0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views13 pagesFloor and Ceiling Function
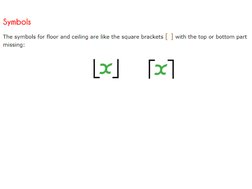
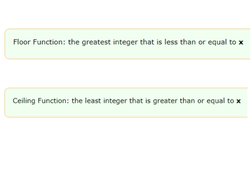
The floor function rounds down to the nearest integer, while the ceiling function rounds up. For example, floor(2.6) = 2 and ceiling(-2.1) = -2. There are several interesting properties of these functions, such as floor(-x) = ceiling(-x), which can be proven. The document also provides examples and definitions of the greatest common divisor function.
Uploaded by
Ronna MagtoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views13 pagesFloor and Ceiling Function
The floor function rounds down to the nearest integer, while the ceiling function rounds up. For example, floor(2.6) = 2 and ceiling(-2.1) = -2. There are several interesting properties of these functions, such as floor(-x) = ceiling(-x), which can be proven. The document also provides examples and definitions of the greatest common divisor function.
Uploaded by
Ronna MagtoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd