: Approaches To Learning - (Atl Skills)PoloNo ratings yet
- Methods J Techniques and Strategies For English LanguageDocument49 pagesMethods J Techniques and Strategies For English LanguageJosé Francisco Cáceres MedinaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document1 pagePresentation 5api-380552709No ratings yet
- LOMLOE Life VisionDocument5 pagesLOMLOE Life VisionLaura GompaNo ratings yet
- Analysis 29.01Document4 pagesAnalysis 29.01Arujan BekmoldanovaNo ratings yet
- 20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered ParadigmsDocument2 pages20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered ParadigmsManisha Pachauri100% (1)
- 20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered Paradigms PDFDocument2 pages20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered Paradigms PDFJanine PalizaNo ratings yet
- Read 680 - Literacy PlanDocument10 pagesRead 680 - Literacy Planapi-666002143No ratings yet
- Turman-670-Locating Texts To Support Your Essential Question-1Document3 pagesTurman-670-Locating Texts To Support Your Essential Question-1api-666002143No ratings yet
- Read 520 Sorting ActivitiesDocument18 pagesRead 520 Sorting Activitiesapi-666002143No ratings yet
- Literacy Profile I-Vi Read 670 Turman EpDocument9 pagesLiteracy Profile I-Vi Read 670 Turman Epapi-666002143No ratings yet
- Module 3 3-2-1Document2 pagesModule 3 3-2-1api-666002143No ratings yet
- Read 680 Classroom Modeling LessonDocument4 pagesRead 680 Classroom Modeling Lessonapi-666002143No ratings yet
- Voices From The Field TurmanDocument2 pagesVoices From The Field Turmanapi-666002143No ratings yet
- Alphabetic BR Case Sum PortfolioDocument6 pagesAlphabetic BR Case Sum Portfolioapi-666002143No ratings yet
- Turmanresume 2023Document1 pageTurmanresume 2023api-666002143No ratings yet
- Modified Lesson Plan-E-Portfolio - TurmanDocument4 pagesModified Lesson Plan-E-Portfolio - Turmanapi-666002143No ratings yet