0% found this document useful (0 votes)
688 views14 pagesEssential Coding Patterns for Interviews
This document discusses 12 common coding patterns and their applications in system design interviews. The patterns covered are sliding window, two heaps, topological sort, two pointers, merge intervals, backtracking, trie, flood fill, segment tree, breadth-first search, depth-first search, and union-find. For each pattern, the document provides a definition, examples of usage, and additional details.
Uploaded by
Ali SamirCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
688 views14 pagesEssential Coding Patterns for Interviews
This document discusses 12 common coding patterns and their applications in system design interviews. The patterns covered are sliding window, two heaps, topological sort, two pointers, merge intervals, backtracking, trie, flood fill, segment tree, breadth-first search, depth-first search, and union-find. For each pattern, the document provides a definition, examples of usage, and additional details.
Uploaded by
Ali SamirCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Coding Patterns: Introduces key coding patterns used in system design interviews and their applications.
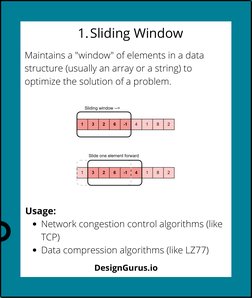
- 1. Sliding Window: Explains the sliding window technique for optimizing problem solutions, with examples such as network congestion control.
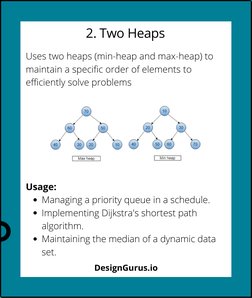
- 2. Two Heaps: Describes the use of two heaps for managing a dynamic dataset or implementing priority queues.
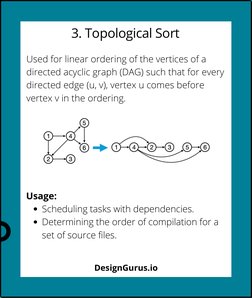
- 3. Topological Sort: Outlines the topological sorting method for ordering vertices in a directed acyclic graph.
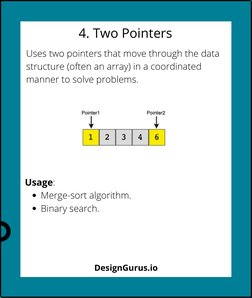
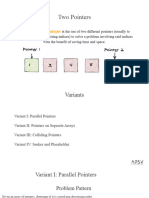
- 4. Two Pointers: Introduces the two-pointer technique to navigate arrays for solutions like binary search.
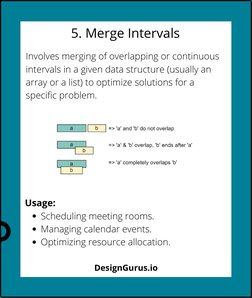
- 5. Merge Intervals: Details how to merge overlapping intervals for resource allocation problems.
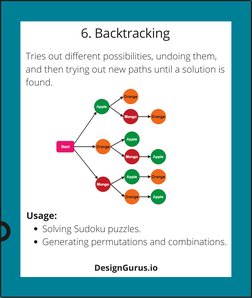
- 6. Backtracking: Explores the backtracking method for generating permutations and solving constraint problems.
- 7. Trie (Prefix Tree): Discusses the trie data structure for efficiently storing strings based on prefixes.
- 8. Flood Fill: Presents the flood fill algorithm for painting in graphics or traversing grids.
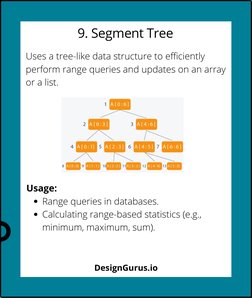
- 9. Segment Tree: Introduces segment trees for performing efficient range queries and updates.
- 10. Breadth-First Search (BFS): Describes BFS for level-order traversal in graphs, applicable in web crawling and network analysis.
- 11. Depth-First Search (DFS): Covers DFS for exhaustive exploration of graph branches, useful in maze solving.
- 12. Union-Find (Disjoint Set): Explains the union-find structure for managing disjoint sets and connectivity queries.
- Conclusion: Encourages the use of introduced techniques for improving design skills in coding interviews.